August Newsletter
... There are five August constellations right above us (in the southern hemisphere) and include some of the most spectacular and well-known objects in the sky. The centre of our Milky Way galaxy is located in the direction of Sagittarius and because of this Sagittarius contains more deep sky objects th ...
... There are five August constellations right above us (in the southern hemisphere) and include some of the most spectacular and well-known objects in the sky. The centre of our Milky Way galaxy is located in the direction of Sagittarius and because of this Sagittarius contains more deep sky objects th ...
The Abundances of the Fe Group Elements in Three Early B Stars in
... near main sequence early B stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud for which the photospheric lines are sharp enough that it is feasible to undertake detailed abundance analyses. They determined chemical abundances from high resolution optical spectra using a combination of LTE and NLTE spectrum synthes ...
... near main sequence early B stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud for which the photospheric lines are sharp enough that it is feasible to undertake detailed abundance analyses. They determined chemical abundances from high resolution optical spectra using a combination of LTE and NLTE spectrum synthes ...
Merak
... Information about Merak Merak’s name means flank of the Great Bear This star is located in the bottom right corner of the Big Dipper constellation It is a White Main Sequence star and it’s sixty-two light years away! ...
... Information about Merak Merak’s name means flank of the Great Bear This star is located in the bottom right corner of the Big Dipper constellation It is a White Main Sequence star and it’s sixty-two light years away! ...
Stars - WhatisOutThere
... helium. These are the two lightest elements. They shine by burning the hydrogen into helium in their cores, then later in life they create heavier elements. Most stars have heavy elements, like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and iron but only small amounts. These elements came from the stars that existed ...
... helium. These are the two lightest elements. They shine by burning the hydrogen into helium in their cores, then later in life they create heavier elements. Most stars have heavy elements, like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and iron but only small amounts. These elements came from the stars that existed ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... a distance of 8.6 light years also has a companion, the first white dwarf to be discovered observationally. At 8.9 light years there is another pair called L 726-8. Thus within a distance of 10 light years we encounter about 9 binary stars out of 14. Therefore, one can be optimistic about the estima ...
... a distance of 8.6 light years also has a companion, the first white dwarf to be discovered observationally. At 8.9 light years there is another pair called L 726-8. Thus within a distance of 10 light years we encounter about 9 binary stars out of 14. Therefore, one can be optimistic about the estima ...
Solutions
... Most of this problem could be answered by thinking about and understanding the H-R diagram of a globular cluster, e.g. such as is found in Figure 16.17 in your text (and perhaps comparing that with the “cluster snapshot” diagrams on the previous page). (a) Because the red giant stars are the most lu ...
... Most of this problem could be answered by thinking about and understanding the H-R diagram of a globular cluster, e.g. such as is found in Figure 16.17 in your text (and perhaps comparing that with the “cluster snapshot” diagrams on the previous page). (a) Because the red giant stars are the most lu ...
Distances of the Stars
... Luminosity Distance Relation A star’s luminosity, apparent brightness, and distance from the earth are related through the inverse square law. If any two of these quantities are known, the third can be calculated. ...
... Luminosity Distance Relation A star’s luminosity, apparent brightness, and distance from the earth are related through the inverse square law. If any two of these quantities are known, the third can be calculated. ...
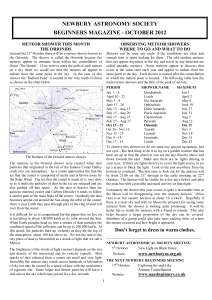
October 2012 - astronomy for beginners
... Very few constellations look like the characters after which they are named. Cygnus the Swan, Leo the Lion and Orion the Hunter are perhaps exceptions and do (with a little imagination) look remotely like those characters. The stars making up the constellations are not generally physically associate ...
... Very few constellations look like the characters after which they are named. Cygnus the Swan, Leo the Lion and Orion the Hunter are perhaps exceptions and do (with a little imagination) look remotely like those characters. The stars making up the constellations are not generally physically associate ...
