3. Carbon nanostructures - Acclab h55.it.helsinki.fi
... - Initially the names “bucky ball” and “buckminsterfullerene” were used a lot, but nowadays most people use just “fullerene”. - As in graphene, the bonding is primarily in strong covalent bonds - Hence there is no H-termination of the C’s at the surface, which makes it differ significantly from the ...
... - Initially the names “bucky ball” and “buckminsterfullerene” were used a lot, but nowadays most people use just “fullerene”. - As in graphene, the bonding is primarily in strong covalent bonds - Hence there is no H-termination of the C’s at the surface, which makes it differ significantly from the ...
ch 1: organic chemistry
... main intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces (electrons of one molecule with the nucleus of another) because these forces are weak, molecules are easily separable from one another small molecules have fewer electrons and weaker Van der Waal forces and therefore have lower boiling & melt ...
... main intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces (electrons of one molecule with the nucleus of another) because these forces are weak, molecules are easily separable from one another small molecules have fewer electrons and weaker Van der Waal forces and therefore have lower boiling & melt ...
Page 1 - WordPress.com
... Write an equation for the reaction of propanoyl chloride with water. An excess of water is added to 1.48 g of propanoyl chloride. Aqueous sodium hydroxide is then added from a burette to the resulting solution. ...
... Write an equation for the reaction of propanoyl chloride with water. An excess of water is added to 1.48 g of propanoyl chloride. Aqueous sodium hydroxide is then added from a burette to the resulting solution. ...
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
... chlorofluoromethanes are gases at room temperature. Higher members are liquids or solids. As we have already learnt, molecules of organic halogen compounds are generally polar. Due to greater polarity as well as higher molecular mass as compared to the parent hydrocarbon, the intermolecular forces o ...
... chlorofluoromethanes are gases at room temperature. Higher members are liquids or solids. As we have already learnt, molecules of organic halogen compounds are generally polar. Due to greater polarity as well as higher molecular mass as compared to the parent hydrocarbon, the intermolecular forces o ...
3.1.1.2 Mass number and isotopes
... 3.1.3.5 Shapes of simple molecules and ions Content Opportunities for skills development Bonding pairs and lone (non-bonding) pairs of electrons as charge clouds that repel each other. Pairs of electrons in the outer shell of atoms arrange themselves as far apart as possible to minimise repulsion. L ...
... 3.1.3.5 Shapes of simple molecules and ions Content Opportunities for skills development Bonding pairs and lone (non-bonding) pairs of electrons as charge clouds that repel each other. Pairs of electrons in the outer shell of atoms arrange themselves as far apart as possible to minimise repulsion. L ...
13C -NMR - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... also have two OH groups. Based on our 13C -NMR table above, the carbons with the shifts of 78.5 and 62.0 ppm must each be bound to an oxygen atom. Aha, we’ve found where our alcohols go! The other two carbons have ordinary R-CH2-R shifts so they’re not attached to any electronegative atoms or pi bon ...
... also have two OH groups. Based on our 13C -NMR table above, the carbons with the shifts of 78.5 and 62.0 ppm must each be bound to an oxygen atom. Aha, we’ve found where our alcohols go! The other two carbons have ordinary R-CH2-R shifts so they’re not attached to any electronegative atoms or pi bon ...
(NH 3 ) 2 - GZ @ Science Class Online
... Atoms that lose electrons form positively charged ions, or cations. Atoms that gain electrons form negatively charged ions, or anions. ...
... Atoms that lose electrons form positively charged ions, or cations. Atoms that gain electrons form negatively charged ions, or anions. ...
1 SECONDARY SCHOOL IMPROVEMENT PROGRAMME (SSIP
... Organic Chemistry is the study of carbon chemistry. Organic molecules are molecules that contain carbon atoms. The great abundance and diversity of organic substances is due to the unique ability of carbon to bond covalently to other carbon atoms, and so build up long chains of carbon atoms. Carbon ...
... Organic Chemistry is the study of carbon chemistry. Organic molecules are molecules that contain carbon atoms. The great abundance and diversity of organic substances is due to the unique ability of carbon to bond covalently to other carbon atoms, and so build up long chains of carbon atoms. Carbon ...
2,5-Diformylbenzene-1,4-diol: A Versatile Building Block for the
... needs to be able to undergo reversible electron transfer itself. Currently, one focus lies on hydroquinone derivatives as bridging ligands since they exist in three different oxidation states (hydroquinone, semiquinone, quinone) and their redox-activity is preserved after ...
... needs to be able to undergo reversible electron transfer itself. Currently, one focus lies on hydroquinone derivatives as bridging ligands since they exist in three different oxidation states (hydroquinone, semiquinone, quinone) and their redox-activity is preserved after ...
chem 217 intermediate chemistry ii assignment #5 3/9/00 due: 3/23/00
... CHEM 217 INTERMEDIATE CHEMISTRY II ASSIGNMENT #5 3/9/00 DUE: 3/23/00 ANSWER KEY ...
