AST 207 Test 2 Answers 20 October 2010
... star A. Prof. Adams says he discovered a new type of star that is fainter than white dwarfs. Has he discovered a new type of star? Explain. The clues are very much like Walter Adams’ discovery that Sirius B is a white dwarf. However, there is a crucial missing clue. Since Sirius A and B were known t ...
... star A. Prof. Adams says he discovered a new type of star that is fainter than white dwarfs. Has he discovered a new type of star? Explain. The clues are very much like Walter Adams’ discovery that Sirius B is a white dwarf. However, there is a crucial missing clue. Since Sirius A and B were known t ...
May 2016 night sky chart
... For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness or magnitude limit of 4.5 are shown on the star chart. To use this star chart, rotate the chart so that the direct ...
... For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness or magnitude limit of 4.5 are shown on the star chart. To use this star chart, rotate the chart so that the direct ...
STAR SYTEMS AND GALAXIES
... • Our sun is a single star but most stars are members of groups of two or more, called star systems. • Two star systems are called binary. Three star systems are called triple. • Proxima Centauri is probably a triple. Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B are part of a binary sytem. • In a binary s ...
... • Our sun is a single star but most stars are members of groups of two or more, called star systems. • Two star systems are called binary. Three star systems are called triple. • Proxima Centauri is probably a triple. Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B are part of a binary sytem. • In a binary s ...
Types of Stars - WordPress.com
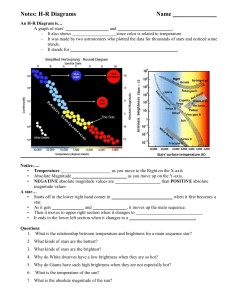
... • The main sequence is a narrow band of stars on the H-R diagram that runs diagonally from the upper left ( bright, hot stars) to the lower right ( dim, cool stars). About 90 percent of stars are on the main sequence, including the Sun. • A star’s position on the main sequence is determined by its i ...
... • The main sequence is a narrow band of stars on the H-R diagram that runs diagonally from the upper left ( bright, hot stars) to the lower right ( dim, cool stars). About 90 percent of stars are on the main sequence, including the Sun. • A star’s position on the main sequence is determined by its i ...
H-R Diagram Notes
... • Starts off in the lower right hand corner in ___________________________ when it first becomes a star. • As it gets ______________ and _______________, it moves up the main sequence. • Then it moves to upper right section when it changes to _____________________________. • It ends in the lower lef ...
... • Starts off in the lower right hand corner in ___________________________ when it first becomes a star. • As it gets ______________ and _______________, it moves up the main sequence. • Then it moves to upper right section when it changes to _____________________________. • It ends in the lower lef ...
File
... The length of a star’s life is determined by its mass. A star with a small mass will live longer than a star with a large mass because it burns less gas. The temperature of a star determines its color. The hottest stars are blue or white and the coolest stars are red or yellow. As a star goes throug ...
... The length of a star’s life is determined by its mass. A star with a small mass will live longer than a star with a large mass because it burns less gas. The temperature of a star determines its color. The hottest stars are blue or white and the coolest stars are red or yellow. As a star goes throug ...
How is a Star`s Color Related to Its temperature?
... How is a Star’s Color Related to Its temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than cthers. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue. and Betelgense is red. Capella and ore" Sun are yellow, in this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russel ...
... How is a Star’s Color Related to Its temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than cthers. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue. and Betelgense is red. Capella and ore" Sun are yellow, in this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russel ...
Characteristics of Stars Stars Analyzing Starlight Star Characteristics
... · spectrographs - device that separates light into different wavelengths (colors) · each star produces a unique spectrum (series of colors and lines) · a star's spectrum tells us elements present (composition) surface temperature how fast the star is moving toward or away from Earth ...
... · spectrographs - device that separates light into different wavelengths (colors) · each star produces a unique spectrum (series of colors and lines) · a star's spectrum tells us elements present (composition) surface temperature how fast the star is moving toward or away from Earth ...
Stars Part 2 - westscidept
... • How bright a star looks in the sky from Earth is called apparent magnitude. • A dim star might look bright to us on Earth if it is close. At the same time, we may barely be able to see a very bright star if it is too far away. • Betelgeuse which is one of the brightest stars in the sky is 310 lig ...
... • How bright a star looks in the sky from Earth is called apparent magnitude. • A dim star might look bright to us on Earth if it is close. At the same time, we may barely be able to see a very bright star if it is too far away. • Betelgeuse which is one of the brightest stars in the sky is 310 lig ...
Nebula – • The most abundant element in the universe is hydrogen
... Eventually, the temperature inside a protostar becomes hot enough (about 10,000,000°C) for nuclear fusion reactions to begin converting hydrogen into helium. ...
... Eventually, the temperature inside a protostar becomes hot enough (about 10,000,000°C) for nuclear fusion reactions to begin converting hydrogen into helium. ...
