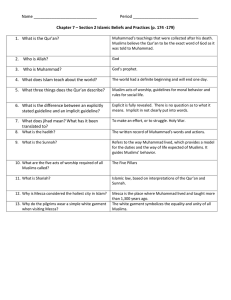
Muhammad Questions 1. What year was Muhammad born? 2. In
... 13. Why was Muhammad kicked out of Mecca? 14. What year was he kicked out of Mecca? 15. Where did he go? 16. What is the name given to this journey by Muslims? 17. Why is 619 C.E. referred to as the year of the sorrow? 18. What does “Medina” mean? 19. Who are the “people of the book”? 20. In what di ...
... 13. Why was Muhammad kicked out of Mecca? 14. What year was he kicked out of Mecca? 15. Where did he go? 16. What is the name given to this journey by Muslims? 17. Why is 619 C.E. referred to as the year of the sorrow? 18. What does “Medina” mean? 19. Who are the “people of the book”? 20. In what di ...
File
... Muhammad’s teachings that were collected after his death. Muslims believe the Qur’an to be the exact word of God as it was told to Muhammad. ...
... Muhammad’s teachings that were collected after his death. Muslims believe the Qur’an to be the exact word of God as it was told to Muhammad. ...
Lesson 10 The Prophet Muhammad
... No other person in history has had such an impact on the life of his followers, according to Muslim beliefs, than Muhammad, the last and final messenger of Allah. His life is the best example for Muslims to follow. He has shown how to obey Allah and how to live as a true Muslim. Muhammad might have ...
... No other person in history has had such an impact on the life of his followers, according to Muslim beliefs, than Muhammad, the last and final messenger of Allah. His life is the best example for Muslims to follow. He has shown how to obey Allah and how to live as a true Muslim. Muhammad might have ...
The Rise of Islam
... Spiritual and moral obligation on Muslimsto conquer vice and evil Muslims to struggle against ignorance and unbelief by spreading the word of Islam and seeking conversions The obligation to take the sword and wage war against unbelievers who threaten Islam ...
... Spiritual and moral obligation on Muslimsto conquer vice and evil Muslims to struggle against ignorance and unbelief by spreading the word of Islam and seeking conversions The obligation to take the sword and wage war against unbelievers who threaten Islam ...
Islam
... destroyed and the dead will be resurrected for judgment by God. All people will be rewarded by God according to their beliefs and deeds. Those who die while believing that “There is no true god but God, and Muhammad is the Messenger (Prophet) of God” and are Muslim will be rewarded on that day and w ...
... destroyed and the dead will be resurrected for judgment by God. All people will be rewarded by God according to their beliefs and deeds. Those who die while believing that “There is no true god but God, and Muhammad is the Messenger (Prophet) of God” and are Muslim will be rewarded on that day and w ...
Five Pillars of Islam
... factions. (This is similar to the different branches of Christianity.) • Shias/Shi’ite Muslims feel that Ali should have been the first caliph and that the caliphate should pass down only to direct descendants of Muhammad • The death of Ali: A supporter murders him, but motive is left unclear. • The ...
... factions. (This is similar to the different branches of Christianity.) • Shias/Shi’ite Muslims feel that Ali should have been the first caliph and that the caliphate should pass down only to direct descendants of Muhammad • The death of Ali: A supporter murders him, but motive is left unclear. • The ...
File - 7th Grade Global Studies
... answered in order. If you miss an answer, for whatever reason, do not bother other students around you. At the end of class you will have an opportunity to ask questions. 1. What was the name “of the ordinary man” who would shape Islam? When and where was he born? ...
... answered in order. If you miss an answer, for whatever reason, do not bother other students around you. At the end of class you will have an opportunity to ask questions. 1. What was the name “of the ordinary man” who would shape Islam? When and where was he born? ...
The Emigration to Medina
... Khadija and Abu Talib his two biggest supporters. • The journey is called the hijrah and marks the beginning of the Muslim calendar • The prophet was welcomed by Jews and Arabs of Yathrib. • Both groups hoped he would stop a civil war ...
