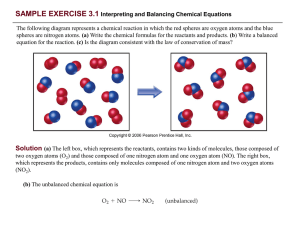
File
... us the mole ratio. • It takes 1 mole of ethanol to react with 3 moles of oxygen. This produces 2 moles of carbon dioxide and 3 moles of water. • The mole ratio will act as our conversion ...
... us the mole ratio. • It takes 1 mole of ethanol to react with 3 moles of oxygen. This produces 2 moles of carbon dioxide and 3 moles of water. • The mole ratio will act as our conversion ...
Chem G 9
... neutrons will have different mass numbers and are called isotopes. Students should appreciate that a natural sample of an element is likely to contain a mixture of two or more isotopes. In determining the atomic mass of the element we must take into account that it is a mixture of isotopes with diff ...
... neutrons will have different mass numbers and are called isotopes. Students should appreciate that a natural sample of an element is likely to contain a mixture of two or more isotopes. In determining the atomic mass of the element we must take into account that it is a mixture of isotopes with diff ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... in analytical physics. As described in Sect. 1.3, Poincaré proved that there are very few classical mechanics problems for which the equations of motions can be solved analytically. This is due to the three-body problem. Poincaré addressed this threebody problem in classical mechanics with the idea ...
... in analytical physics. As described in Sect. 1.3, Poincaré proved that there are very few classical mechanics problems for which the equations of motions can be solved analytically. This is due to the three-body problem. Poincaré addressed this threebody problem in classical mechanics with the idea ...
Excitation of Rydberg states in rubidium with near infrared diode lasers
... With the application of a small electric field, a dipole-dipole energy exchange between pairs of atoms can be tuned into resonance [1, 2]. This interaction can also lead to a blockade effect, which limits the number of excited Rydberg atoms [3, 4] and can even limit the excitation in a small sample ...
... With the application of a small electric field, a dipole-dipole energy exchange between pairs of atoms can be tuned into resonance [1, 2]. This interaction can also lead to a blockade effect, which limits the number of excited Rydberg atoms [3, 4] and can even limit the excitation in a small sample ...
Chemical bonding and structure
... as protons and electrons. This is because the number of protons (+) is equal to the number of electrons (−), and so their charges cancel each other out. The positively charged protons, located within the nucleus of the atom, are not transferred during chemical reactions. Electrons, however, position ...
... as protons and electrons. This is because the number of protons (+) is equal to the number of electrons (−), and so their charges cancel each other out. The positively charged protons, located within the nucleus of the atom, are not transferred during chemical reactions. Electrons, however, position ...
Chem 107 - Hughbanks Exam 1
... (4) (7 points) Which of the following choices correctly completes this statement: A cation with a charge of +2 that has an atomic number of 12 and a mass number of 25, (a) has the same number of electrons as a Si atom. (b) has 10 electrons. (c) has the same number of protons as an Ne atom. (d) has ...
... (4) (7 points) Which of the following choices correctly completes this statement: A cation with a charge of +2 that has an atomic number of 12 and a mass number of 25, (a) has the same number of electrons as a Si atom. (b) has 10 electrons. (c) has the same number of protons as an Ne atom. (d) has ...
AP Ch 3 Stoichiometry
... mass spectrometer—a device for measuring the mass of atoms or molecules atoms or molecules are passed into a beam of high-speed electrons this knocks electrons OFF the atoms or molecules transforming them into cations o apply an electric field this accelerates the cations since they are repelle ...
... mass spectrometer—a device for measuring the mass of atoms or molecules atoms or molecules are passed into a beam of high-speed electrons this knocks electrons OFF the atoms or molecules transforming them into cations o apply an electric field this accelerates the cations since they are repelle ...
PowerPoint Version
... Generate and test a pseudopotential for Ba with the semicore explicitly included in the valence The pseudopotential constructed is not expected to reproduce perfectly the 6s and 6p states, as their eigenvalues are more than 1 eV from those of the reference states 5s and 5p, but the actual results a ...
... Generate and test a pseudopotential for Ba with the semicore explicitly included in the valence The pseudopotential constructed is not expected to reproduce perfectly the 6s and 6p states, as their eigenvalues are more than 1 eV from those of the reference states 5s and 5p, but the actual results a ...
Chapter 13 Radioactive Decay
... The “blurring” function ρ(Eif ) is sometimes referred to as the “density of final states”. We had to introduce it, in a somewhat ad hoc fashion to recognize that excited states are, indeed, “blurred”. However, it is fascinating to note, that this blurring is directly connected to the existence of fi ...
... The “blurring” function ρ(Eif ) is sometimes referred to as the “density of final states”. We had to introduce it, in a somewhat ad hoc fashion to recognize that excited states are, indeed, “blurred”. However, it is fascinating to note, that this blurring is directly connected to the existence of fi ...
Atomic structure via highly charged ions and
... tantalizing way with the experimental fact that the BeH2 molecule is straight, but NH2 is bent. The connection becomes clear when one interprets the shape of the trimer as a rough measurement of the relative position of the two bonding electrons contributed by the central atom. Our exact quantum sta ...
... tantalizing way with the experimental fact that the BeH2 molecule is straight, but NH2 is bent. The connection becomes clear when one interprets the shape of the trimer as a rough measurement of the relative position of the two bonding electrons contributed by the central atom. Our exact quantum sta ...