A Star is Born – Worksheet and Key – Ben Kwok
... Are white dwarfs very hot or very cold? What comes after a white dwarf? What is a supergiant star? Is the lifespan of a supergiant longer or shorter than that of a main sequence? 13. How big can a supergiant get? 14. What are 2 characteristics of a neutron star? 15. How many black holes have been fo ...
... Are white dwarfs very hot or very cold? What comes after a white dwarf? What is a supergiant star? Is the lifespan of a supergiant longer or shorter than that of a main sequence? 13. How big can a supergiant get? 14. What are 2 characteristics of a neutron star? 15. How many black holes have been fo ...
a. Recognize the physical attributes of stars in the night sky such as
... This is not meant to be printed off and given as a test…this document is to give you ideas of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard ...
... This is not meant to be printed off and given as a test…this document is to give you ideas of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard ...
Astronomy Snakes and Ladders Earth, third planet in Solar System
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
KOI-3158: An extremely compact system of five
... Kepler’s ultra-precise, long-duration photometry is ideal for detecting systems with multiple transiting planets. These systems provide important data for understanding the dynamics, formation, and evolution of planetary systems. Here, we present a detailed analysis of an extremely compact and old f ...
... Kepler’s ultra-precise, long-duration photometry is ideal for detecting systems with multiple transiting planets. These systems provide important data for understanding the dynamics, formation, and evolution of planetary systems. Here, we present a detailed analysis of an extremely compact and old f ...
Lab 21.1 Classifying Stars
... 1. Compare the star’s mass to its luminosity and to its temperature. Can you find any basic relationship between these traits? (i.e. the greater the mass, the ….) _____________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. (a) What is a red giant? ________ ...
... 1. Compare the star’s mass to its luminosity and to its temperature. Can you find any basic relationship between these traits? (i.e. the greater the mass, the ….) _____________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. (a) What is a red giant? ________ ...
Jeopardy Questions
... Q: What is the period-luminosity relationship A: An observed relationship between the period of a Cepheid Variable star’s variability and its luminosity. This relation enabled accurate distances to stars in the Milky Way to be measured for the first time ...
... Q: What is the period-luminosity relationship A: An observed relationship between the period of a Cepheid Variable star’s variability and its luminosity. This relation enabled accurate distances to stars in the Milky Way to be measured for the first time ...
Spring Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... • If you really want to challenge yourself, use binoculars and go straight out from the nose of the lion. You should run into the “Beehive Cluster”. ...
... • If you really want to challenge yourself, use binoculars and go straight out from the nose of the lion. You should run into the “Beehive Cluster”. ...
Phys133-Sample MT2
... 2) Why did the solar nebula heat up as it collapsed? A) Radiation from other nearby stars that had formed earlier heated the nebula. B) As the cloud shrank, its gravitational potential energy was converted to kinetic energy and then into thermal energy. C) Collisions among planetesimals generated fr ...
... 2) Why did the solar nebula heat up as it collapsed? A) Radiation from other nearby stars that had formed earlier heated the nebula. B) As the cloud shrank, its gravitational potential energy was converted to kinetic energy and then into thermal energy. C) Collisions among planetesimals generated fr ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least luminous stars are quite common, but are so faint they are hard to see even if they are close. 2. The parallax of the bright star Vega is 0.129 seconds of arc. What is the distance of Vega in parsecs ? In light-years ? We have ...
... of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least luminous stars are quite common, but are so faint they are hard to see even if they are close. 2. The parallax of the bright star Vega is 0.129 seconds of arc. What is the distance of Vega in parsecs ? In light-years ? We have ...
red shift blue shift
... The event horizon is the boundary that marks the “point of no return” for a black hole. Also thought of as the size of the black hole. There is a super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. ...
... The event horizon is the boundary that marks the “point of no return” for a black hole. Also thought of as the size of the black hole. There is a super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. ...
The Hertzsprung – Russell Diagram
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R Diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R Diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
Solutions to problems
... 2. Following the work of Annie Jump Cannon, we divide stars into the seven major spectral types, O, B, A, F, G, K, M. The differences in the spectral type correspond to differences in temperature, with the hottest stars of type O and the coolest type M. The differences in temperature of the stars de ...
... 2. Following the work of Annie Jump Cannon, we divide stars into the seven major spectral types, O, B, A, F, G, K, M. The differences in the spectral type correspond to differences in temperature, with the hottest stars of type O and the coolest type M. The differences in temperature of the stars de ...
Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The
... 2. How does the mass of stars relate to how long they live? 3.a) How would our sun be classified? b) How long is the life time of our sun? c) As our sun ages how will it change? 4. Which star type in the table would be considered a dwarf star? Explain your answer. 5. Which star type is most similar ...
... 2. How does the mass of stars relate to how long they live? 3.a) How would our sun be classified? b) How long is the life time of our sun? c) As our sun ages how will it change? 4. Which star type in the table would be considered a dwarf star? Explain your answer. 5. Which star type is most similar ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.