... Khadija and Abu Talib his two biggest supporters. • The journey is called the hijrah and marks the beginning of the Muslim calendar • The prophet was welcomed by Jews and Arabs of Yathrib. • Both groups hoped he would stop a civil war ...
The Arab Empire and its Successors
... Islam and defeated Byzantium army at Syria – Jihad – “struggle for God” Abu Bakr had little control over military commanders of the clans ...
... Islam and defeated Byzantium army at Syria – Jihad – “struggle for God” Abu Bakr had little control over military commanders of the clans ...
7TH GRADE HONORS 3 MAJOR RELIGIONS PART 2 STUDY
... STUDY GUIDE: 1. Be able to write a paragraph based on information given in a paragraph. 2. Be able to describe the 2 rites (sacraments) all Christians practice. 3. Be able to describe the belief system of Christianity and describe how the geopolitical environment of Judah formed Jesus’ ideas. 4. Be ...
... STUDY GUIDE: 1. Be able to write a paragraph based on information given in a paragraph. 2. Be able to describe the 2 rites (sacraments) all Christians practice. 3. Be able to describe the belief system of Christianity and describe how the geopolitical environment of Judah formed Jesus’ ideas. 4. Be ...
Islam and The Qur`an
... • La ilaha illa Allah: Muhammadun rasulu Allah • Five Pillars: 1) Belief in one God - revealed his message to Muhammad 2) Pray five times a day facing Mecca 3) Charity to the poor and the aged 4) Fasting during the holy month of Ramadan 5) The hajj, or pilgrimage to Mecca ...
... • La ilaha illa Allah: Muhammadun rasulu Allah • Five Pillars: 1) Belief in one God - revealed his message to Muhammad 2) Pray five times a day facing Mecca 3) Charity to the poor and the aged 4) Fasting during the holy month of Ramadan 5) The hajj, or pilgrimage to Mecca ...
Development of Islam
... Refers to foods that are OK for Muslims to eat Similar to Jewish “kosher” food Mammals that both chew their cud and have cloven hooves can be kosher. Animals with one characteristic but not the other (the camel, the hyrax and the hare because they have no cloven hooves, and the pig because it does n ...
... Refers to foods that are OK for Muslims to eat Similar to Jewish “kosher” food Mammals that both chew their cud and have cloven hooves can be kosher. Animals with one characteristic but not the other (the camel, the hyrax and the hare because they have no cloven hooves, and the pig because it does n ...
AP Emergence of Islam
... – Center of an polytheistic religion – Site of annual pilgrimage during which warfare was suspended ...
... – Center of an polytheistic religion – Site of annual pilgrimage during which warfare was suspended ...
The Muslim World 600-1250
... • By 750, the Muslim empire stretched from the Atlantic Ocean to the Indus River • http://mapsofwar.com/ind/history-of-religion.html ...
... • By 750, the Muslim empire stretched from the Atlantic Ocean to the Indus River • http://mapsofwar.com/ind/history-of-religion.html ...
File
... In the 7th century CE the angel Gabriel appeared to Muhammad, in the city of Mecca, who persuaded him to begin reciting the word of God and to act as a Prophet. Muslims believe that God sent Muhammad as the final prophet (much like he had sent Moses or Jesus) to help bring people back to the one tru ...
... In the 7th century CE the angel Gabriel appeared to Muhammad, in the city of Mecca, who persuaded him to begin reciting the word of God and to act as a Prophet. Muslims believe that God sent Muhammad as the final prophet (much like he had sent Moses or Jesus) to help bring people back to the one tru ...
The Arab Empire and its Successors
... Islam and defeated Byzantium army at Syria – Jihad – “struggle for God” Abu Bakr had little control over military commanders of the clans ...
... Islam and defeated Byzantium army at Syria – Jihad – “struggle for God” Abu Bakr had little control over military commanders of the clans ...
History of Islam and Divisions
... The death of Muhammad brought confusion to the Muslim community. After his death, the issue of leadership came to the forefront. The Prophet had been an incredibly gifted leader – making him difficult to replace. 2 claims to Muslim leadership that surfaced immediately after Muhammad’s death: 1) Abu- ...
