Chapter 11 Surveying the Stars How do we measure stellar
... Off the Main Sequence • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white ...
... Off the Main Sequence • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white ...
Star - Uplift Education
... Calculation shows that the helium produced by nuclear fusion within stars cannot account for the real amount of helium in Universe (24%). In 1960 it was proposed that sometime during the early history of the Universe, long before any star, Universe was at a sufficiently high temperature to produce ...
... Calculation shows that the helium produced by nuclear fusion within stars cannot account for the real amount of helium in Universe (24%). In 1960 it was proposed that sometime during the early history of the Universe, long before any star, Universe was at a sufficiently high temperature to produce ...
Tutorial: Luminosity
... energy/sec through the surface of this sphere is the same as the energy/sec emitted through the surface of the star, since there is no mechanism to create or destroy photons in the space outside the star. The surface of the sphere has an area given by 4πd2 , where d is the radius of the sphere. Dire ...
... energy/sec through the surface of this sphere is the same as the energy/sec emitted through the surface of the star, since there is no mechanism to create or destroy photons in the space outside the star. The surface of the sphere has an area given by 4πd2 , where d is the radius of the sphere. Dire ...
Precession of Earth
... our Sun is not stationary; it moves as the planets tug on it, causing it to orbit the solar system's barycenter; the Sun never strays too far from the solar system barycenter ...
... our Sun is not stationary; it moves as the planets tug on it, causing it to orbit the solar system's barycenter; the Sun never strays too far from the solar system barycenter ...
Lecture 10-11 - OSU Astronomy
... interpretation of stellar spectra. • Based on the then new atomic physics. ...
... interpretation of stellar spectra. • Based on the then new atomic physics. ...
The Solar Neighborhood
... The globular star clusters are bright, and can be seen for a long distance. Their distances can be estimated accurately from their main sequence turnoffs, as well as by measuring the periods of variable stars that belong to each cluster. In the table below are listed several dozen Galactic globular ...
... The globular star clusters are bright, and can be seen for a long distance. Their distances can be estimated accurately from their main sequence turnoffs, as well as by measuring the periods of variable stars that belong to each cluster. In the table below are listed several dozen Galactic globular ...
Finish up Sun and begin Stars of the Sun Test 1 Study
... 4.3 light years = 4 x 1013 km (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation same meaning) • Can “easily” measure distance using parallax to a few 100 LY. Need telescope: first observed in 1838. Study close stars in detai ...
... 4.3 light years = 4 x 1013 km (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation same meaning) • Can “easily” measure distance using parallax to a few 100 LY. Need telescope: first observed in 1838. Study close stars in detai ...
slides - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Many ancient cultures saw patterns in the sky and established their own constellations and star lore based on their culture and mythology. Most northern constellations dates back to Babylonians times, 4-5 millennia ago, – Later Greeks adopted them and interpreted according to their mythology ...
... Many ancient cultures saw patterns in the sky and established their own constellations and star lore based on their culture and mythology. Most northern constellations dates back to Babylonians times, 4-5 millennia ago, – Later Greeks adopted them and interpreted according to their mythology ...
Exam #2 Solutions
... The cooler giant stars are mostly K and M giants with temperatures around 5,000 K to 3,000K and luminosities between 50 and 5,000 solar luminosities. The stars are all larger in radius than the Sun, being between 1 and 100 solar radii. All these stars will have very short lifetimes compared to ...
... The cooler giant stars are mostly K and M giants with temperatures around 5,000 K to 3,000K and luminosities between 50 and 5,000 solar luminosities. The stars are all larger in radius than the Sun, being between 1 and 100 solar radii. All these stars will have very short lifetimes compared to ...
StarIntro_sb12
... whole number) for an amount greater than or (X a decimal number) for an amount less than the AM of the Sun. ...
... whole number) for an amount greater than or (X a decimal number) for an amount less than the AM of the Sun. ...
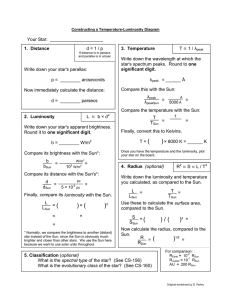
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... Autumn Stars – The stars of fall are not very well-known. Capella is a double system containing two nearly-identical stars with temperatures very similar to the Sun's; Epsilon Eridani is a faint star with the distinction of having a recently discovered planet orbiting it. Name Sun Fomalhaut Aldebara ...
... Autumn Stars – The stars of fall are not very well-known. Capella is a double system containing two nearly-identical stars with temperatures very similar to the Sun's; Epsilon Eridani is a faint star with the distinction of having a recently discovered planet orbiting it. Name Sun Fomalhaut Aldebara ...
Absolute Magnitudes of Supernovae
... Figure 1: Six views of a distance galaxy with a supernova to the lower left of the galaxy. Notice the decreasing brightness and changing color of the supernova with time. (Hubble Space Telescope) ...
... Figure 1: Six views of a distance galaxy with a supernova to the lower left of the galaxy. Notice the decreasing brightness and changing color of the supernova with time. (Hubble Space Telescope) ...
