Hydrocarbons - calciochemist
... elements besides hydrogen may be attached to the carbon –halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and even other carbons –any atom that takes the place of a hydrogen on a parent hydrocarbon is called a substituent, or the branched part ...
... elements besides hydrogen may be attached to the carbon –halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and even other carbons –any atom that takes the place of a hydrogen on a parent hydrocarbon is called a substituent, or the branched part ...
Organic_chemistry
... • As carbon has four electrons in its valence level (2,4 or 1s2 2s2 2p2) it forms four covalent bonds. • When these are all single bonds, they have a tetrahedral arrangement. • In organic molecules carbon always forms four bonds, oxygen two, hydrogen and the halogens one (refer Section 4.2) ...
... • As carbon has four electrons in its valence level (2,4 or 1s2 2s2 2p2) it forms four covalent bonds. • When these are all single bonds, they have a tetrahedral arrangement. • In organic molecules carbon always forms four bonds, oxygen two, hydrogen and the halogens one (refer Section 4.2) ...
Chapter 18 Reactions of aromatics
... • The reaction involves an elimination reaction that gives a triple bond, followed by rapid addition of water • The intermediate is called benzyne ...
... • The reaction involves an elimination reaction that gives a triple bond, followed by rapid addition of water • The intermediate is called benzyne ...
Review for Exam #1
... Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons • do not contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that could be attached to each carbon atom. • are alkenes when they contain double C=C bonds. • are alkynes when they contain triple C≡C bonds. • http://www.bhsu.edu/danasu nskis/Courses/CHEM107/ ...
... Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons • do not contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that could be attached to each carbon atom. • are alkenes when they contain double C=C bonds. • are alkynes when they contain triple C≡C bonds. • http://www.bhsu.edu/danasu nskis/Courses/CHEM107/ ...
excess
... 5. From the Ka values in the table, calculate the pKa for each compound. Using these data, arrange the compounds in order of increasing acidity and explain the trend. (Hint: be sure to identify the hydrogen to which the Ka applies.) Ka Ka pKa pKa ...
... 5. From the Ka values in the table, calculate the pKa for each compound. Using these data, arrange the compounds in order of increasing acidity and explain the trend. (Hint: be sure to identify the hydrogen to which the Ka applies.) Ka Ka pKa pKa ...
10th Carbon and Its Compounds Solved Paper-3
... 10. An organic compound A is widely used as a preservative in pickles and has a molecular formula C2H4O2. This compound reacts with ethanol to form a sweet smelling compound B. i) Identify the compound A. ii) Write the chemical equation for its reaction with Ethanol to form compound B. iii) How can ...
... 10. An organic compound A is widely used as a preservative in pickles and has a molecular formula C2H4O2. This compound reacts with ethanol to form a sweet smelling compound B. i) Identify the compound A. ii) Write the chemical equation for its reaction with Ethanol to form compound B. iii) How can ...
6.5 Organic Lecture
... – Alkenes are hydrocarbons with at least one double carbon to carbon bond. • To show the presence of the double bond, the –ane suffix from the alkane name is changed to –ene. – The alkenes are unsaturated with respect to hydrogen • This means it does not have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms as ...
... – Alkenes are hydrocarbons with at least one double carbon to carbon bond. • To show the presence of the double bond, the –ane suffix from the alkane name is changed to –ene. – The alkenes are unsaturated with respect to hydrogen • This means it does not have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms as ...
Chem 3.5 Questions 09
... Describe chemical tests that could be used to distinguish between the compounds in each of the pairs of substances below. For each test description: ...
... Describe chemical tests that could be used to distinguish between the compounds in each of the pairs of substances below. For each test description: ...
C07B - Cooperative Patent Classification
... 1. In this subclass, the functional group which is present already in some residue being introduced and is not substantially involved in a chemical reaction, is not considered as the functional group which is formed or introduced as a result of the chemical reaction. 2. In this subclass, the followi ...
... 1. In this subclass, the functional group which is present already in some residue being introduced and is not substantially involved in a chemical reaction, is not considered as the functional group which is formed or introduced as a result of the chemical reaction. 2. In this subclass, the followi ...
Document
... (a) Magnesium has atomic number 12, so all atoms of magnesium contain 12 protons and 12 electrons. The three isotopes are therefore represented by 24/12Mg, 25/12Mg, and 26/12Mg. (b) The number of neutrons in each isotope is the mass number minus the number of protons. The numbers of neutrons in an a ...
... (a) Magnesium has atomic number 12, so all atoms of magnesium contain 12 protons and 12 electrons. The three isotopes are therefore represented by 24/12Mg, 25/12Mg, and 26/12Mg. (b) The number of neutrons in each isotope is the mass number minus the number of protons. The numbers of neutrons in an a ...
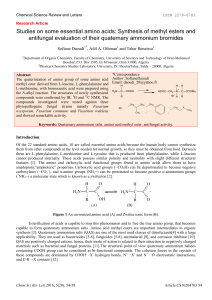
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
... carboxylates (−CO2−), and α-amino groups (NH2−) can be protonated to become positive α-ammonium groups (+NH3−) a molecular state which is known as a zwitterion [2]. ...
