AST 207 Test 2 Answers 20 October 2010
... with a much larger mass. Therefore Kepler’s1st law applies. A star orbits the black body in an ellipse with the black hole at one focus. b. (3 pts.) A star has been observed to orbit at a distance of 100AU. How long does it take to complete one orbit? (Assume the orbit is circular for this calculati ...
... with a much larger mass. Therefore Kepler’s1st law applies. A star orbits the black body in an ellipse with the black hole at one focus. b. (3 pts.) A star has been observed to orbit at a distance of 100AU. How long does it take to complete one orbit? (Assume the orbit is circular for this calculati ...
Distances to Stars: Parsecs and Light Years
... Think back to descriptions of solar system distances (light minutes to light days) and compare the situation for nearby stars to get an idea of the immensity of interstellar ...
... Think back to descriptions of solar system distances (light minutes to light days) and compare the situation for nearby stars to get an idea of the immensity of interstellar ...
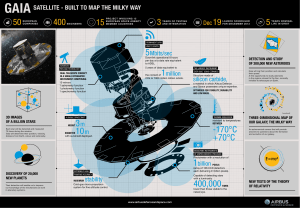
3m 10m -170°C +70°C 400,000
... in the regions closest to the Sun, normally invisible to telescopes on Earth. ...
... in the regions closest to the Sun, normally invisible to telescopes on Earth. ...
Slide 1
... Get at least one exposure in another color to be able to make a CMD. III. Calculate the PSF at every position. Use one PDF per epoch. IV. Remove distortions and mitigate distortions by returning to approx same pixel at each epoch. V. Fit PSF to data. Recalculate centroids and photometry till ...
... Get at least one exposure in another color to be able to make a CMD. III. Calculate the PSF at every position. Use one PDF per epoch. IV. Remove distortions and mitigate distortions by returning to approx same pixel at each epoch. V. Fit PSF to data. Recalculate centroids and photometry till ...
Folie 1 - univie.ac.at
... two- color information: one satellite carries a blue and the other a red filter. The 20cm cube structure houses three orthogonal reaction wheels and three magnetorquer coils for three-axis attitude control and momentum dumping. Attitude determination is provided by a magnetometer, six sun sensors an ...
... two- color information: one satellite carries a blue and the other a red filter. The 20cm cube structure houses three orthogonal reaction wheels and three magnetorquer coils for three-axis attitude control and momentum dumping. Attitude determination is provided by a magnetometer, six sun sensors an ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... – If two stars have the same color and distance, difference in brightness is due to difference in size – Dwarf and giant stars are literally dwarfs or giants ...
... – If two stars have the same color and distance, difference in brightness is due to difference in size – Dwarf and giant stars are literally dwarfs or giants ...
ABOUT PARALLAX AND… CONSTELLATIONS Abstract
... of stellar parallax and the proper motions of stars. The project was named in honour of Hipparchus. Ideas behind such a mission dated from 1967, with the mission accepted by ESA in 1980. The satellite was launched by Ariane 4 on August 8th 1989. The program was divided in two parts: the Hipparcos ex ...
... of stellar parallax and the proper motions of stars. The project was named in honour of Hipparchus. Ideas behind such a mission dated from 1967, with the mission accepted by ESA in 1980. The satellite was launched by Ariane 4 on August 8th 1989. The program was divided in two parts: the Hipparcos ex ...
Pistol Star of the Pistol Nebula
... a projected separation of 110 AUs (Figer et al, 1998). Indeed, the star may have started with as much as 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 Solarmasses, extremely high luminosity, a variable spectra, and surrounding ejecta, it is classified as ...
... a projected separation of 110 AUs (Figer et al, 1998). Indeed, the star may have started with as much as 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 Solarmasses, extremely high luminosity, a variable spectra, and surrounding ejecta, it is classified as ...
Characteristics of Stars
... distances between stars and galaxies • Proxima Centauri is 4.3 light years away • Looking back in time ...
... distances between stars and galaxies • Proxima Centauri is 4.3 light years away • Looking back in time ...
ppt
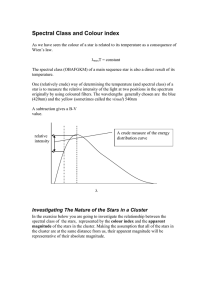
... If same luminosity, this means that they are about 300,000 times further away (i.e. 300,000 AU, or about 5 light years). ...
... If same luminosity, this means that they are about 300,000 times further away (i.e. 300,000 AU, or about 5 light years). ...
Stellar Distances and Magnitudes
... • As stars get further away, their parallax becomes smaller. • Parallax can not be measured to better than ~0.02” from the ground (d < 50 pc). – Interferometry is improving on this for selected applications ...
... • As stars get further away, their parallax becomes smaller. • Parallax can not be measured to better than ~0.02” from the ground (d < 50 pc). – Interferometry is improving on this for selected applications ...
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide Name Why
... 5. A shock wave may be the stimulus that causes a nebula to start condensing to form new ...
... 5. A shock wave may be the stimulus that causes a nebula to start condensing to form new ...
STARS - AN INTRODUCTION
... Stars are balls of burning gas. Different types of gases make the star burn. They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
... Stars are balls of burning gas. Different types of gases make the star burn. They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
Lecture 10: Stars
... & Your left eye is the Earth in January & Your right eye is the Earth in June Watch the apparent motion of your thumb against a distant reference point (repeat at arm’s length) Which “move” more -- closer or farther objects? ...
... & Your left eye is the Earth in January & Your right eye is the Earth in June Watch the apparent motion of your thumb against a distant reference point (repeat at arm’s length) Which “move” more -- closer or farther objects? ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... Evolution of Stars Nebula - Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust Main sequence – pressure from heat is in balance with gravity Giant – outer layers of the star expand and cool Supernova – star explodes White dwarf – outer layer contracts (about size of Earth) Neutron star – only neutrons ca ...
... Evolution of Stars Nebula - Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust Main sequence – pressure from heat is in balance with gravity Giant – outer layers of the star expand and cool Supernova – star explodes White dwarf – outer layer contracts (about size of Earth) Neutron star – only neutrons ca ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.