Measuring Distances
... Measuring Distances Hold your finger out in front of your face at arm’s length. Look at your finger through each eye separately. What do you notice? This change in perspective is known as parallax. Ancient Greek astronomers expected to see a similar change in the positions of nearby stars if Earth ...
... Measuring Distances Hold your finger out in front of your face at arm’s length. Look at your finger through each eye separately. What do you notice? This change in perspective is known as parallax. Ancient Greek astronomers expected to see a similar change in the positions of nearby stars if Earth ...
18 are exactly the same ones as for galactic star clusters of early
... 5. A DISCUSSION OF NGC 4755 AND SOME OTHER YOUNG CLUSTERS IN THE GALAXY AND THE MAGELLANIC CLOUDS ...
... 5. A DISCUSSION OF NGC 4755 AND SOME OTHER YOUNG CLUSTERS IN THE GALAXY AND THE MAGELLANIC CLOUDS ...
Chapter 1 Seeing the Light: The Art and Science of Astronomy
... Chapter 1: Seeing the Light: The Art and Science of Astronomy When you look at a star atlas, you discover that the individual stars in a constellation aren’t marked α Canis Majoris, β Canis Majoris, and so on. Usually, the creator of the atlas marks the area of the whole constellation as Canis Majo ...
... Chapter 1: Seeing the Light: The Art and Science of Astronomy When you look at a star atlas, you discover that the individual stars in a constellation aren’t marked α Canis Majoris, β Canis Majoris, and so on. Usually, the creator of the atlas marks the area of the whole constellation as Canis Majo ...
Chapter 13 section 3
... the time it reaches 100 million K, the star is huge. Its outer layers are much cooler than when it was a main sequence star. In about 5 billion years, the Sun will become a giant. ...
... the time it reaches 100 million K, the star is huge. Its outer layers are much cooler than when it was a main sequence star. In about 5 billion years, the Sun will become a giant. ...
Determining the Sizes of Stars Using the HR Diagram
... the diagram and lower luminosity (intrinsically faint) stars lie at the bottom of the diagram. 5. Explain that stars are grouped into four different categories: ● Main Sequence Stars: The characteristic of all these stars are that they are all generating energy by nuclear fusion deep in their cores. ...
... the diagram and lower luminosity (intrinsically faint) stars lie at the bottom of the diagram. 5. Explain that stars are grouped into four different categories: ● Main Sequence Stars: The characteristic of all these stars are that they are all generating energy by nuclear fusion deep in their cores. ...
DTU 8e Chap 11 Characterizing Stars
... stars are plotted against their spectral types. Each dot on this graph represents a star whose luminosity and spectral type have been determined. The data points are grouped in just a few regions of the diagram, revealing that luminosity and spectral type are correlated: Mainsequence stars fall alon ...
... stars are plotted against their spectral types. Each dot on this graph represents a star whose luminosity and spectral type have been determined. The data points are grouped in just a few regions of the diagram, revealing that luminosity and spectral type are correlated: Mainsequence stars fall alon ...
October 2014 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... its normal life. The luminosity of the star is compared with our Sun on the vertical scale on the left (therefore our Sun is classified as 1). The absolute magnitude is shown on the vertical scale on the right. This is the magnitude of a star (brightness) if it was located at a standard distance fro ...
... its normal life. The luminosity of the star is compared with our Sun on the vertical scale on the left (therefore our Sun is classified as 1). The absolute magnitude is shown on the vertical scale on the right. This is the magnitude of a star (brightness) if it was located at a standard distance fro ...
Astronomy - Scioly.org
... precisely the same wavelengths as the dark lines, thus making them invisible. c. Hot hydrogen and helium gas in the interstellar medium produces bright lines to fill in the dark lines. d. The resolution of many spectrographs is too poor to show the extremely thin spectral lines for hydrogen and heli ...
... precisely the same wavelengths as the dark lines, thus making them invisible. c. Hot hydrogen and helium gas in the interstellar medium produces bright lines to fill in the dark lines. d. The resolution of many spectrographs is too poor to show the extremely thin spectral lines for hydrogen and heli ...
