Whiteq
... white dwarf. White dwarves themselves can be no more massive than 1.4 times the mass of the sun. However, it is believed that the progenitor star can be as much as 4 times as massive as the sun, because during the end of their nuclear fuel burning stage most stars eject a large portion of their mass ...
... white dwarf. White dwarves themselves can be no more massive than 1.4 times the mass of the sun. However, it is believed that the progenitor star can be as much as 4 times as massive as the sun, because during the end of their nuclear fuel burning stage most stars eject a large portion of their mass ...
Project 4: The HR diagram. Open clusters
... temperature, high luminosity stars to low temperature, low luminosity stars. These are the main sequence stars. Our Sun is one of them. There are a few stars that are not in this diagonal strip. There are some low temperature, high luminosity stars ‐ these are called giants and super ...
... temperature, high luminosity stars to low temperature, low luminosity stars. These are the main sequence stars. Our Sun is one of them. There are a few stars that are not in this diagonal strip. There are some low temperature, high luminosity stars ‐ these are called giants and super ...
How big are stars? How do we know?
... • Many stars are found orbiting another star. These star systems are called binary stars. • Three types: – If we can see from pictures taken over time that the stars are orbiting each other, the system is a visual binary – If the stars are so close together (or distant from Earth) that their spectra ...
... • Many stars are found orbiting another star. These star systems are called binary stars. • Three types: – If we can see from pictures taken over time that the stars are orbiting each other, the system is a visual binary – If the stars are so close together (or distant from Earth) that their spectra ...
Luminosity - U of L Class Index
... the main sequence of an H-R diagram A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high-mass: luminous and blue; low-mass: faint and red) ...
... the main sequence of an H-R diagram A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high-mass: luminous and blue; low-mass: faint and red) ...
ppt
... • An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud, and are still gravitationally bound to each other • Open clusters are found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring. • The Pleiades is an open c ...
... • An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud, and are still gravitationally bound to each other • Open clusters are found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring. • The Pleiades is an open c ...
ph507lecnote06
... Because stellar colours and spectral types are roughly correlated, we may construct a plot of absolute magnitude versus colour - called a colour-magnitude diagram. The relative ease and convenience with which colour indices (such as B - V) may be determined for vast numbers of stars dictates the pop ...
... Because stellar colours and spectral types are roughly correlated, we may construct a plot of absolute magnitude versus colour - called a colour-magnitude diagram. The relative ease and convenience with which colour indices (such as B - V) may be determined for vast numbers of stars dictates the pop ...
Astronomy Activity: The Life-Line of the Stars
... The brightness that a star has as seen from the Earth is called the apparent brightness . Stars which are very bright are called magnitude 1 stars . The next brightest are magnitude 2 stars. Then comes magnitude 3, 4, 5, and down to the very faintest stars visible with the naked eye, magnitude 6 sta ...
... The brightness that a star has as seen from the Earth is called the apparent brightness . Stars which are very bright are called magnitude 1 stars . The next brightest are magnitude 2 stars. Then comes magnitude 3, 4, 5, and down to the very faintest stars visible with the naked eye, magnitude 6 sta ...
sa`d al-malik - WordPress.com
... he pleaded with Zeus to be allowed to help them and was given permission to send down rain. Eventually he was glorified as Aquarius, god of rain, and placed amongst the stars. http://www.heavens-above.com/myth.aspx?con=aqr ...
... he pleaded with Zeus to be allowed to help them and was given permission to send down rain. Eventually he was glorified as Aquarius, god of rain, and placed amongst the stars. http://www.heavens-above.com/myth.aspx?con=aqr ...
Astrophysics
... supernova make a lovely sight (see Hubble telescope picture of it.) 4. Whole new worlds - the discovery of galaxies • Hubble found (using Cepheids) that certain 'nebulae' were not dust clouds, as had been thought, but distant galaxies. He used Cepheid variables in the nebulae to show that they were ...
... supernova make a lovely sight (see Hubble telescope picture of it.) 4. Whole new worlds - the discovery of galaxies • Hubble found (using Cepheids) that certain 'nebulae' were not dust clouds, as had been thought, but distant galaxies. He used Cepheid variables in the nebulae to show that they were ...
