H-R Diagrams
... main sequence star? 2. What kinds of stars are the hottest? 3. What kinds of stars are the brightest? 4. Why do White dwarves have a low brightness when they are so hot? ...
... main sequence star? 2. What kinds of stars are the hottest? 3. What kinds of stars are the brightest? 4. Why do White dwarves have a low brightness when they are so hot? ...
The Science behind the Stars ctY Astrophysics by Spencer McClung
... of stars with three helium atoms combining to form a carbon atom. For the most massive stars, this continues until finally iron is formed. Then the weight is so great that the star collapses in on itself and explodes in a supernova, which is how almost every atom heavier than iron is created. That m ...
... of stars with three helium atoms combining to form a carbon atom. For the most massive stars, this continues until finally iron is formed. Then the weight is so great that the star collapses in on itself and explodes in a supernova, which is how almost every atom heavier than iron is created. That m ...
Astronomical Ideas – Math Review practice problems 1. The radius
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
Star Vocabulary
... 1. Apparent Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star appears to an observer. 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4.Doppler Effect- ...
... 1. Apparent Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star appears to an observer. 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4.Doppler Effect- ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
Notes - CH 12
... contract until it is about the size of Earth Some become so hot they emit a blue light The Sun will become a dwarf star in billions of years Supernova: the explosion of a supergiant star A supergiant star can explode before it dies The debris is still visible as an interstellar cloud ...
... contract until it is about the size of Earth Some become so hot they emit a blue light The Sun will become a dwarf star in billions of years Supernova: the explosion of a supergiant star A supergiant star can explode before it dies The debris is still visible as an interstellar cloud ...
Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Stars
... A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are not visible all year because Earth revolves around the Sun 4. Circumpolar constellations in the northern sky appe ...
... A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are not visible all year because Earth revolves around the Sun 4. Circumpolar constellations in the northern sky appe ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
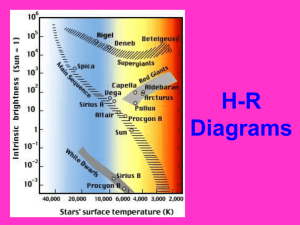
Stars, H-R and Life Cycle of Star
... Two astronomers discovered a relationship between the absolute magnitude (real brightness) of a star and its surface temperature. They plotted the data on a graph. ...
... Two astronomers discovered a relationship between the absolute magnitude (real brightness) of a star and its surface temperature. They plotted the data on a graph. ...
Universe CBA Review - cms16-17
... 22.) When a scientist looks at a galaxy that is 12 billion light years away and is red shifted, what does that tell you about the galaxy? 23.) What is the name of the effect caused by motion of an object causing wavelengths to compress in front of it and expand behind it? Use the diagram below to an ...
... 22.) When a scientist looks at a galaxy that is 12 billion light years away and is red shifted, what does that tell you about the galaxy? 23.) What is the name of the effect caused by motion of an object causing wavelengths to compress in front of it and expand behind it? Use the diagram below to an ...
Mars Project
... The mass of a star will tell you how long it will live. You may think that if a star is bigger it lasts longer. But you are wrong. Its kind of like a car the smaller it is the longer it lasts. If the star is very small it will live for about 200billion years. If it is a medium size (like the sun) ...
... The mass of a star will tell you how long it will live. You may think that if a star is bigger it lasts longer. But you are wrong. Its kind of like a car the smaller it is the longer it lasts. If the star is very small it will live for about 200billion years. If it is a medium size (like the sun) ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... 3) As you move across the X axis of the diagram, what happens to surface temperature? Surface temperature decreases 4) Where is the sun found within the H-R diagram? In the Main Sequence 5) Sketch an H-R diagram and label the main sequence, white dwarf, and giant/super giant regions on the diagram. ...
... 3) As you move across the X axis of the diagram, what happens to surface temperature? Surface temperature decreases 4) Where is the sun found within the H-R diagram? In the Main Sequence 5) Sketch an H-R diagram and label the main sequence, white dwarf, and giant/super giant regions on the diagram. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Mira Stars • Mira (=wonderful, lat.) [o Ceti]: sometimes ...
... Mira Stars • Mira (=wonderful, lat.) [o Ceti]: sometimes ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... The apparent magnitude of a star tells you how bright the star is as viewed from A nebula is a huge cloud of gas, primarily composed of ...
... The apparent magnitude of a star tells you how bright the star is as viewed from A nebula is a huge cloud of gas, primarily composed of ...
How Do Astronomers Measure the Brightness of a Star?
... Apparent magnitudes only tell us how bright stars appear to be, NOT how bright they actually are. Look at the above example: -There are 2 stars that both shine with the exact same amount of light, BUT one of them is 10x further than the other ...
... Apparent magnitudes only tell us how bright stars appear to be, NOT how bright they actually are. Look at the above example: -There are 2 stars that both shine with the exact same amount of light, BUT one of them is 10x further than the other ...
ASTRO REVIEW 14
... _____ 2. In the year 14,000, Earth’s axis will point toward a. Polaris b. Vega c. the Sun d. the moon _____ 3. What is the shape of a planet’s orbit? a. circular b. irregular c. elliptical d. constantly changing _____ 4. Which type of radiation has the shortest wavelength? a. gamma rays b. visible l ...
... _____ 2. In the year 14,000, Earth’s axis will point toward a. Polaris b. Vega c. the Sun d. the moon _____ 3. What is the shape of a planet’s orbit? a. circular b. irregular c. elliptical d. constantly changing _____ 4. Which type of radiation has the shortest wavelength? a. gamma rays b. visible l ...
Chapter 7 Vocabulary212
... 1. Spectroscope- used to study star’s characteristics by spreading light into different wavelengths 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 yea ...
... 1. Spectroscope- used to study star’s characteristics by spreading light into different wavelengths 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 yea ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.