Constellation Packet - Mr. Jenkins` Classroom
... “go to the coast of cassiopeia’s land and lay waste to the land, and kill the people, and kill the cattle.” Cetus in the form of a monstrous whale began the slaughter. The frightened people gathered and pleaded to their king to save them. The only way to stop the slaughter was to offer up his daught ...
... “go to the coast of cassiopeia’s land and lay waste to the land, and kill the people, and kill the cattle.” Cetus in the form of a monstrous whale began the slaughter. The frightened people gathered and pleaded to their king to save them. The only way to stop the slaughter was to offer up his daught ...
Lecture 6: Stellar Distances and Brightness
... Apparent Brightness of Stars The apparent brightness of stars is what we can measure How bright any given star will appear depends on 2 things: How bright it is physically (Luminosity) How far away it is (Distance) Related through the inverse square law ...
... Apparent Brightness of Stars The apparent brightness of stars is what we can measure How bright any given star will appear depends on 2 things: How bright it is physically (Luminosity) How far away it is (Distance) Related through the inverse square law ...
What is a star?
... • The sun is a star and is composed mostly of hydrogen and helium. It also contains oxygen, carbon, neon, and iron. • At the center of the sun lies the core, where gases are compressed and heated and temperatures reach 15 million degrees Celsius. • The sun’s core is where matter is converted into ...
... • The sun is a star and is composed mostly of hydrogen and helium. It also contains oxygen, carbon, neon, and iron. • At the center of the sun lies the core, where gases are compressed and heated and temperatures reach 15 million degrees Celsius. • The sun’s core is where matter is converted into ...
The Classification of Stellar Spectra
... them. Many of the Fraunhofer lines in the solar spectrum retain the notations he created to designate them. In 1864, Sir William Huggins matched some of these dark lines in spectra from other stars with terrestrial substances, demonstrating that stars are made of the same materials of everyday mater ...
... them. Many of the Fraunhofer lines in the solar spectrum retain the notations he created to designate them. In 1864, Sir William Huggins matched some of these dark lines in spectra from other stars with terrestrial substances, demonstrating that stars are made of the same materials of everyday mater ...
The Sothicentric Model part 2.2
... an image adapted from perspective Drunvalo this is noMelchizedek’s surprise, as Sirius associated the bookisthe Ancient with Secret of6the Flower Minor groove dimension, of Life. the morphogenetic field. Major groove This is to clearly illustrate that the Dogon tribe was intimated exact knowledge ab ...
... an image adapted from perspective Drunvalo this is noMelchizedek’s surprise, as Sirius associated the bookisthe Ancient with Secret of6the Flower Minor groove dimension, of Life. the morphogenetic field. Major groove This is to clearly illustrate that the Dogon tribe was intimated exact knowledge ab ...
Module code: AA1
... The hypothetical question how the night sky would appear if all stars would possess the same luminosity as the sun or Barnard’s star was analysed with Excel diagrams leading to the conclusion that in case of the sun the night sky would have less bright stars and in case of Barnard’s star with the na ...
... The hypothetical question how the night sky would appear if all stars would possess the same luminosity as the sun or Barnard’s star was analysed with Excel diagrams leading to the conclusion that in case of the sun the night sky would have less bright stars and in case of Barnard’s star with the na ...
Stellar Classification - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... B 10,000 - 30,000 K Blue-white stars A 7,500 - 10,000 K White stars F 6,000 - 7,500 K Yellow-white stars G 5,000 - 6,000 K Yellow stars (like the Sun) K 3,500 - 5,000K Yellow-orange stars M < 3,500 K Red stars ...
... B 10,000 - 30,000 K Blue-white stars A 7,500 - 10,000 K White stars F 6,000 - 7,500 K Yellow-white stars G 5,000 - 6,000 K Yellow stars (like the Sun) K 3,500 - 5,000K Yellow-orange stars M < 3,500 K Red stars ...