Student Worksheet - Indiana University Astronomy
... energy is needed to describe the brightness of astronomical sources because, being at very large distances, the stars appear to be extremely faint. The graph labeled "Flux Densities for IC 4665" displays the expected brightness of stars of different temperatures at a distance of 352 parsecs, the dis ...
... energy is needed to describe the brightness of astronomical sources because, being at very large distances, the stars appear to be extremely faint. The graph labeled "Flux Densities for IC 4665" displays the expected brightness of stars of different temperatures at a distance of 352 parsecs, the dis ...
Definitions of Magnitudes and Surface Brightness
... Suppose then that a star is located at a distance of D pc and that the flux received from the star is F W m – 2 . Then the flux received from 10 pc would be ...
... Suppose then that a star is located at a distance of D pc and that the flux received from the star is F W m – 2 . Then the flux received from 10 pc would be ...
5-E Galaxy T - McDonald Observatory
... The Hubble Space Telescope has revealed a universe full of galaxies, and stunning detailed structures within nearby galaxies. A galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars, gas, and dust. They range in size from a few thousand light years to a few hundred thousand light-years in diameter for t ...
... The Hubble Space Telescope has revealed a universe full of galaxies, and stunning detailed structures within nearby galaxies. A galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars, gas, and dust. They range in size from a few thousand light years to a few hundred thousand light-years in diameter for t ...
V: 0
... The student is expected to explore how different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum such as light and radio waves are used to gain information about distances and properties of components in the universe. ...
... The student is expected to explore how different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum such as light and radio waves are used to gain information about distances and properties of components in the universe. ...
apparent magnitude - Harding University
... be measured. If the stars temperature (color) is known, and if its spectral class can be determined from its spectra, the stars luminosity (or absolute magnitude) can be determined. Knowing the absolute magnitude (the maganitude at 10 parsecs) and its apparent magnitude (as seen from the Earth) ...
... be measured. If the stars temperature (color) is known, and if its spectral class can be determined from its spectra, the stars luminosity (or absolute magnitude) can be determined. Knowing the absolute magnitude (the maganitude at 10 parsecs) and its apparent magnitude (as seen from the Earth) ...
Reach for the Stars – Div. B
... – Tycho’s SNR died as type 1a super novae remnants – Type 1a are important measuring sticks of the universe – Cygnus X-1 is a binary star system with one component as a black hole (sucking material from its companion and making xrays) ...
... – Tycho’s SNR died as type 1a super novae remnants – Type 1a are important measuring sticks of the universe – Cygnus X-1 is a binary star system with one component as a black hole (sucking material from its companion and making xrays) ...
DP11 Foundations of Astronomy
... know its distance, we can determine its luminosity, from the socalled inverse square law: b = L/4 d2 ...
... know its distance, we can determine its luminosity, from the socalled inverse square law: b = L/4 d2 ...
Stellar Distances - Red Hook Central School District
... If 2 stars have magnitudes of m1 and m2, and apparent brightness of b1 & b2This relationship holds true: ...
... If 2 stars have magnitudes of m1 and m2, and apparent brightness of b1 & b2This relationship holds true: ...
GET WORKSHEETS FROM MY ASSIGNMENTS PAGE Mrs
... 4.The most likely star color to have a planet with life would be ____ because: a. b. Consider Life Span and Life Zone size ...
... 4.The most likely star color to have a planet with life would be ____ because: a. b. Consider Life Span and Life Zone size ...
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife
... Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs) are amongst the most massive objects in the galaxy, with masses of 104 – 106 MŸ. They are not necessarily gravitationally bound and, like all clouds in the galaxy, are transient structures with lifetimes on the scale of 10’s of millions of years. Their lifetimes are lin ...
... Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs) are amongst the most massive objects in the galaxy, with masses of 104 – 106 MŸ. They are not necessarily gravitationally bound and, like all clouds in the galaxy, are transient structures with lifetimes on the scale of 10’s of millions of years. Their lifetimes are lin ...
How do stars appear to move to an observer on the
... brighter for a short time. Some white dwarfs do not just cool, they have one or more large explosions. Astronomers think this may be caused by a companion star that is having material taken from it by the white dwarf. ...
... brighter for a short time. Some white dwarfs do not just cool, they have one or more large explosions. Astronomers think this may be caused by a companion star that is having material taken from it by the white dwarf. ...
using a cepheid variable to determine distance
... 4. Distance modulus ( m - M ) = _________ 5. Distance to the Cepheid ( r ) = _______ parsecs Distance to the Cepheid ( r ) = _______light years ...
... 4. Distance modulus ( m - M ) = _________ 5. Distance to the Cepheid ( r ) = _______ parsecs Distance to the Cepheid ( r ) = _______light years ...
Events: - Temecula Valley Astronomers
... As the sun sets, I try to point out the first stars visible - usually the summer triangle. I talk about constellations and asterisms. Once the sky is dark, our first targets are man-made satellites. Many web sites and cell phone apps help you find what is visible. While we are waiting for them to co ...
... As the sun sets, I try to point out the first stars visible - usually the summer triangle. I talk about constellations and asterisms. Once the sky is dark, our first targets are man-made satellites. Many web sites and cell phone apps help you find what is visible. While we are waiting for them to co ...