Stars - Weebly
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univ ...
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univ ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity ...
... compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... 1. Briefly describe the "milestones" that separate protostars from pre-main-sequence stars, and pre-main-sequence stars from main-sequence stars. 2. Briefly describe how a reflection nebula differs from an emission nebula in origin and appearance. 3. Estimate the main-sequence lifetime of a star wit ...
... 1. Briefly describe the "milestones" that separate protostars from pre-main-sequence stars, and pre-main-sequence stars from main-sequence stars. 2. Briefly describe how a reflection nebula differs from an emission nebula in origin and appearance. 3. Estimate the main-sequence lifetime of a star wit ...
Ch. 25 Properties of Stars
... The more negative, the brighter and the more positive, the dimmer Astronomers estimate that there are 200-400 billion stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, but we can only see about 2,500 visible to the naked eye on Earth ...
... The more negative, the brighter and the more positive, the dimmer Astronomers estimate that there are 200-400 billion stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, but we can only see about 2,500 visible to the naked eye on Earth ...
How Technology is Used to Observe Objects in Outer Space
... How is technology used to view distant objects in space? Name 3 different types of technology that can be used to study objects in space and explain ...
... How is technology used to view distant objects in space? Name 3 different types of technology that can be used to study objects in space and explain ...
Homework Problems for Quiz 1 – AY 5 – Spring 2013
... dust toward either star) a) What are the relative distances of the two stars? ...
... dust toward either star) a) What are the relative distances of the two stars? ...
Name: Astronomy Study Guide Part 1 Define Astronomy
... Day- 24 hours for Earth to rotate once about its axis Month- Length of time for the moon to revolve around earth Year- Length of time for Earth to revolve around sun 365.25 days Calendar- years, months, and days based on our celestial objects Leap Year- Feb 29 once every 4 years to make up for our 3 ...
... Day- 24 hours for Earth to rotate once about its axis Month- Length of time for the moon to revolve around earth Year- Length of time for Earth to revolve around sun 365.25 days Calendar- years, months, and days based on our celestial objects Leap Year- Feb 29 once every 4 years to make up for our 3 ...
a. Recognize the physical attributes of stars in the night sky such as
... of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard to help you guide your instruction based on students needs. A good formative assessment sh ...
... of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard to help you guide your instruction based on students needs. A good formative assessment sh ...
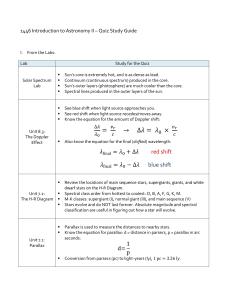
red shift blue shift
... dwarf stars on the H-R Diagram. Spectral class order from hottest to coolest: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. M-K classes: supergiant (I), normal giant (III), and main sequence (V) Stars evolve and do NOT last forever. Absolute magnitude and spectral classification are useful in figuring out how a star will ev ...
... dwarf stars on the H-R Diagram. Spectral class order from hottest to coolest: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. M-K classes: supergiant (I), normal giant (III), and main sequence (V) Stars evolve and do NOT last forever. Absolute magnitude and spectral classification are useful in figuring out how a star will ev ...
The Milky Way
... • How does the sky appear to move as Earth rotates? • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most ...
... • How does the sky appear to move as Earth rotates? • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most ...
Notes- Stars
... Black Holes • Gravity is so strong that not even light can escape! • Often at the center of galaxies! • A Galaxy is a huge group of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity • Milky way is a spiral galaxy, but galaxies can also be irregular or elliptical in shape ...
... Black Holes • Gravity is so strong that not even light can escape! • Often at the center of galaxies! • A Galaxy is a huge group of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity • Milky way is a spiral galaxy, but galaxies can also be irregular or elliptical in shape ...
Exploring Space
... million K, pressure is so great that nuclear fusion occurs- a star is born Heat from fusion of hydrogen is released When balance is maintained from inward pressure (gravity) and outward pressure (heat) the Main-Sequence stage is ...
... million K, pressure is so great that nuclear fusion occurs- a star is born Heat from fusion of hydrogen is released When balance is maintained from inward pressure (gravity) and outward pressure (heat) the Main-Sequence stage is ...
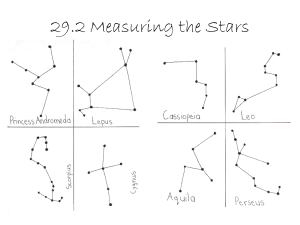
Constellations
... Asterism: Smaller groups of stars that form patterns within a constellation, from the Greek word aster, meaning star ...
... Asterism: Smaller groups of stars that form patterns within a constellation, from the Greek word aster, meaning star ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Which star has strong lines of ionized helium in its spectrum? Which star is the white dwarf? Which star has spectrum lines due to molecules? ...
... Which star has strong lines of ionized helium in its spectrum? Which star is the white dwarf? Which star has spectrum lines due to molecules? ...
Measuring the Stars
... the period and semi-major axis of the orbit must be measured. •Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. •Relative speeds of the two stars can be measured using the Doppler effect •Speed will be inversely proportional to the mass. This allows us to calculate the mass of each s ...
... the period and semi-major axis of the orbit must be measured. •Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. •Relative speeds of the two stars can be measured using the Doppler effect •Speed will be inversely proportional to the mass. This allows us to calculate the mass of each s ...
Document
... _____ 6. If the universe expands forever, a. the universe will collapse. b. the universe will repeat itself. c. the universe will remain just as it is today. d. stars will age and die and the universe will become cold and dark. _____ 7. The majority of stars in our galaxy are a. blue stars. c. main- ...
... _____ 6. If the universe expands forever, a. the universe will collapse. b. the universe will repeat itself. c. the universe will remain just as it is today. d. stars will age and die and the universe will become cold and dark. _____ 7. The majority of stars in our galaxy are a. blue stars. c. main- ...
- MrKowalik.com
... 4. If Earth and another celestial object were coming closer together, the electromagnetic waves are bunched together resulting in _____________________________________ 5. If Earth and another celestial object were moving apart, the electromagnetic waves are spread out causing a _____________________ ...
... 4. If Earth and another celestial object were coming closer together, the electromagnetic waves are bunched together resulting in _____________________________________ 5. If Earth and another celestial object were moving apart, the electromagnetic waves are spread out causing a _____________________ ...
ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... Universe - http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/StarChild/universe_level2/universe.html Using the website find the following box and Click on the topics to find your answers: The Milky Way ...
... Universe - http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/StarChild/universe_level2/universe.html Using the website find the following box and Click on the topics to find your answers: The Milky Way ...
Document
... • When two stars are gravitationally bound to each other, they orbit a common center of mass • Often appear bound to each other, even with a telescope ...
... • When two stars are gravitationally bound to each other, they orbit a common center of mass • Often appear bound to each other, even with a telescope ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.