Chapter23
... The symbol R represents any carbon chain or ring attached to the functional group. Double and triple bonds of alkenes and alkynes affect reactivity and are also considered to be functional groups, but are not listed in the table. Like the table above, Reference table R shows the main functional grou ...
... The symbol R represents any carbon chain or ring attached to the functional group. Double and triple bonds of alkenes and alkynes affect reactivity and are also considered to be functional groups, but are not listed in the table. Like the table above, Reference table R shows the main functional grou ...
NC Exam Questions - Rosshall Academy
... (b) Name an aldehyde that would not take part in an aldol condensation. (1) (c) Apart from the structure of the reactants, suggest what is unusual about applying the term “condensation” to this particular type of reaction. (1) 22. Primary, secondary and tertiary alkanols can be prepared by the react ...
... (b) Name an aldehyde that would not take part in an aldol condensation. (1) (c) Apart from the structure of the reactants, suggest what is unusual about applying the term “condensation” to this particular type of reaction. (1) 22. Primary, secondary and tertiary alkanols can be prepared by the react ...
Section 8-2
... also results in noble-gas electron configurations. • The chemical bond that results from sharing electrons is a covalent bond. ...
... also results in noble-gas electron configurations. • The chemical bond that results from sharing electrons is a covalent bond. ...
List Definition Chemistry - A Level / Secondary Chemistry Tuition
... protein involving folding or coiling of the chains. It shows how protein molecules are arranged in relation to each other. There are four types of R group interactions which hold the tertiary structure in its shape. van der Waals’ forces (induced dipole-induced dipole bonding) exist when non-polar ...
... protein involving folding or coiling of the chains. It shows how protein molecules are arranged in relation to each other. There are four types of R group interactions which hold the tertiary structure in its shape. van der Waals’ forces (induced dipole-induced dipole bonding) exist when non-polar ...
Chapter 22
... continuous carbon chain and use this name as the base (a). If two chains of equal length are present, choose the one with the more branch points as the parent. ...
... continuous carbon chain and use this name as the base (a). If two chains of equal length are present, choose the one with the more branch points as the parent. ...
Carbon and its Compounds Summary Study of the compounds of
... 'R' can be a 'H' atom or an alkyl group attached to an aldehdye group (CHO). Question (9): What are homologous series? Write a short note. Answer: The extremely large numbers of carbon compounds discovered so far are better and more systematically studied by classifying them into ...
... 'R' can be a 'H' atom or an alkyl group attached to an aldehdye group (CHO). Question (9): What are homologous series? Write a short note. Answer: The extremely large numbers of carbon compounds discovered so far are better and more systematically studied by classifying them into ...
Naming Compounds
... Solubilized – meaning dissolved in water, and therefore, usually represented with an (aq) phase symbol Hydrates – ionic salts with water molecules weakly attached Organic – carbon based in which C is covalently bonded, mainly with hydrogen (H). However, organic compounds may at times contain some ni ...
... Solubilized – meaning dissolved in water, and therefore, usually represented with an (aq) phase symbol Hydrates – ionic salts with water molecules weakly attached Organic – carbon based in which C is covalently bonded, mainly with hydrogen (H). However, organic compounds may at times contain some ni ...
Review for Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
... molecular orbitals. A bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy and greater in stability than the atomic orbitals from which it was formed. An antibonding molecular orbital is higher in energy and lower in stability than the atomic orbitals from which it was formed. 15. Know how to draw molecular ...
... molecular orbitals. A bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy and greater in stability than the atomic orbitals from which it was formed. An antibonding molecular orbital is higher in energy and lower in stability than the atomic orbitals from which it was formed. 15. Know how to draw molecular ...
CHAPTER 2
... To some students the prospect of studying chemistry in a biology or physiology class is frightening. However, it is possible to simplify the vast field of chemistry painlessly and to apply many of the basic chemical concepts directly to those in physiology. Chapter 2 does this well. Of the entire pe ...
... To some students the prospect of studying chemistry in a biology or physiology class is frightening. However, it is possible to simplify the vast field of chemistry painlessly and to apply many of the basic chemical concepts directly to those in physiology. Chapter 2 does this well. Of the entire pe ...
