functional groups - U of L Class Index
... 2. Determine the total number of valence electrons. 3. Use one pair of electrons to make a single bond between each pair of bonded atoms. 4. Use any remaining electrons as lone pairs around each terminal atom (except H) so that each terminal atom has a complete octet, ...
... 2. Determine the total number of valence electrons. 3. Use one pair of electrons to make a single bond between each pair of bonded atoms. 4. Use any remaining electrons as lone pairs around each terminal atom (except H) so that each terminal atom has a complete octet, ...
amination.phenyl-2-c..
... l-Aryl-2-chloropropanes.-The procedure for preparachloride by these techniques. These compounds tion of 2-chloro-1-(o-chloropheny1)-propaneand Zchloro-1(Table I) are suitable as intermediates in the syn- (p-chloropheny1)-propaneis given as typical for this class of The isolation and proof of structu ...
... l-Aryl-2-chloropropanes.-The procedure for preparachloride by these techniques. These compounds tion of 2-chloro-1-(o-chloropheny1)-propaneand Zchloro-1(Table I) are suitable as intermediates in the syn- (p-chloropheny1)-propaneis given as typical for this class of The isolation and proof of structu ...
Class Presentation – Naming and Formula Writing
... HW - Set C Key Set C Key: Formula to Name (Transition Metals) ...
... HW - Set C Key Set C Key: Formula to Name (Transition Metals) ...
Organic Chemistry
... What is the formula for a compound with 22C atoms or one with 38H atoms Structural formulashows all atoms and bonds within a molecule Condensed structural formula does not show all the bonds, but is similar to a structural formula Ex. #1CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 Ex. #2 CH3(CH2)5CH3 ...
... What is the formula for a compound with 22C atoms or one with 38H atoms Structural formulashows all atoms and bonds within a molecule Condensed structural formula does not show all the bonds, but is similar to a structural formula Ex. #1CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 Ex. #2 CH3(CH2)5CH3 ...
Organic Naming Guide
... double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typical molecule, we have to specify where it is ...
... double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typical molecule, we have to specify where it is ...
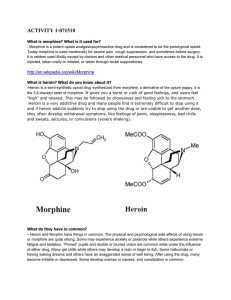
activity 1-071510 - ids
... confused with the element actinium). The acetyl group contains a methyl group single-bonded to a carbonyl. The carbonyl center of an acyl radical has one nonbonded electron with which it forms a chemical bond to the remainder R of the molecule. In IUPAC nomenclature, acetyl is called ethanoyl, altho ...
... confused with the element actinium). The acetyl group contains a methyl group single-bonded to a carbonyl. The carbonyl center of an acyl radical has one nonbonded electron with which it forms a chemical bond to the remainder R of the molecule. In IUPAC nomenclature, acetyl is called ethanoyl, altho ...
periodic table - Mesa Community College
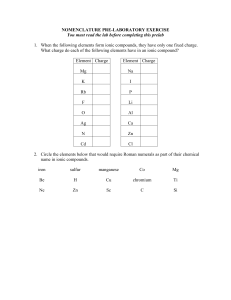
... Oxidation number (or oxidation state): the charge on an element once it has gained or lost electron(s) DISCUSSION: After the names and symbols of the elements are mastered, we can now move to the second task: assembling these symbols and names and learning how to write formulas and name compounds. C ...
... Oxidation number (or oxidation state): the charge on an element once it has gained or lost electron(s) DISCUSSION: After the names and symbols of the elements are mastered, we can now move to the second task: assembling these symbols and names and learning how to write formulas and name compounds. C ...
amino group - salemmbrothers
... Each member C3 - C10 differs by one CH2 unit. This is called a homologous series. Methane to butane are gases at normal pressures. Pentane to decane are liquids at normal pressures. ...
... Each member C3 - C10 differs by one CH2 unit. This is called a homologous series. Methane to butane are gases at normal pressures. Pentane to decane are liquids at normal pressures. ...
PowerPoint - Organic Chemistry
... • You will need to memorize family name and associated general structure (use study H2N notes: includes ether group) C CH • Handout Molecular model kits • Build this structure: O H2C CH2 ...
... • You will need to memorize family name and associated general structure (use study H2N notes: includes ether group) C CH • Handout Molecular model kits • Build this structure: O H2C CH2 ...
Physical properties
... thousands of years. Distillation was probably first used by ancient Arab chemists to isolate perfumes evidence of which dates back to 3500 BC. • In the modern organic chemistry laboratory, distillation is a powerful tool, both for the identification and the purification of organic compounds. ...
... thousands of years. Distillation was probably first used by ancient Arab chemists to isolate perfumes evidence of which dates back to 3500 BC. • In the modern organic chemistry laboratory, distillation is a powerful tool, both for the identification and the purification of organic compounds. ...
Coordination properties of the diethyl (pyridin-3-ylmethyl)phosphonate ligand (3-pmpe)
... shifts upon the formation of the M(II) complex. The far IR region of all the compounds shows one band attributed to the ν (M–N) stretching vibration. The infrared spectra of all the studied compounds show a very strong band at 1384 cm–1, characteristic of an ionic nitrate [26, 27]. The presence of w ...