3.1 Introduction
... In the case of a halo globular cluster, with little foreground contamination, the density of points in the HR diagram approximately reflects the length of time a star spends in different evolutionary stages. Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence (MS), burning hydrogen in their cores. ...
... In the case of a halo globular cluster, with little foreground contamination, the density of points in the HR diagram approximately reflects the length of time a star spends in different evolutionary stages. Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence (MS), burning hydrogen in their cores. ...
C H A P T E R 2
... and set the magnitude limit to –30.0 to 5.0 and turn off the display of all objects except stars, planets, moon, and sun. For now turn off all reference lines, including the constellation reference lines. Now you’re ready to begin the demonstration. Press Alt+> and the program will display the daily ...
... and set the magnitude limit to –30.0 to 5.0 and turn off the display of all objects except stars, planets, moon, and sun. For now turn off all reference lines, including the constellation reference lines. Now you’re ready to begin the demonstration. Press Alt+> and the program will display the daily ...
FREE Sample Here
... and set the magnitude limit to –30.0 to 5.0 and turn off the display of all objects except stars, planets, moon, and sun. For now turn off all reference lines, including the constellation reference lines. Now you’re ready to begin the demonstration. Press Alt+> and the program will display the daily ...
... and set the magnitude limit to –30.0 to 5.0 and turn off the display of all objects except stars, planets, moon, and sun. For now turn off all reference lines, including the constellation reference lines. Now you’re ready to begin the demonstration. Press Alt+> and the program will display the daily ...
Transcript - Chandra X
... Slide 7: More detailed information about the H-R diagram will be presented further along. Since the presentation of the deep sky objects includes their spectral class and luminosity classes, the H-R diagram terminology is given here for those unfamiliar with H-R diagrams. The H-R diagram is a plot ...
... Slide 7: More detailed information about the H-R diagram will be presented further along. Since the presentation of the deep sky objects includes their spectral class and luminosity classes, the H-R diagram terminology is given here for those unfamiliar with H-R diagrams. The H-R diagram is a plot ...
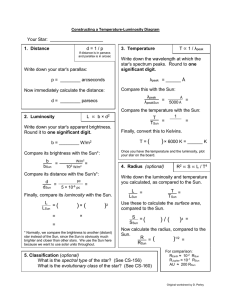
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
... Autumn Stars – The stars of fall are not very well-known. Capella is a double system containing two nearly-identical stars with temperatures very similar to the Sun's; Epsilon Eridani is a faint star with the distinction of having a recently discovered planet orbiting it. Name ...
... Autumn Stars – The stars of fall are not very well-known. Capella is a double system containing two nearly-identical stars with temperatures very similar to the Sun's; Epsilon Eridani is a faint star with the distinction of having a recently discovered planet orbiting it. Name ...
THE HR DIAGRAM
... This is a plot of 22,000 stars from the Hipparcos Catalogue together with 1,000 low‐luminosity stars (red and white dwarfs) from the Gliese Catalogue of Nearby Stars. The ordinary hydrogen‐ burning dwarf stars like the Sun are found in a band running from top‐left to bottom‐right called the Main ...
... This is a plot of 22,000 stars from the Hipparcos Catalogue together with 1,000 low‐luminosity stars (red and white dwarfs) from the Gliese Catalogue of Nearby Stars. The ordinary hydrogen‐ burning dwarf stars like the Sun are found in a band running from top‐left to bottom‐right called the Main ...
H R Diagram Online Activity
... 5. “On this diagram, the higher (_____________) temperatures are on the _____________, and the lower (_________________) temperatures are on the ____________________.” 6. “A star in the ____________ ____________ corner of the diagram would be ________ and ___________. A star in the _____________ ___ ...
... 5. “On this diagram, the higher (_____________) temperatures are on the _____________, and the lower (_________________) temperatures are on the ____________________.” 6. “A star in the ____________ ____________ corner of the diagram would be ________ and ___________. A star in the _____________ ___ ...
Observing the Night Sky - Constellations
... instructor will demonstrate the celestial pipes to you. The use of this instructional tool and your hand at arm's length as a measuring device will assist you in locating objects in the night sky. Once you have located Polaris, you can orient your star maps to find other objects. Indicate on your di ...
