III - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... Function of the Double Cluster h and x Persei”. You may not want to read the entire paper, but scanning sections of it will illustrate the process an astronomer might follow. To begin, the interplay of reading other’s research and learning all that is known about a subject will lead a scientists to ...
... Function of the Double Cluster h and x Persei”. You may not want to read the entire paper, but scanning sections of it will illustrate the process an astronomer might follow. To begin, the interplay of reading other’s research and learning all that is known about a subject will lead a scientists to ...
After Dark in Allenspark
... working on for five years. Wish us luck! January 21: Venus begins to be visible in the in the eastern morning sky. January 22: Last quarter moon. January 27: Saturn at opposition (on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun), so it's the brightest and closest it will be all year and up all night. ...
... working on for five years. Wish us luck! January 21: Venus begins to be visible in the in the eastern morning sky. January 22: Last quarter moon. January 27: Saturn at opposition (on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun), so it's the brightest and closest it will be all year and up all night. ...
Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics
... from Earth does not look very bright. But the sun looks very bright because it is so close to Earth. ...
... from Earth does not look very bright. But the sun looks very bright because it is so close to Earth. ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #2 Problem 1
... c) In the Milky Way, Salpeter thought x = 1.35. Using your results from (a) and (b) and the scale heights of stars in the Galaxy given in the included table, describe how the fractions of stars of different luminosities should vary in all-sky samples of various magnitudes. Below what apparent bolome ...
... c) In the Milky Way, Salpeter thought x = 1.35. Using your results from (a) and (b) and the scale heights of stars in the Galaxy given in the included table, describe how the fractions of stars of different luminosities should vary in all-sky samples of various magnitudes. Below what apparent bolome ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... 1. Rank these stars in order of luminosity, from brightest to dimmest : Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ __ ...
... 1. Rank these stars in order of luminosity, from brightest to dimmest : Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ __ ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
Table Number: _____
... Using the distance modulus equation, d= 10 x 10(m-M)/5 , in the Introduction to calculate the distance to the cluster in parsecs. Then convert your answer to light years. Show all work in the ...
... Using the distance modulus equation, d= 10 x 10(m-M)/5 , in the Introduction to calculate the distance to the cluster in parsecs. Then convert your answer to light years. Show all work in the ...
the Study Guide
... Celestial Objects: Stars, planets, comets, asteroids, black holes, galaxies, nebulae, and any other body in space. "Celestial" means "of the sky." Chlorofluorocarbons: These chemicals are thought to be partly responsible for the hole in the Ozone Layer. They are used to make Styrofoam, air condition ...
... Celestial Objects: Stars, planets, comets, asteroids, black holes, galaxies, nebulae, and any other body in space. "Celestial" means "of the sky." Chlorofluorocarbons: These chemicals are thought to be partly responsible for the hole in the Ozone Layer. They are used to make Styrofoam, air condition ...
Astronomy Lecture Notes: Stellar Nomenclature I Introduction
... ii. Many formal names of stars are middle eastern in origin to honor the middle eastern astronomers that carried on work in astronomy after the fall of the Roman Empire. iii. Examples: See the names of stars in the Big Dipper c. Apparent Magnitudes i. Apparent magnitude is a code for brightness ii. ...
... ii. Many formal names of stars are middle eastern in origin to honor the middle eastern astronomers that carried on work in astronomy after the fall of the Roman Empire. iii. Examples: See the names of stars in the Big Dipper c. Apparent Magnitudes i. Apparent magnitude is a code for brightness ii. ...
Luminosity
... Blurring of atmosphere restricts ground based to ±o.oo2” One arc second is a typewriter period at 100 meters 10,000 stars from ground; 120,000 Hipparcos; 1 Billion Gaia ...
... Blurring of atmosphere restricts ground based to ±o.oo2” One arc second is a typewriter period at 100 meters 10,000 stars from ground; 120,000 Hipparcos; 1 Billion Gaia ...
Ch. 27 Stars & Galaxies
... Distance to the stars Light Years: The distance that light travels in one year. Speed of light is 300,000 km/sec. Light travels about 9.5 trillion km in one year. Fun Fact: Light from the sun takes 8 min. to reach Earth!!! ...
... Distance to the stars Light Years: The distance that light travels in one year. Speed of light is 300,000 km/sec. Light travels about 9.5 trillion km in one year. Fun Fact: Light from the sun takes 8 min. to reach Earth!!! ...
Astronomy Galaxies & The Universe
... Star Brightness luminosity – depends on size & temperature apparent magnitude – as seen from Earth: brightest are ≤ 1 faintest are ≥ 6 absolute magnitude – expresses luminosity of stars as if they were all seen 32.6 lightyears from Earth (our sun = 4.8) ...
... Star Brightness luminosity – depends on size & temperature apparent magnitude – as seen from Earth: brightest are ≤ 1 faintest are ≥ 6 absolute magnitude – expresses luminosity of stars as if they were all seen 32.6 lightyears from Earth (our sun = 4.8) ...
About the Universe The Universe is everything that exists, including
... called a neutron star, which shrinks, pulled in by its own gravity. Some of the matter in the supernova is thrown off into space as dust and gas. Some of this dust and gas will go on to make new stars. Our Sun contains heavy elements, which suggests that it was probably created from the dust of an o ...
... called a neutron star, which shrinks, pulled in by its own gravity. Some of the matter in the supernova is thrown off into space as dust and gas. Some of this dust and gas will go on to make new stars. Our Sun contains heavy elements, which suggests that it was probably created from the dust of an o ...
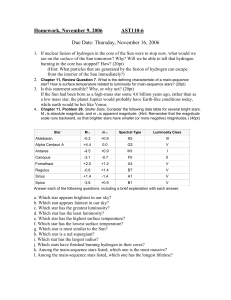
Homework, August 29, 2002 AST110-6
... e. Which star has the highest surface temperature? f. Which star has the lowest surface temperature? g. Which star is most similar to the Sun? h. Which star is a red supergiant? i. Which star has the largest radius? j. Which stars have finished burning hydrogen in their cores? k. Among the main-sequ ...
... e. Which star has the highest surface temperature? f. Which star has the lowest surface temperature? g. Which star is most similar to the Sun? h. Which star is a red supergiant? i. Which star has the largest radius? j. Which stars have finished burning hydrogen in their cores? k. Among the main-sequ ...
Chapter 21 power point - Laconia School District
... diagram that runs from the upper left to the lower right and includes more than 90% of all stars. ...
... diagram that runs from the upper left to the lower right and includes more than 90% of all stars. ...
Stars
... • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left be ...
... • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left be ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... So what about the origins of life? • There is evidence that the organic material (_________ _______) necessary for life arrived on Earth in ___________. • Organic material is ______ based compounds and is part of all life as we know it. • It may have been lightning that made these compounds become ...
... So what about the origins of life? • There is evidence that the organic material (_________ _______) necessary for life arrived on Earth in ___________. • Organic material is ______ based compounds and is part of all life as we know it. • It may have been lightning that made these compounds become ...
molecular clouds
... • Today stars form in a complex environment • Hydrogen and helium are the predominant components of the ISM, but it is enriched with heavier elements from earlier stars (created in ...
... • Today stars form in a complex environment • Hydrogen and helium are the predominant components of the ISM, but it is enriched with heavier elements from earlier stars (created in ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.