here - University of Toronto Astronomy
... of stars moving towards or away can be studied; shift in wavelength divided by the wavelength at rest equals approach or recession speed divided by the velocity of light; can determine the following basic properties of stars- rotation, atmospheric motions, circumstellar material and motion; evidence ...
... of stars moving towards or away can be studied; shift in wavelength divided by the wavelength at rest equals approach or recession speed divided by the velocity of light; can determine the following basic properties of stars- rotation, atmospheric motions, circumstellar material and motion; evidence ...
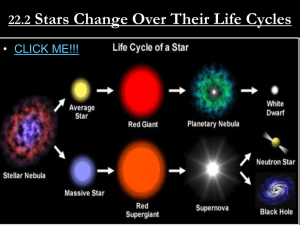
Stars
... Stars A ‘Star’ is a large celestial body composed of gravitationally contained hot gases emitting electromagnetic radiation, especially light, as a result of nuclear reactions inside the star. The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in ...
... Stars A ‘Star’ is a large celestial body composed of gravitationally contained hot gases emitting electromagnetic radiation, especially light, as a result of nuclear reactions inside the star. The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in ...
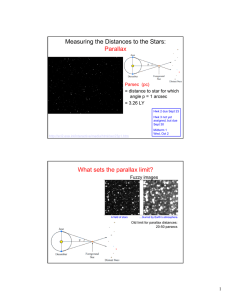
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
Chapter 30.1
... Circumpolar: stars that never go below the horizon. (Circling stars). Different stars become visible during different seasons. Three actual motions: ...
... Circumpolar: stars that never go below the horizon. (Circling stars). Different stars become visible during different seasons. Three actual motions: ...
Stars are classified according to their color
... between the stars. • Distance that light travels in one year. Its about 9.5 million million kilometers. That is not a typo! ...
... between the stars. • Distance that light travels in one year. Its about 9.5 million million kilometers. That is not a typo! ...
The Hipparcos Star Globe Booklet - Cosmos
... gathered data for four years. The satellite span slowly, controlled in such a way as to gradually shift the axis of rotation so that over time the telescope could repeatedly scan the entire celestial sphere. A simultaneous onboard experiment named Tycho was also to provide astrometric and two-colour ...
... gathered data for four years. The satellite span slowly, controlled in such a way as to gradually shift the axis of rotation so that over time the telescope could repeatedly scan the entire celestial sphere. A simultaneous onboard experiment named Tycho was also to provide astrometric and two-colour ...
Measuring the Stars
... mind-bogglingly big it is. I mean, you may think it's a long way down the road to the chemist, but that's just peanuts to space…” To be fair though, when confronted by the sheer enormity of the distances between the stars, better minds than the one responsible for the Guide's introduction have falte ...
... mind-bogglingly big it is. I mean, you may think it's a long way down the road to the chemist, but that's just peanuts to space…” To be fair though, when confronted by the sheer enormity of the distances between the stars, better minds than the one responsible for the Guide's introduction have falte ...
Proper Motion
... spectroscopy nor employing the Doppler principal.” • Changes in parallax and proper motion over time reveal radial velocity. • Possible only with precise measurements. • Hipparcos satellite data in combination with older stellar data. • Changing angular separation of stars sharing the same space vel ...
... spectroscopy nor employing the Doppler principal.” • Changes in parallax and proper motion over time reveal radial velocity. • Possible only with precise measurements. • Hipparcos satellite data in combination with older stellar data. • Changing angular separation of stars sharing the same space vel ...
Section 2
... is if it was the standard distance from the earth. temperature is based on the color of the star • Blue or blue white is the hottest and red is the coolest ...
... is if it was the standard distance from the earth. temperature is based on the color of the star • Blue or blue white is the hottest and red is the coolest ...
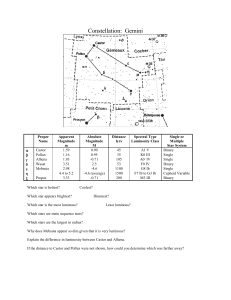
Gemini
... several yellow and orange giants of spectral type late G to early K). Its hottest main sequence star is given as of spectral class B3 (Sky Catalogue 2000.0), and its Trumpler classification as III,3,r by all sources. It is approaching us at 5 km/sec. Even the naked eye finds this cluster easily near ...
... several yellow and orange giants of spectral type late G to early K). Its hottest main sequence star is given as of spectral class B3 (Sky Catalogue 2000.0), and its Trumpler classification as III,3,r by all sources. It is approaching us at 5 km/sec. Even the naked eye finds this cluster easily near ...
SHELL H II REGIONS IN NGC 6334
... The radial velocity of a source can be obtained from a single measurement and the application of the Doppler effect. In contrast, the plane-of-the-sky velocity requires of at least two measurements, as separated in time as possible. ...
... The radial velocity of a source can be obtained from a single measurement and the application of the Doppler effect. In contrast, the plane-of-the-sky velocity requires of at least two measurements, as separated in time as possible. ...
Chapter 29
... of a star • How bright a star appears to be • How bright a star really is (also called Luminosity) ...
... of a star • How bright a star appears to be • How bright a star really is (also called Luminosity) ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.