... instructor will demonstrate the celestial pipes to you. The use of this instructional tool and your hand at arm's length as a measuring device will assist you in locating objects in the night sky. Once you have located Polaris, you can orient your star maps to find other objects. Indicate on your di ...
Picture: Alnitak is the left-hand star in Orion`s Belt. Image: NASA
... absorption bands of carbon-containing molecules; the Swan bands of C2 are especially prominent, with absorption by CN, CH, C3, SiC2, and CaII present to varying degrees, with often a strong sodium D line. Carbon stars, also known as C stars, have carbon/oxygen ratios that are typically four to five ...
... absorption bands of carbon-containing molecules; the Swan bands of C2 are especially prominent, with absorption by CN, CH, C3, SiC2, and CaII present to varying degrees, with often a strong sodium D line. Carbon stars, also known as C stars, have carbon/oxygen ratios that are typically four to five ...
1 pracovni list HR diagram I EN
... to know the star’s luminosity (or absolute magnitude) and effective temperature (or spectral type or colour index). From the catalogue it is possible to obtain the absolute magnitude (calculated in column M from the apparent magnitude – column Vmag and distance to star calculated from the parallax – ...
... to know the star’s luminosity (or absolute magnitude) and effective temperature (or spectral type or colour index). From the catalogue it is possible to obtain the absolute magnitude (calculated in column M from the apparent magnitude – column Vmag and distance to star calculated from the parallax – ...
Option E Sum Pages
... used. This is the distance travelled by light in one year (= 60 x 60 x 24 x 365 seconds = 31536000s) so 1 ly = 3.00 x 108 ms-1 x 31536000s = 9.46 x 1015 m The nearest stars are 4 ly (Alpha Centauri, a triple star) and 6 ly (Barnard's star) from us. For comparison, Earth is about 8 light minutes from ...
... used. This is the distance travelled by light in one year (= 60 x 60 x 24 x 365 seconds = 31536000s) so 1 ly = 3.00 x 108 ms-1 x 31536000s = 9.46 x 1015 m The nearest stars are 4 ly (Alpha Centauri, a triple star) and 6 ly (Barnard's star) from us. For comparison, Earth is about 8 light minutes from ...
Lecture 9a: More on Star formation and evolution 10/22
... Larger electric repulsion than p-p as larger electric charge (2 for He and 4 for Be). Therefore need about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning ! Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
... Larger electric repulsion than p-p as larger electric charge (2 for He and 4 for Be). Therefore need about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning ! Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
Stellar Evolution Review
... a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shifted into the infrared ...
... a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shifted into the infrared ...
Spring Constellations
... centaur’s front hooves, Rigil Kentaurus and Hadar, also called ά- and β-Centauri. Our closest neighbor, Proxima Centauri, a red dwarf star 4 LY away, is due south of alpha Centauri. It’s so faint that it can’t be seen with the naked eye. It’s only about 5 times larger than the earth. ...
... centaur’s front hooves, Rigil Kentaurus and Hadar, also called ά- and β-Centauri. Our closest neighbor, Proxima Centauri, a red dwarf star 4 LY away, is due south of alpha Centauri. It’s so faint that it can’t be seen with the naked eye. It’s only about 5 times larger than the earth. ...
Luminosity
... • What is the significance of the main sequence? — Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. — A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high mass: luminous and blue; low mass: faint and red). ...
... • What is the significance of the main sequence? — Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. — A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high mass: luminous and blue; low mass: faint and red). ...
March 2016 BRAS Addendum Newsletter
... light year). Tau CMa is the brightest star of the open cluster NGC 2362 (Caldwell 64), which is why the cluster is sometimes called the Tau Canis Major Cluster. HD B47536, mag. 5.25, 06 37 47.54 -32 20 23.6, is an orange giant star with two planets in orbit. NO CMa, mag. 5.40, 07 23 00.70 -31 55 25. ...
... light year). Tau CMa is the brightest star of the open cluster NGC 2362 (Caldwell 64), which is why the cluster is sometimes called the Tau Canis Major Cluster. HD B47536, mag. 5.25, 06 37 47.54 -32 20 23.6, is an orange giant star with two planets in orbit. NO CMa, mag. 5.40, 07 23 00.70 -31 55 25. ...