Observing Orion
... The Great Hunter. Orion boasted that no animal could defeat him and he boasted that so great was his might and skill as a hunter that he could kill all the animals on the face of the Earth. Gaea, Goddess of Earth, was alarmed at such an unecological and inappropriate statement. She decided that Orio ...
... The Great Hunter. Orion boasted that no animal could defeat him and he boasted that so great was his might and skill as a hunter that he could kill all the animals on the face of the Earth. Gaea, Goddess of Earth, was alarmed at such an unecological and inappropriate statement. She decided that Orio ...
The Argonauts, background to the constellation Carina Argo Navis
... through Carina, there are also a large number of open clusters in the constellation. These include the "Southern Pleiades." The most notable object in Carina is Homunculus Nebula (from the Latin meaning Little Man), a planetary nebula visible to the naked eye believed to have been ejected in an enor ...
... through Carina, there are also a large number of open clusters in the constellation. These include the "Southern Pleiades." The most notable object in Carina is Homunculus Nebula (from the Latin meaning Little Man), a planetary nebula visible to the naked eye believed to have been ejected in an enor ...
IMR_Star Theater
... Your planetarium projects stars that are visible from the northern hemisphere. To see all the stars that are visible from the northern hemisphere, slowly rotate the light wand to the left (westward) while the projection lamp is on. Do you notice that some stars around Polaris never set while some of ...
... Your planetarium projects stars that are visible from the northern hemisphere. To see all the stars that are visible from the northern hemisphere, slowly rotate the light wand to the left (westward) while the projection lamp is on. Do you notice that some stars around Polaris never set while some of ...
Letot STELLAR EVOLUTION By Kyle Letot Grade Level: 6
... Sun will start off at the beginning of the end zone. Next the four inner planets (or terrestrial) cram close together simulating the closer knit orbits. These planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Then we have the four gas planets; Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These planets are much ...
... Sun will start off at the beginning of the end zone. Next the four inner planets (or terrestrial) cram close together simulating the closer knit orbits. These planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Then we have the four gas planets; Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These planets are much ...
The Bigger Picture
... Stellar parallax • Even the largest parallax (that for the nearest star) is small. The atmosphere blurs stellar images to about 1 arcsecond so `astrometrists’ are trying to measure a tiny motion of the centroid as it moves back and forth every six months. The lack of parallax apparent to the unaid ...
... Stellar parallax • Even the largest parallax (that for the nearest star) is small. The atmosphere blurs stellar images to about 1 arcsecond so `astrometrists’ are trying to measure a tiny motion of the centroid as it moves back and forth every six months. The lack of parallax apparent to the unaid ...
Draco: The Dragon - Courtney Stookey
... includes a white giant and a red or white dwarf. These stars are more than 300 light years away from Earth. The Cat’s Eye Nebula, NGC 6543, is a planetary nebula that was formed by a bright, hot star. It is about 3,000 light years away from Earth. This nebula was originally discovered by William Her ...
... includes a white giant and a red or white dwarf. These stars are more than 300 light years away from Earth. The Cat’s Eye Nebula, NGC 6543, is a planetary nebula that was formed by a bright, hot star. It is about 3,000 light years away from Earth. This nebula was originally discovered by William Her ...
HR Diagram of Messier 80 using Hubble Space Telescope Data
... (4) Is the F450W a “red”, “green” or “blue” filter, meaning what color would things be if you looked through the filter at something? (5) Is the F814W a “red”, “green” or “blue” filter? (6) Is there any overlap to the filters? (7) How many other filters does the Hubble Space Telescope use? (8) Name ...
... (4) Is the F450W a “red”, “green” or “blue” filter, meaning what color would things be if you looked through the filter at something? (5) Is the F814W a “red”, “green” or “blue” filter? (6) Is there any overlap to the filters? (7) How many other filters does the Hubble Space Telescope use? (8) Name ...
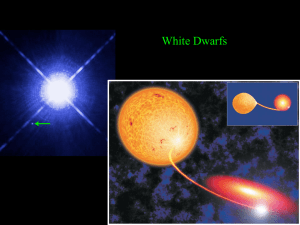
white dwarf supernova
... More massive white dwarfs are smaller than less massive white dwarfs. (Degeneracy pressure only depends on density) ...