... shifts upon the formation of the M(II) complex. The far IR region of all the compounds shows one band attributed to the ν (M–N) stretching vibration. The infrared spectra of all the studied compounds show a very strong band at 1384 cm–1, characteristic of an ionic nitrate [26, 27]. The presence of w ...
CHM1032 Study Guide for Final Exam (including Details for sections... This study guide is only for additional information not covered... Revised December 3, 2014
... functional groups, branched alkanes, isomers, substituent groups: (methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo) (see Table 11.5, p.369), haloalkanes, properties of alkanes, combustion reaction, cis and trans isomers, addition reactions, hydrogenation, hydration, aromatic compounds ...
... functional groups, branched alkanes, isomers, substituent groups: (methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo) (see Table 11.5, p.369), haloalkanes, properties of alkanes, combustion reaction, cis and trans isomers, addition reactions, hydrogenation, hydration, aromatic compounds ...
functional group review
... & attached to three other atoms (2-C & 1-H atom) O. Bond angles in benzene are 1200. O. all carbon-carbon bonds length are equal & =1.39A. (Evidence revealed from x-ray diffraction experiments) ...
... & attached to three other atoms (2-C & 1-H atom) O. Bond angles in benzene are 1200. O. all carbon-carbon bonds length are equal & =1.39A. (Evidence revealed from x-ray diffraction experiments) ...
Exam 1 Solution Key
... The resonance structures illustrate the fact that there is extensive electron delocalization within the conjugate base, which makes the conjugate base exceptionally stable and a “weak base”; therefore, the undissociated acid would have considerable tendency to dissociate, making it a strong acid. ...
... The resonance structures illustrate the fact that there is extensive electron delocalization within the conjugate base, which makes the conjugate base exceptionally stable and a “weak base”; therefore, the undissociated acid would have considerable tendency to dissociate, making it a strong acid. ...
Chapter 2 cont’
... when atoms gain or lose electrons, they acquire a charge charged particles are called ions when atoms gain electrons, they become negatively charged ions, called anions (Cl-) when atoms lose electrons, they become positively charged ions, called cations (Na+) ions behave much differently than the ne ...
... when atoms gain or lose electrons, they acquire a charge charged particles are called ions when atoms gain electrons, they become negatively charged ions, called anions (Cl-) when atoms lose electrons, they become positively charged ions, called cations (Na+) ions behave much differently than the ne ...
Terroir_geo_W8T-post
... clay and organic components of the soil • The CEC of soil clays are generally independent of pH, but CEC of organics are very pH-dependent (higher pH higher CEC of soil organic matter) ...
... clay and organic components of the soil • The CEC of soil clays are generally independent of pH, but CEC of organics are very pH-dependent (higher pH higher CEC of soil organic matter) ...
Organic Chemistry PP
... Organic ChemistryThe study of organic compounds, which are those compounds containing carbon. (Chains of carbon) ...
... Organic ChemistryThe study of organic compounds, which are those compounds containing carbon. (Chains of carbon) ...
Hydrocarbons - mccormack-sch4u-2013
... Organic Compounds • Contain C bonded to other elements, commonly H, O, N, S, and halogens • Carbon – Can form many different compounds due to its hybrid orbitals – Has intermediate electonegativity, so its most likely to form molecular compounds (Recall: molecular compounds have diverse properties) ...
... Organic Compounds • Contain C bonded to other elements, commonly H, O, N, S, and halogens • Carbon – Can form many different compounds due to its hybrid orbitals – Has intermediate electonegativity, so its most likely to form molecular compounds (Recall: molecular compounds have diverse properties) ...
unit (7) organic compounds: hydrocarbons
... a) The longest chain has 5 carbons with the double bond starts at carbon 2. The name is 2-pentene. The two identical groups (the hydrogen atoms) are on the same side of the double, so we use the prefix “cis”. The full name is cis-2-pentene. b) The longest chain has 5 carbons with the double bond sta ...
... a) The longest chain has 5 carbons with the double bond starts at carbon 2. The name is 2-pentene. The two identical groups (the hydrogen atoms) are on the same side of the double, so we use the prefix “cis”. The full name is cis-2-pentene. b) The longest chain has 5 carbons with the double bond sta ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry/Practical
... Both of the following have four carbon atoms and ten hydrogen atoms they are called isomers CH3 CH3 –CH2 –CH2 –CH3 ...
... Both of the following have four carbon atoms and ten hydrogen atoms they are called isomers CH3 CH3 –CH2 –CH2 –CH3 ...
Nature’s Chemistry
... the parent name e.g. 'ethyl' before 'methyl'. If there are 2 identical groups the prefix 'di' is placed before the name of the branch e.g. 'dimethyl', 'diethyl' etc The prefixes 'tri' and 'tetra' are used if there are 3 or 4 repetitions respectively of the same group on the parent chain. To specify ...
... the parent name e.g. 'ethyl' before 'methyl'. If there are 2 identical groups the prefix 'di' is placed before the name of the branch e.g. 'dimethyl', 'diethyl' etc The prefixes 'tri' and 'tetra' are used if there are 3 or 4 repetitions respectively of the same group on the parent chain. To specify ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.