Chapter 15
... • Aromatic hydrocarbons are known generally as arenes. • An Aryl group is formed by the removal of a hydrogen, and is symbolized with Ar• We have already talked about how stable the double bonds are in arenes due to conjugation. • They resist typical addition reactions ...
... • Aromatic hydrocarbons are known generally as arenes. • An Aryl group is formed by the removal of a hydrogen, and is symbolized with Ar• We have already talked about how stable the double bonds are in arenes due to conjugation. • They resist typical addition reactions ...
3.6 Organic analysis
... Between 1000 – 1500 cm-1 is called the fingerprint region. These are unique to a particular molecule. This means that this region can be compared with a database to identify a specific compound. ...
... Between 1000 – 1500 cm-1 is called the fingerprint region. These are unique to a particular molecule. This means that this region can be compared with a database to identify a specific compound. ...
Organic for Chem II
... Functional Groups Aromatic rings • Several structures are aromatic, but we will look at only one: the benzene ring, also called an aromatic ring. • Benzene is NOT three alkenes! It is a unique structure where six electrons are shared among all 6 carbon atoms. That is why the line angle structure is ...
... Functional Groups Aromatic rings • Several structures are aromatic, but we will look at only one: the benzene ring, also called an aromatic ring. • Benzene is NOT three alkenes! It is a unique structure where six electrons are shared among all 6 carbon atoms. That is why the line angle structure is ...
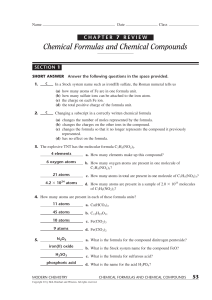
Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... 7. The oxidation numbers assigned to the atoms in some organic compounds have unexpected values. Assign oxidation numbers to each atom in the following compounds: (Note: Some oxidation numbers may not be whole numbers.) a. CO2 Carbon is ⫹4 and each oxygen is ⫺2. b. CH4 (methane) Carbon is ⫺4 and eac ...
... 7. The oxidation numbers assigned to the atoms in some organic compounds have unexpected values. Assign oxidation numbers to each atom in the following compounds: (Note: Some oxidation numbers may not be whole numbers.) a. CO2 Carbon is ⫹4 and each oxygen is ⫺2. b. CH4 (methane) Carbon is ⫺4 and eac ...
Chapter 4
... BaCI2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) Ba2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + 2Na+(aq)+ SO4 2-(aq) 2. Match cation from one salt with the anion from the other salt” Ba2+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Na+(aq)+ SO4 2-(aq) NaCl+ BaSO4 Note: Always keep the metal on the left in all salts! 3. Balance charges in salts and put in coefficients Ba2+( ...
... BaCI2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) Ba2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + 2Na+(aq)+ SO4 2-(aq) 2. Match cation from one salt with the anion from the other salt” Ba2+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Na+(aq)+ SO4 2-(aq) NaCl+ BaSO4 Note: Always keep the metal on the left in all salts! 3. Balance charges in salts and put in coefficients Ba2+( ...
Name: _______Date:_______________Per:____ Sodium, chlorine
... 1. Sodium, chlorine, and aluminum are all alike because they all three____ a. are compounds b. are nonmetals c. have one valence electron d. have 3 energy levels 2. Which of the following has similar reactivity to oxygen? a. nitrogen b. potassium c. sulfur d. neon 3. A boron model is made of____ a. ...
... 1. Sodium, chlorine, and aluminum are all alike because they all three____ a. are compounds b. are nonmetals c. have one valence electron d. have 3 energy levels 2. Which of the following has similar reactivity to oxygen? a. nitrogen b. potassium c. sulfur d. neon 3. A boron model is made of____ a. ...
Chapter 1 Glossary The Nature of Chemistry
... atom bonded to a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atom in another molecule. Metallic bond The attraction between the positive metal cations that form the basic structure of a solid metal and the negative charge from the mobile sea of electrons that surround the cations. London dispersion forces, London ...
... atom bonded to a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atom in another molecule. Metallic bond The attraction between the positive metal cations that form the basic structure of a solid metal and the negative charge from the mobile sea of electrons that surround the cations. London dispersion forces, London ...
