Mountain-Skies-2016-0718
... To the northeast of Lyra is the bright star Deneb that represents the tail of the beautiful swan Cygnus. Tracing a line of stars from Deneb towards the south, we note the body and long neck of the swan terminating in the star Albir ...
... To the northeast of Lyra is the bright star Deneb that represents the tail of the beautiful swan Cygnus. Tracing a line of stars from Deneb towards the south, we note the body and long neck of the swan terminating in the star Albir ...
here - Boise State University
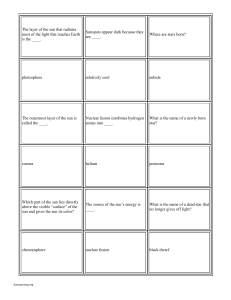
... 8. As you watched the Youtube clip, how big was our sun compared to the other stars? 9. Explain the relationship between star color and temperature: What color stars are the hottest in space? What color stars are the coolest? 10. Explain the relationship between star size and true brightness: Which ...
... 8. As you watched the Youtube clip, how big was our sun compared to the other stars? 9. Explain the relationship between star color and temperature: What color stars are the hottest in space? What color stars are the coolest? 10. Explain the relationship between star size and true brightness: Which ...
Properties of Stars
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Parallax is determined by taking a picture of a star at one time, and another picture six months later; using the angle between its apparent shift, astronomers can determine how far away it is • The nearest stars have large parallax angles, while those of distant stars ...
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Parallax is determined by taking a picture of a star at one time, and another picture six months later; using the angle between its apparent shift, astronomers can determine how far away it is • The nearest stars have large parallax angles, while those of distant stars ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... variation of its luminosity is 12 days. Using the relation M 2.83log10 T 1.81 between period T (in days) and average absolute magnitude M calculate the distance to this star. ...
... variation of its luminosity is 12 days. Using the relation M 2.83log10 T 1.81 between period T (in days) and average absolute magnitude M calculate the distance to this star. ...
18-3 constellations RG
... 13. When a star or galaxy moves quickly away from an observer, the light it emits appears redder than it usually would, this effect is called _____________________________________________. 14. When a star or galaxy moves quickly toward an observer, the light it emits appears bluer than it usually w ...
... 13. When a star or galaxy moves quickly away from an observer, the light it emits appears redder than it usually would, this effect is called _____________________________________________. 14. When a star or galaxy moves quickly toward an observer, the light it emits appears bluer than it usually w ...
Star Game Cards
... What is the name of a dying star that has shrunk down to the size of a planet and no longer supports fusion? ...
... What is the name of a dying star that has shrunk down to the size of a planet and no longer supports fusion? ...
WHAT IS A STAR? - cloudfront.net
... If you remember feeling hot or pressured, this is similar to what happens to hydrogen atoms in the core of a star, where the temperature and pressure are very high. ...
... If you remember feeling hot or pressured, this is similar to what happens to hydrogen atoms in the core of a star, where the temperature and pressure are very high. ...
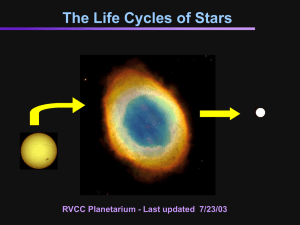
The Life of a Star
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... • These life forms were the simplest form of life – _______ _________. • There is evidence of multi-cellular life as far back as ___________ years. • As organisms with _________ and eventually __________ arrive the fossil record becomes more detailed because these are more easily ___________. ...
... • These life forms were the simplest form of life – _______ _________. • There is evidence of multi-cellular life as far back as ___________ years. • As organisms with _________ and eventually __________ arrive the fossil record becomes more detailed because these are more easily ___________. ...
Solving the Mystery of Massive Star Birth
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
Stars - Images
... Gravity squeezes the clumps of gas and dust together with so much friction/pressure that it caused them to begin to glow and get hot. Sizes can vary ...
... Gravity squeezes the clumps of gas and dust together with so much friction/pressure that it caused them to begin to glow and get hot. Sizes can vary ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
Mr - White Plains Public Schools
... There is a relationship between the temperatures of stars and how bright they are (luminosity). In general, the hotter a star the brighter. This is not always true though. For example, Polaris is the same temperature as our Sun, but is around 4000X brighter. This difference is due to the mass and si ...
... There is a relationship between the temperatures of stars and how bright they are (luminosity). In general, the hotter a star the brighter. This is not always true though. For example, Polaris is the same temperature as our Sun, but is around 4000X brighter. This difference is due to the mass and si ...
Mountain Skies - Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute
... To the northeast of Lyra is the bright star Deneb that represents the tail of the beautiful swan Cygnus. Tracing a line of stars from Deneb towards the south, we note the body and long neck of the swan terminating in the star Albireo that marks the eye of the swan. (Look at Albireo with a small tele ...
... To the northeast of Lyra is the bright star Deneb that represents the tail of the beautiful swan Cygnus. Tracing a line of stars from Deneb towards the south, we note the body and long neck of the swan terminating in the star Albireo that marks the eye of the swan. (Look at Albireo with a small tele ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large star is usually brighter than a small star. The closer it is to earth, the brighter it appears to us. The brightness of a star as seen from Earth is called the ...
... The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large star is usually brighter than a small star. The closer it is to earth, the brighter it appears to us. The brightness of a star as seen from Earth is called the ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... 10. Name five constellations that are visible between sunset and midnight in your hemisphere during: a. The summer months. b. The winter months. 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are ...
... 10. Name five constellations that are visible between sunset and midnight in your hemisphere during: a. The summer months. b. The winter months. 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will cover: Brief review
... Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “RR..RZ...SS...SZ...ZZ”, and then “AA...A ...
... Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “RR..RZ...SS...SZ...ZZ”, and then “AA...A ...
Lecture4
... mass star is about a million times brighter than the Sun. It has 100 times more fuel but uses it up a million times faster. It therefore lives only about 10-4 times as long as the Sun. Since the Sun lives 10 billion years, a 100 solar mass star lives only about one million years. ...
... mass star is about a million times brighter than the Sun. It has 100 times more fuel but uses it up a million times faster. It therefore lives only about 10-4 times as long as the Sun. Since the Sun lives 10 billion years, a 100 solar mass star lives only about one million years. ...
Life Cycle of a Star Notes
... Stars glow because of a nuclear fusion reaction whereby hydrogen fuses together to form heavier elements such as helium and release energy. If enough matter is left behind, this may be so dense, and its gravitational field so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light or other forms of e ...
... Stars glow because of a nuclear fusion reaction whereby hydrogen fuses together to form heavier elements such as helium and release energy. If enough matter is left behind, this may be so dense, and its gravitational field so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light or other forms of e ...
Amie Bickert - ColonialAcademyScience
... Protostar- earliest stage of a stars life White dwarf: blue-white core of the star that is left behind cools forms this. Supernovas: an explosion of a suergiant Neutron star: the remains of high-mass stars. Black holes- an object with gravity so strong that nothing, not even light, can esc ...
... Protostar- earliest stage of a stars life White dwarf: blue-white core of the star that is left behind cools forms this. Supernovas: an explosion of a suergiant Neutron star: the remains of high-mass stars. Black holes- an object with gravity so strong that nothing, not even light, can esc ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.