Locating Objects in Space
... Supernova: referred to as Type II supernova for paths 2 and 3 Black Hole: density so high that escape velocity of star becomes equal to the speed of light, so ...
... Supernova: referred to as Type II supernova for paths 2 and 3 Black Hole: density so high that escape velocity of star becomes equal to the speed of light, so ...
Star Life Cycle
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
stars and The Solar System 8th Science test2
... 7. Name a constellation which can be seen (a) during summer (b) during winter 8. How can we locate pole star using the constellation Ursa major (draw diagram also) 9. Name the brightest star in the sky which is located closed to Orion 10. (a) Name the planet nearest to Sun (b)Name the brightest plan ...
... 7. Name a constellation which can be seen (a) during summer (b) during winter 8. How can we locate pole star using the constellation Ursa major (draw diagram also) 9. Name the brightest star in the sky which is located closed to Orion 10. (a) Name the planet nearest to Sun (b)Name the brightest plan ...
Astronomy
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
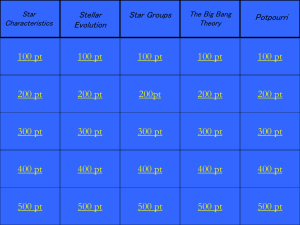
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 10
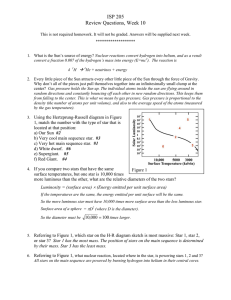
... density (the number of atoms per unit volume), and also to the average speed of the atoms (measured by the gas temperature). 3. Using the Hertzprung-Russell diagram in Figure ...
... density (the number of atoms per unit volume), and also to the average speed of the atoms (measured by the gas temperature). 3. Using the Hertzprung-Russell diagram in Figure ...
A Red Giant - Cloudfront.net
... Becoming a Red Supergiant for about 15 million years. In the cool outer layers flakes of Carbon and Silicon form They are blown away by photons from the Core taking the outer layers of gas with them forming a … ...
... Becoming a Red Supergiant for about 15 million years. In the cool outer layers flakes of Carbon and Silicon form They are blown away by photons from the Core taking the outer layers of gas with them forming a … ...
coSmoS in youR PockET
... Inspired by The 826 Pocket Activity Book: Illustrated by Irene Cecile: Funded by: ...
... Inspired by The 826 Pocket Activity Book: Illustrated by Irene Cecile: Funded by: ...
Monday Sept 14
... the planets, moons, and other objects and materials that orbit that star. Until very recently, there was only one known planetary system Even though many People suspected that most stars had planets orbiting them, we had no scientific evidence to support this suspicion. The one planetary science we ...
... the planets, moons, and other objects and materials that orbit that star. Until very recently, there was only one known planetary system Even though many People suspected that most stars had planets orbiting them, we had no scientific evidence to support this suspicion. The one planetary science we ...
stars - allenscience
... massive explosion called a Supernova. The end result is also a planetary nebula. Supernova are so bright that they can outshine an entire galaxy for a period of time. ...
... massive explosion called a Supernova. The end result is also a planetary nebula. Supernova are so bright that they can outshine an entire galaxy for a period of time. ...
Protostar, Initial mass, Main Sequence
... Red dwarf stars with less than half a solar mass do not achieve red giant status they begin to fade as soon as their hydrogen fuel is exhausted. White dwarfs, planetary nebulae Our Sun, and any star with similar mass, will fuse to carbon and, possibly, oxygen and neon before shrinking to become a wh ...
... Red dwarf stars with less than half a solar mass do not achieve red giant status they begin to fade as soon as their hydrogen fuel is exhausted. White dwarfs, planetary nebulae Our Sun, and any star with similar mass, will fuse to carbon and, possibly, oxygen and neon before shrinking to become a wh ...
White Dwarf star. Are
... 13.7 billion years. The solar system is 4.6 billion years old. The solar system is not the same age as the entire universe. ...
... 13.7 billion years. The solar system is 4.6 billion years old. The solar system is not the same age as the entire universe. ...
Codes of Life
... start to use helium as a fuel producing carbon. It also begins burning hydrogen in its atmosphere and will expand 100 times to become the red giant • When this happens to our Sun (in about 4 billion years) all inner planets and the Earth will be incinerated. ...
... start to use helium as a fuel producing carbon. It also begins burning hydrogen in its atmosphere and will expand 100 times to become the red giant • When this happens to our Sun (in about 4 billion years) all inner planets and the Earth will be incinerated. ...
100 X size of Sun - East Penn School District
... • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon fixed distance of ten parsecs (about 32.6 light years) • How is brightness ...
... • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon fixed distance of ten parsecs (about 32.6 light years) • How is brightness ...
Maui Stargazing April Observing List DEEP SPACE OBJECTS
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
Lecture 10 February 13
... Might die in 1031 years if protons prove to be unstable themselves. That’s 10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 years! Really don’t know if universe will still be here. ...
... Might die in 1031 years if protons prove to be unstable themselves. That’s 10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 years! Really don’t know if universe will still be here. ...
Groups_of_Stars_spectra
... In space there is no up down left or right, only towards or away • Motion towards & away causes the light given off to be squeezed or stretched • Blue-shift: wavelengths from objects moving toward another get squeezed • Red-shift: wavelengths from objects moving away get stretched ...
... In space there is no up down left or right, only towards or away • Motion towards & away causes the light given off to be squeezed or stretched • Blue-shift: wavelengths from objects moving toward another get squeezed • Red-shift: wavelengths from objects moving away get stretched ...
EMS, HR, Star Lives classwork/homework
... 1. Inertia tends to make the planets travel in straight lines. Gravity from the sun pulls the planets toward the sun. These two factors acting together cause the planets to stay in their orbits. 2. gamma rays 3. ultraviolet 4. gamma rays 5. B 6. infrared 7. D 8. Barnard’s star 9. Both stars are yell ...
... 1. Inertia tends to make the planets travel in straight lines. Gravity from the sun pulls the planets toward the sun. These two factors acting together cause the planets to stay in their orbits. 2. gamma rays 3. ultraviolet 4. gamma rays 5. B 6. infrared 7. D 8. Barnard’s star 9. Both stars are yell ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... from the upper left (high, high) to the lower right (low, low) – Called main sequence stars • Stars vary in surface temperature and absolute magnitudes • commonality: actively fusing hydrogen into helium ...
... from the upper left (high, high) to the lower right (low, low) – Called main sequence stars • Stars vary in surface temperature and absolute magnitudes • commonality: actively fusing hydrogen into helium ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.