... More massive white dwarfs are smaller than less massive white dwarfs. (Degeneracy pressure only depends on density) ...
Ch13_Lecture - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • A spectrum also can reveal a star’s composition, temperature, luminosity, velocity in space, rotation speed, and other properties • On certain occasions, it may reveal mass and ...
... • A spectrum also can reveal a star’s composition, temperature, luminosity, velocity in space, rotation speed, and other properties • On certain occasions, it may reveal mass and ...
1/20/09 301 Physics Chapter 12 The Family of Stars Triangulation
... while high-temperature (blue) stars are on the left with cool (red) stars on the right (Note: temperature does not run in a traditional direction) ...
... while high-temperature (blue) stars are on the left with cool (red) stars on the right (Note: temperature does not run in a traditional direction) ...
For stars
... Earth’s Orbital Motion The Twelve constellations (some say thirteen) that the Sun moves through during the year are called the zodiac; The view of the night sky changes as Earth moves in its orbit about the Sun. As drawn here, the night side of Earth faces a different set of constellations at diffe ...
... Earth’s Orbital Motion The Twelve constellations (some say thirteen) that the Sun moves through during the year are called the zodiac; The view of the night sky changes as Earth moves in its orbit about the Sun. As drawn here, the night side of Earth faces a different set of constellations at diffe ...
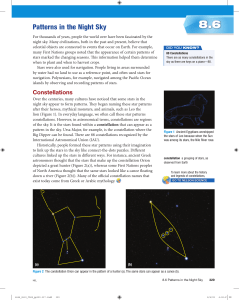
Patterns in the Night Sky
... Patterns in the Night Sky For thousands of years, people the world over have been fascinated by the night sky. Many civilizations, both in the past and present, believe that celestial objects are connected to events that occur on Earth. For example, many First Nations groups noted that the appearanc ...
... Patterns in the Night Sky For thousands of years, people the world over have been fascinated by the night sky. Many civilizations, both in the past and present, believe that celestial objects are connected to events that occur on Earth. For example, many First Nations groups noted that the appearanc ...
Astronomy 102, Spring 2003 Solutions to Review Problems
... size R. You can get L by solving F = 4πd 2 , where F is the flux you measure— but you then also need d, the distance, in order to calculate L. For mass, if it’s a binary star, you can measure the period of the orbit without knowing the distance, but again to get the physical semi-major axis of the o ...
... size R. You can get L by solving F = 4πd 2 , where F is the flux you measure— but you then also need d, the distance, in order to calculate L. For mass, if it’s a binary star, you can measure the period of the orbit without knowing the distance, but again to get the physical semi-major axis of the o ...
The Star of Bethlehem: a Type Ia/Ic Supernova in the Andromeda
... magnitude of 6. But such a faint “new star” would be noticed by very few (most ancient recorded supernovae have[30] an apparent magnitude brigher than −2), consistent, as pointed out by Hughes[14] , with the statement in Matthew that Herod and his court were unaware of the “new star”. Hughes[14],[15 ...
... magnitude of 6. But such a faint “new star” would be noticed by very few (most ancient recorded supernovae have[30] an apparent magnitude brigher than −2), consistent, as pointed out by Hughes[14] , with the statement in Matthew that Herod and his court were unaware of the “new star”. Hughes[14],[15 ...
Solutions
... by the newly formed OB Association stars that emit most of their energy as high-energy short-wavelength hardUV photons. The photons from the OB Association stars “power up” the HII region and keep it fluorescing. Thus the OB Association forms first and then the HII region is created around the vicin ...
... by the newly formed OB Association stars that emit most of their energy as high-energy short-wavelength hardUV photons. The photons from the OB Association stars “power up” the HII region and keep it fluorescing. Thus the OB Association forms first and then the HII region is created around the vicin ...
Astrophysics - Part 2
... night sky is a measure of its brightness which depends on the intensity of the light received from the star. Stars were in ancient times divided into six levels of apparent magnitude. The brightest were called FIRST MAGNITUDE stars, those just visible to the unaided eye in the darkest sky, SIXTH MAG ...