Electronic and Electrochemical Properties of Platinum(H) and
... waves are observed. Compounds 2-5 could be oxidized in a single step in the potential range 1.05-l .40 V (Table I; Figure la, b). For compound 1 three oxidation waves were observed (0.87, 1.17 and 1.31 V), the relative intensity varied with the number of cycles (vide infra). All the oxidations are c ...
... waves are observed. Compounds 2-5 could be oxidized in a single step in the potential range 1.05-l .40 V (Table I; Figure la, b). For compound 1 three oxidation waves were observed (0.87, 1.17 and 1.31 V), the relative intensity varied with the number of cycles (vide infra). All the oxidations are c ...
Skill Sheet 19-B Chemical Formulas
... Have you ever heard of sodium nitrate? It’s a preservative used in foods like hot dogs. The chemical formula for sodium nitrate is NaNO3. How many types of atoms does this compound contain? You are right if you said three: sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen. The nitrogen and oxygen atoms have a shared-ele ...
... Have you ever heard of sodium nitrate? It’s a preservative used in foods like hot dogs. The chemical formula for sodium nitrate is NaNO3. How many types of atoms does this compound contain? You are right if you said three: sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen. The nitrogen and oxygen atoms have a shared-ele ...
15.2 Electrons and Chemical Bonds
... was why elements combined with other elements only in particular ratios (or not at all). For example, why do two hydrogen atoms bond with one oxygen atom to make water? Why isn’t there a molecule with three (H3O) or even four (H4O) hydrogen atoms? Why does sodium chloride have a precise ratio of one ...
... was why elements combined with other elements only in particular ratios (or not at all). For example, why do two hydrogen atoms bond with one oxygen atom to make water? Why isn’t there a molecule with three (H3O) or even four (H4O) hydrogen atoms? Why does sodium chloride have a precise ratio of one ...
PPT - Gmu
... d. Alkyl groups are electron releasing The 2 electrons in filled sp3 orbitals of alkyl groups can overlap with empty p-orbitals of positively charged adjacent Carbon atoms that produces a stabilizing affect on the Carbocation (Hyperconjugation). Electron density shifts toward the positive charge ...
... d. Alkyl groups are electron releasing The 2 electrons in filled sp3 orbitals of alkyl groups can overlap with empty p-orbitals of positively charged adjacent Carbon atoms that produces a stabilizing affect on the Carbocation (Hyperconjugation). Electron density shifts toward the positive charge ...
RESONANCE AND INDUCTION TUTORIAL Jack DeRuiter The
... which there is an alternating single bond-double (pi) bond pattern, or an atom with non-bonded electron pairs (or lacking an electron pair) bound to a double bond system. It is important to realize that resonance is not possible when such an electronic configuration is NOT possible. Consider the exa ...
... which there is an alternating single bond-double (pi) bond pattern, or an atom with non-bonded electron pairs (or lacking an electron pair) bound to a double bond system. It is important to realize that resonance is not possible when such an electronic configuration is NOT possible. Consider the exa ...
File
... Aromatics possess a benzene ring, that is what distinguishes the aromatic hydrocarbons from the aliphatic hydrocarbons. The benzene ring consists of six carbon atoms, each of which is bonded to a hydrogen atom. Resonance means that there are two or more possible distributions of bonding electrons fo ...
... Aromatics possess a benzene ring, that is what distinguishes the aromatic hydrocarbons from the aliphatic hydrocarbons. The benzene ring consists of six carbon atoms, each of which is bonded to a hydrogen atom. Resonance means that there are two or more possible distributions of bonding electrons fo ...
File - Fortrose Chemistry
... 19Hydrocarbons (General) Hydrocarbons are: compounds that contain only carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms obtained from crude oil by fractional distillation and can be classified into different groups. The two groups that you need to know about for Standard Grade are called alkanes and alkenes. Remembe ...
... 19Hydrocarbons (General) Hydrocarbons are: compounds that contain only carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms obtained from crude oil by fractional distillation and can be classified into different groups. The two groups that you need to know about for Standard Grade are called alkanes and alkenes. Remembe ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.