... The death of Muhammad brought confusion to the Muslim community. After his death, the issue of leadership came to the forefront. The Prophet had been an incredibly gifted leader – making him difficult to replace. 2 claims to Muslim leadership that surfaced immediately after Muhammad’s death: 1) Abu- ...
The Spread of Islam
... The Empire Continues to Spread Despite the split, the Empire continues to grow. In711 A.D. a Berber general named Tariq crossed into Spain at The Straight of Gibraltar and conquered Spain quickly. After crossing the Pyrenees to raid central France, they were defeated by Charles Martel of the Franks ...
... The Empire Continues to Spread Despite the split, the Empire continues to grow. In711 A.D. a Berber general named Tariq crossed into Spain at The Straight of Gibraltar and conquered Spain quickly. After crossing the Pyrenees to raid central France, they were defeated by Charles Martel of the Franks ...
Southwest Asia - People Server at UNCW
... claim to the caliphate. He died within a year, allegedly poisoned. Ali's younger son Hussein agreed to put his claim to the caliphate on hold until Mu'awiya's death. However, when Mu'awiya finally died in 680, his son Yazid usurped the caliphate. Hussein led an army against Yazid but, hopelessly out ...
... claim to the caliphate. He died within a year, allegedly poisoned. Ali's younger son Hussein agreed to put his claim to the caliphate on hold until Mu'awiya's death. However, when Mu'awiya finally died in 680, his son Yazid usurped the caliphate. Hussein led an army against Yazid but, hopelessly out ...
Rise and spread of Muslim Empires Sam Miyashita • 620 CE
... respected or treated as scripture. Most Muslims believe that the misconception of the 72 virgins when you go to heaven is actually not true. Islam means ‘Submission.’ A Muslim is one who Submits. Ummah: The community or nation. Refers to the whole Muslim world. *Quraysh Tribe- Tribe that Muhammad wa ...
... respected or treated as scripture. Most Muslims believe that the misconception of the 72 virgins when you go to heaven is actually not true. Islam means ‘Submission.’ A Muslim is one who Submits. Ummah: The community or nation. Refers to the whole Muslim world. *Quraysh Tribe- Tribe that Muhammad wa ...
The Rise of Islam
... The Origins of Islam • During his marriage to Khadija, Muhammad was plagued by incessant headaches. He would retire to a cave outside of Mecca. • Muhammad was visited by the angel Gabriel. ...
... The Origins of Islam • During his marriage to Khadija, Muhammad was plagued by incessant headaches. He would retire to a cave outside of Mecca. • Muhammad was visited by the angel Gabriel. ...
II. Islam
... Fasting: during the month of Ramadan, during the day. Are exceptions Tithing: tax to help the needy (10%) (sharing) Pilgrimage (Hijra): pilgrimage to Mecca once in lifetime to the Ka’bah ...
... Fasting: during the month of Ramadan, during the day. Are exceptions Tithing: tax to help the needy (10%) (sharing) Pilgrimage (Hijra): pilgrimage to Mecca once in lifetime to the Ka’bah ...
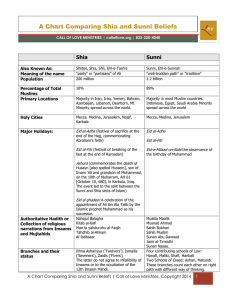
A Chart Comparing Shia and Sunni Beliefs
... The Four Rightly Guided Caliphs: Abu Bakr Umar bin Al Khattab Uthman bin Afan Ali bin Abi Talib ...
... The Four Rightly Guided Caliphs: Abu Bakr Umar bin Al Khattab Uthman bin Afan Ali bin Abi Talib ...
Chapter 11.2 Spread of Islam
... Why were they able to Succeed • Weakness of the Byzantine and Persian Empire • People of the Fertile Crescent saw them as liberators • Common faith Muhammad had given his people, Islam brought many Arab tribes together ...
... Why were they able to Succeed • Weakness of the Byzantine and Persian Empire • People of the Fertile Crescent saw them as liberators • Common faith Muhammad had given his people, Islam brought many Arab tribes together ...