* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download here - University of Toronto Astronomy
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
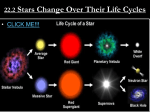
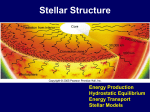
Chemistry Spectral Lines: Spectral lines correspond to temperature in the 7 different classes of stars- The coolest stars demonstrate spectral lines of molecules and neutral metals while the hottest, bluest stars’ source of spectral lines are ionized helium atoms; the hotter the gas, the faster the molecules or atoms move, the more likely electrons will be disturbed or disrupted; emission and absorption lines depend on electron orbital structure of atoms. Star Equilibrium: Main-sequence star equilibrium is determined by individual mass and chemical compositions. Nuclear reactions result in disturbance of equilibrium, leading the stellar evolution. Hydrogen-burning lifetime = (mass/luminosity) x 9 billion years, since larger stars have higher interior temperatures, faster use of nuclear fuel and faster evolution. Nuclear Reactions: Main-sequence stars convert hydrogen to helium. Physics Doppler Effect: Blue-shifts or red-shifts in stars; by measuring wavelengths, velocities of stars moving towards or away can be studied; shift in wavelength divided by the wavelength at rest equals approach or recession speed divided by the velocity of light; can determine the following basic properties of stars- rotation, atmospheric motions, circumstellar material and motion; evidence for the expansion of universe. Measuring tangential velocity: This is the motion of the star perpendicular to the line of sight, determined from measurements of the distance to the star, and the rate of angular motion across the sky. Stellar Forces: Gravity pulls inward on stellar particles, while gas pressure, radiation pressure and magnetic support push outwards. The balance between pressure and gravity is called hydrostatic equilibrium. Wien’s Law: W= 0.00290/T, where W is the wavelength at which the maximum amount of radiation comes from a body of temperature T. The law has implications for the prediction of infrared stars or star-nebula complexes. Mathematics Inverse Square Law: This is the relation describing any entity, like radiation or gravity, that varies as 1/r^2, where r is the distance of the entity from source. Parallax determination: Parallax, the apparent shift in the position of an object caused by a shift in the observer’s position, gives the distance to the object using trigonometry.