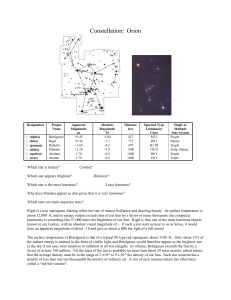
Support worksheet – Topic 3 Questions
... Suggest why the stellar parallax method is limited to distances of about 300 pc for Earth-based telescopes but can be extended to 1000 pc for satellite-based telescopes. ...
... Suggest why the stellar parallax method is limited to distances of about 300 pc for Earth-based telescopes but can be extended to 1000 pc for satellite-based telescopes. ...
Star Life Cycle - GSHS Mrs. Francomb
... Pumbaa: Oh. Gee. I always thought that they were balls of gas burning billions of miles away. Timon: Pumbaa, wit' you, everything's gas. ...
... Pumbaa: Oh. Gee. I always thought that they were balls of gas burning billions of miles away. Timon: Pumbaa, wit' you, everything's gas. ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Astronomy Project Purpose: To
... 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner planets inside it. Something to put it into perspective. 4.) Determin ...
... 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner planets inside it. Something to put it into perspective. 4.) Determin ...
Supernovae - Cloudfront.net
... the amount of energy created in a Type Ia Supernova is always about the same. Thus its luminosity is always the same. A Type Ia Supernova in another galaxy is thus a good standard candle to use to find the distance to the galaxy ...
... the amount of energy created in a Type Ia Supernova is always about the same. Thus its luminosity is always the same. A Type Ia Supernova in another galaxy is thus a good standard candle to use to find the distance to the galaxy ...
Section 25.2 Stellar Evolution
... remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse into a white dwarf. Death of Medium-Mass Stars Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as lowmass stars. During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium- ...
... remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse into a white dwarf. Death of Medium-Mass Stars Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as lowmass stars. During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium- ...
Life cycle of a star
... between 1.4 and 3 times as much mass as the Sun, but are compressed into a ball with a radius of about 10 km. A thimbleful of a neutron star would weigh more than 100 million tons on earth ...
... between 1.4 and 3 times as much mass as the Sun, but are compressed into a ball with a radius of about 10 km. A thimbleful of a neutron star would weigh more than 100 million tons on earth ...
Useful Things to Study (#2)
... What is degenerate electron matter? What is the maximum mass of a white dwarf star? Stars less than 0.4 MSun are fully convective. What does this mean? How long do they last as main sequence stars? Do they become giant stars? How is a star’s evolution changed if it has a really close companion? What ...
... What is degenerate electron matter? What is the maximum mass of a white dwarf star? Stars less than 0.4 MSun are fully convective. What does this mean? How long do they last as main sequence stars? Do they become giant stars? How is a star’s evolution changed if it has a really close companion? What ...
Homework, November 16, 2006 AST110-6
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 9
... 26. What is a coronal mass ejection? 27. Although the trigger for a solar flare is unknown, scientists know that… 28. The sun is composed mainly of _______________________ and ______________________. 29. Can the sun’s magnetic field stop ALL subatomic particles? 30. What is a prominence? 31. What is ...
... 26. What is a coronal mass ejection? 27. Although the trigger for a solar flare is unknown, scientists know that… 28. The sun is composed mainly of _______________________ and ______________________. 29. Can the sun’s magnetic field stop ALL subatomic particles? 30. What is a prominence? 31. What is ...
KOI-54 Claude Plymate There is a star system about 45 light years
... turns out, the system is anything but typical or uninteresting. KOI-54 has been found to be a close binary system, consisting of nearly twin A stars in highly eccentric (e = 0.83) 41.8 day orbits about their mutual center of mass. These main sequence stars reside right at the bottom of the instabili ...
... turns out, the system is anything but typical or uninteresting. KOI-54 has been found to be a close binary system, consisting of nearly twin A stars in highly eccentric (e = 0.83) 41.8 day orbits about their mutual center of mass. These main sequence stars reside right at the bottom of the instabili ...
The life cycle of a star
... of hydrogen and other fuels needed to produce energy Pressure decreases in the star so the star swells (gets bigger) and cools down (turns red) Stars equal to or smaller than the sun become red giants Stars much larger than the Sun become red supergiants ...
... of hydrogen and other fuels needed to produce energy Pressure decreases in the star so the star swells (gets bigger) and cools down (turns red) Stars equal to or smaller than the sun become red giants Stars much larger than the Sun become red supergiants ...
G030485-00 - DCC
... • Once fuel is burned up (core is made of Iron), nuclear fusion ceases and the forces of gravity take over to initiate collapse • Providing the star is large enough (>1.5 times the mass of the sun) the death will follow a Supernovae sequence LIGO-G030485-00-D ...
... • Once fuel is burned up (core is made of Iron), nuclear fusion ceases and the forces of gravity take over to initiate collapse • Providing the star is large enough (>1.5 times the mass of the sun) the death will follow a Supernovae sequence LIGO-G030485-00-D ...
Red Dwarfs and Barnard`s star. Their origin and significance to
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...
stars concept review
... smashed together to form neutrons b. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born c. a shrinking, spinning region in space with a central concentration of matter d. a large explosion on a star that makes it brighter e. an object so dense that even light cannot escape its gravity ...
... smashed together to form neutrons b. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born c. a shrinking, spinning region in space with a central concentration of matter d. a large explosion on a star that makes it brighter e. an object so dense that even light cannot escape its gravity ...
Star Name __Direction ___ Degrees
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.