... CHEM 217 INTERMEDIATE CHEMISTRY II ASSIGNMENT #5 3/9/00 DUE: 3/23/00 ANSWER KEY ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... 1. Results when there is an oxygen atom between two carbons in the chain 2. Ethers are represented as R-O-R', where R and R' can be the same or different hydrocarbon units. Ether Nomenclature 1. Identify the two attached groups and add the word ether. 2. If there are more than 2 attached groups name ...
... 1. Results when there is an oxygen atom between two carbons in the chain 2. Ethers are represented as R-O-R', where R and R' can be the same or different hydrocarbon units. Ether Nomenclature 1. Identify the two attached groups and add the word ether. 2. If there are more than 2 attached groups name ...
Chemistry 209 - Experiment 3, Fall 2002
... In this lab we will again examine how the structure of a molecule determines the properties of the compound. In particular, you will explore some of the properties of a small group of oxygen and nitrogen-containing compounds. The reactivity of each compound with a series of reactants (3 M HCl(aq), 3 ...
... In this lab we will again examine how the structure of a molecule determines the properties of the compound. In particular, you will explore some of the properties of a small group of oxygen and nitrogen-containing compounds. The reactivity of each compound with a series of reactants (3 M HCl(aq), 3 ...
Functional Groups & Naming Organic Compounds
... Molecular: actual number of atoms of each present. It can be deduced if both the empirical formula and relative molecular mass, Mr, are known. ...
... Molecular: actual number of atoms of each present. It can be deduced if both the empirical formula and relative molecular mass, Mr, are known. ...
CHEM 210 Nomenclature Lecture 1
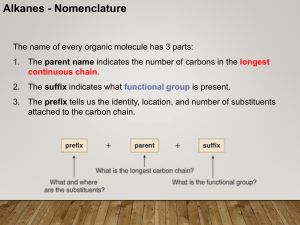
... • If two or more identical substituents are bonded to the longest chain, use prefixes to indicate how many: di- for two groups, trifor three groups, tetra- for four groups, and so forth. ...
... • If two or more identical substituents are bonded to the longest chain, use prefixes to indicate how many: di- for two groups, trifor three groups, tetra- for four groups, and so forth. ...
Aromatic heterocycles 1: structures and reactions
... Benzene is aromatic because it has six electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. We know it is aromatic because it is exceptionally stable and it has a ring current and hence large chemical shifts in the proton NMR spectrum as well as a special chemistry involving substitution rather than addition wi ...
... Benzene is aromatic because it has six electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. We know it is aromatic because it is exceptionally stable and it has a ring current and hence large chemical shifts in the proton NMR spectrum as well as a special chemistry involving substitution rather than addition wi ...
Cycloalkanes - faculty at Chemeketa
... Cyclobutane has less angle strain than cyclopropane but more torsional strain because of its larger number of ring hydrogens Cyclobutane is slightly bent out of plane - one carbon atom is about 25° above ◦ The bend increases angle strain but decreases torsional strain ...
... Cyclobutane has less angle strain than cyclopropane but more torsional strain because of its larger number of ring hydrogens Cyclobutane is slightly bent out of plane - one carbon atom is about 25° above ◦ The bend increases angle strain but decreases torsional strain ...
Document
... times as strong as van der Waals’ forces, and about one-tenth as strong as covalent bonds. Two conditions are necessary for formation of hydrogen bonds: (i) A H atom must be covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom usually N, O or F. Hydrogen only has one electron which is used when hydrog ...
... times as strong as van der Waals’ forces, and about one-tenth as strong as covalent bonds. Two conditions are necessary for formation of hydrogen bonds: (i) A H atom must be covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom usually N, O or F. Hydrogen only has one electron which is used when hydrog ...
Structure Determination for Organic Compounds - Rose
... many scans on FTIR, it is frequently possible to pick out these aromatic overtones; different substitution patterns result in different patterns, so it is often possible to determine the number and position of substitutents on benzene ring. The handout contains spectra that show the different peak a ...
... many scans on FTIR, it is frequently possible to pick out these aromatic overtones; different substitution patterns result in different patterns, so it is often possible to determine the number and position of substitutents on benzene ring. The handout contains spectra that show the different peak a ...
Principles of Drug Action I, Spring 2004
... 7. How many different (regioisomeric and stereoisomeric) electrophilic addition products could form in the following reaction? Two regioisomers are possible by addition of OH- and Cl+ across the double bond. During addition a chiral center is created at each addition site (for each regioisomer). Thu ...
... 7. How many different (regioisomeric and stereoisomeric) electrophilic addition products could form in the following reaction? Two regioisomers are possible by addition of OH- and Cl+ across the double bond. During addition a chiral center is created at each addition site (for each regioisomer). Thu ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.