... carboxylates (−CO2−), and α-amino groups (NH2−) can be protonated to become positive α-ammonium groups (+NH3−) a molecular state which is known as a zwitterion [2]. ...
IN VITRO Research Article S. NITHIYA *, N. KARTHIK
... clinical and preclinical studies1.Besides the interesting structural features, these compounds are also of pharmaceutical interest as they exhibit a wide range of biological activities2. Nevertheless, the variety of functionality and substitution patterns found in piperidine ...
... clinical and preclinical studies1.Besides the interesting structural features, these compounds are also of pharmaceutical interest as they exhibit a wide range of biological activities2. Nevertheless, the variety of functionality and substitution patterns found in piperidine ...
Functional Groups and Biomolecules
... Functional groups are specific combinations of bonded atoms that always react in the same way, regardless of the particular carbon skeleton. Much of biomolecule’s chemistry can be attributed to its functional ...
... Functional groups are specific combinations of bonded atoms that always react in the same way, regardless of the particular carbon skeleton. Much of biomolecule’s chemistry can be attributed to its functional ...
What is Organic Chemistry? - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... 3. Proteins (made of amino acids) Proteins are the "workhorse" molecules of life, taking part in essentially every structure and activity of life. They are building materials for living cells, appearing in the structures inside the cell and within the cell membrane. While many of the proteins are st ...
... 3. Proteins (made of amino acids) Proteins are the "workhorse" molecules of life, taking part in essentially every structure and activity of life. They are building materials for living cells, appearing in the structures inside the cell and within the cell membrane. While many of the proteins are st ...
Name Page 1 F.05.215e3p1 I.
... related oxidizing agents, a 1,2-diol is formed. When phenylacetylene (Compound E) is treated with oxidizing agents such as OsO4, the corresponding addition reaction product is not observed; instead it is proposed that the initial addition reaction product, which is an ene-diol, undergoes an isomeriz ...
... related oxidizing agents, a 1,2-diol is formed. When phenylacetylene (Compound E) is treated with oxidizing agents such as OsO4, the corresponding addition reaction product is not observed; instead it is proposed that the initial addition reaction product, which is an ene-diol, undergoes an isomeriz ...
Stereochemistry of organic compounds
... • In chemistry, Racemization refers to the conversion of an enantiomerically pure mixture (one where only one enantiomer is present) into a mixture where more than one of the enantiomers are present. If the racemization results in a mixture where the enantiomers are present in equal quantities, the ...
... • In chemistry, Racemization refers to the conversion of an enantiomerically pure mixture (one where only one enantiomer is present) into a mixture where more than one of the enantiomers are present. If the racemization results in a mixture where the enantiomers are present in equal quantities, the ...
Organic 10.1 SL
... 10.1.7 Deduce structural formulas for the isomers of the straightchain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.8 Apply IUPAC rules for naming the isomers of the straight-chain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.9 Deduce structural formulas for compounds containing up to six carbon atoms with one of the following functional grou ...
... 10.1.7 Deduce structural formulas for the isomers of the straightchain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.8 Apply IUPAC rules for naming the isomers of the straight-chain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.9 Deduce structural formulas for compounds containing up to six carbon atoms with one of the following functional grou ...
Sp09 Survival Organic Chem
... manipulating molecular models helps their understanding of the spatial relationships of atoms in molecules. Using computer graphics will also provide a new way to view and manipulate molecular models. Finally, a simple understanding of organic compounds early in the semester will provide you with st ...
... manipulating molecular models helps their understanding of the spatial relationships of atoms in molecules. Using computer graphics will also provide a new way to view and manipulate molecular models. Finally, a simple understanding of organic compounds early in the semester will provide you with st ...
Synthesis of hetero cyclic compounds pyrazole and pyridiazine from
... Hydrazide derivatives have been frequently found in heterocyclic chemistry as key intermediates for synthesis of hetero cyclic compound and they have been reported to exhibit biological activity[1].The hydrazide is still used in many fields of chemical and biological as anti-TB or Tuberculosis mater ...
... Hydrazide derivatives have been frequently found in heterocyclic chemistry as key intermediates for synthesis of hetero cyclic compound and they have been reported to exhibit biological activity[1].The hydrazide is still used in many fields of chemical and biological as anti-TB or Tuberculosis mater ...
Full Text - Iraqi National Journal of Chemistry
... Hydrazide derivatives have been frequently found in heterocyclic chemistry as key intermediates for synthesis of hetero cyclic compound and they have been reported to exhibit biological activity[1].The hydrazide is still used in many fields of chemical and biological as anti-TB or Tuberculosis mater ...
... Hydrazide derivatives have been frequently found in heterocyclic chemistry as key intermediates for synthesis of hetero cyclic compound and they have been reported to exhibit biological activity[1].The hydrazide is still used in many fields of chemical and biological as anti-TB or Tuberculosis mater ...
Chemistry 223 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Ala-Gly-Glu-Ala denotes the order in which the amino acids are connected. What is meant by secondary structure? Give an example. Secondary structure is the orientation the primary structure obtains (alpha helix or ...
... Ala-Gly-Glu-Ala denotes the order in which the amino acids are connected. What is meant by secondary structure? Give an example. Secondary structure is the orientation the primary structure obtains (alpha helix or ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.