... night sky is a measure of its brightness which depends on the intensity of the light received from the star. Stars were in ancient times divided into six levels of apparent magnitude. The brightest were called FIRST MAGNITUDE stars, those just visible to the unaided eye in the darkest sky, SIXTH MAG ...
10 - Keele Astrophysics Group
... Firstly it was necessary to account for the fact that stars have very different radii at different stages in their evolution (i.e. their surface gravity is very different), with larger stars being more luminous. The luminosity together with the temperature completely ...
... Firstly it was necessary to account for the fact that stars have very different radii at different stages in their evolution (i.e. their surface gravity is very different), with larger stars being more luminous. The luminosity together with the temperature completely ...
1 Introduction - High Point University
... they reach their peak brightness and begin to fade. They are only useful as distance indicators if it is possible to calibrate them—to relate their observed brightness profile to absolute magnitudes. Type I supernovae are very uniform—the light curves and spectra for Type I supernovae are all fairly ...
... they reach their peak brightness and begin to fade. They are only useful as distance indicators if it is possible to calibrate them—to relate their observed brightness profile to absolute magnitudes. Type I supernovae are very uniform—the light curves and spectra for Type I supernovae are all fairly ...
Variable star information
... Classical Cepheid variables are highly luminous, yellow giant or supergiant stars that pulsate on a very regular basis. Some of them change in brightness very quickly, over a period of only one day, whereas others are characterised by slower changes and have periods of up to 70 days. Their masses ra ...
... Classical Cepheid variables are highly luminous, yellow giant or supergiant stars that pulsate on a very regular basis. Some of them change in brightness very quickly, over a period of only one day, whereas others are characterised by slower changes and have periods of up to 70 days. Their masses ra ...
Astronomy 252: Short Project 2 Stellar Spectra: Their Classification
... have temperatures on the order of 2000 - 3000 K. As you might guess, the appearance of the spectrum of a star is very strongly dependent on its temperature. For instance the very hottest stars (called the O-type stars) show absorption lines due to ionized helium (He II), and doubly and even triply i ...
... have temperatures on the order of 2000 - 3000 K. As you might guess, the appearance of the spectrum of a star is very strongly dependent on its temperature. For instance the very hottest stars (called the O-type stars) show absorption lines due to ionized helium (He II), and doubly and even triply i ...
Measuring the Properties of Stars - Sierra College Astronomy Home
... The sizes of a few very large stars have been measured directly by interferometry. Knowing the temperature of a star gives its energy emitted per square meter. Knowing the total energy emitted (from the absolute magnitude) one can then calculate the surface area of the star. From that the di ...
... The sizes of a few very large stars have been measured directly by interferometry. Knowing the temperature of a star gives its energy emitted per square meter. Knowing the total energy emitted (from the absolute magnitude) one can then calculate the surface area of the star. From that the di ...
Lab 6
... Astronomers, including Edwin Hubble, began to use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram as a powerful tool to determine stellar properties. Initially, the method of standard candles for individual stars was applied to whole clusters within the Milky Way; this method relies on the inverse-square law you sa ...
... Astronomers, including Edwin Hubble, began to use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram as a powerful tool to determine stellar properties. Initially, the method of standard candles for individual stars was applied to whole clusters within the Milky Way; this method relies on the inverse-square law you sa ...
Measuring Stars` Properties - Test 1 Study Guide
... (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation ! same meaning) • Can “easily” measure distance using parallax to a few 100 LY. Need telescope: first observed in 1838. Study close stars in detail. Other techniques for dist ...
... (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation ! same meaning) • Can “easily” measure distance using parallax to a few 100 LY. Need telescope: first observed in 1838. Study close stars in detail. Other techniques for dist ...
Pulsating Variable Stars and The Hertzsprung - Chandra X
... repeating cycle of size changes. The change in size can be observed as a change in apparent brightness (apparent magnitude.) Cepheids have a repeating cycle of change that is periodic - as regular as the beating of a heart, with a period of 1 to 70 days with an amplitude variation of 0.1 to 2.0 magn ...
... repeating cycle of size changes. The change in size can be observed as a change in apparent brightness (apparent magnitude.) Cepheids have a repeating cycle of change that is periodic - as regular as the beating of a heart, with a period of 1 to 70 days with an amplitude variation of 0.1 to 2.0 magn ...