Surveying the Stars
... the Spectral Types… • White Stars, with prominent hydrogen lines. Called them “A stars.” • Blue-white stars, with less prominent H lines, and weak helium lines. Called them “B stars” • Then, no more in this color direction, so skip some letters and… Cream colored stars, with weaker H lines and lots ...
... the Spectral Types… • White Stars, with prominent hydrogen lines. Called them “A stars.” • Blue-white stars, with less prominent H lines, and weak helium lines. Called them “B stars” • Then, no more in this color direction, so skip some letters and… Cream colored stars, with weaker H lines and lots ...
section 17 powerpoint
... Parsec. A measure of distance for an object that has a parallax of 1 arcsecond = 3.26 light years. Magnitude, m. A scale developed by Hipparchus to rank the naked-eye stars in terms of brightness. Luminosity. The rate at which a star emits light, often measured using absolute magnitude. Absolute Mag ...
... Parsec. A measure of distance for an object that has a parallax of 1 arcsecond = 3.26 light years. Magnitude, m. A scale developed by Hipparchus to rank the naked-eye stars in terms of brightness. Luminosity. The rate at which a star emits light, often measured using absolute magnitude. Absolute Mag ...
Spectroscopy Lecture 10
... – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The first “w hite dwarf” Adams found Sirius B is also an A star ...
... – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The first “w hite dwarf” Adams found Sirius B is also an A star ...
SRP_Space_Lesson 5 - Scientist in Residence Program
... A constellation is an identifiable cluster of stars that make a given shape. Constellations are not real, that is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and ...
... A constellation is an identifiable cluster of stars that make a given shape. Constellations are not real, that is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and ...
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
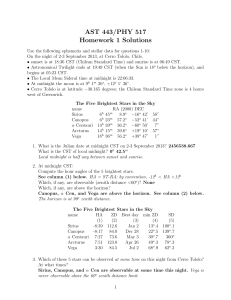
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
Celestial Distances - Wayne State University
... Thus, completely new techniques are needed for more distant stars The breakthrough in measuring the enormous distances came from the study of variable stars, or variables These are stars that vary in luminosity Thus, their brightness changes with time In contrast, most stars are constant in their lu ...
... Thus, completely new techniques are needed for more distant stars The breakthrough in measuring the enormous distances came from the study of variable stars, or variables These are stars that vary in luminosity Thus, their brightness changes with time In contrast, most stars are constant in their lu ...
Stars in the night Sky - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... Find north by using the Big Dipper to locate Polaris, the north star. Polaris is closer to true north than a magnetic compass. o Note: In Japan, azimuth is measured clockwise starting from the south. The point directly overhead is called an observer's zenith. Opposite the zenith is the ...
... Find north by using the Big Dipper to locate Polaris, the north star. Polaris is closer to true north than a magnetic compass. o Note: In Japan, azimuth is measured clockwise starting from the south. The point directly overhead is called an observer's zenith. Opposite the zenith is the ...
The Stars of Namaqualand
... astronomers believe, that Rigel is the most luminous star in our Milky Way galaxy. The Three Kings are a part of Orion. They were used for navigation, because they are situated on the celestial equator, right above the earth’s surface equator. The Great Nebula of Orion represents the middle star in ...
... astronomers believe, that Rigel is the most luminous star in our Milky Way galaxy. The Three Kings are a part of Orion. They were used for navigation, because they are situated on the celestial equator, right above the earth’s surface equator. The Great Nebula of Orion represents the middle star in ...
btg_2016_astromony
... Bunjil is represented in the sky by the star Altair (Alpha Aquilae) in the constellation Aquila. There are no prizes for guessing that Aquila is another eagle in the sky, but one of the classical 88-constellations as used by astronomers today. Bunjil has two wives in the form of black swans that sit ...
... Bunjil is represented in the sky by the star Altair (Alpha Aquilae) in the constellation Aquila. There are no prizes for guessing that Aquila is another eagle in the sky, but one of the classical 88-constellations as used by astronomers today. Bunjil has two wives in the form of black swans that sit ...
Magnitudes - Astronomy @ Walton High School
... We measure the brightness of a star by its magnitude. There are two types of magnitude: Apparent magnitude is how bright an object is to us on Earth. Absolute magnitude is how bright a star would appear in space from a certain distance. ...
... We measure the brightness of a star by its magnitude. There are two types of magnitude: Apparent magnitude is how bright an object is to us on Earth. Absolute magnitude is how bright a star would appear in space from a certain distance. ...
Astrophysics by Daniel Yang
... ascertain if they are actually in motion around each other, they may need to be observed for many years. The more massive star orbits in a smaller ellipse around the centre of mass. Eclipsing binary An eclipsing binary is a binary system whose orbital plane is parallel to our observation. Periodical ...
... ascertain if they are actually in motion around each other, they may need to be observed for many years. The more massive star orbits in a smaller ellipse around the centre of mass. Eclipsing binary An eclipsing binary is a binary system whose orbital plane is parallel to our observation. Periodical ...
same
... is in the state of New York, we specify for example that Betelgeuse is in Orion. However, there are also reasons why we use right ascension and declination (i.e., exact coordinates) as you will find out. Actually, professional astronomers only use the exact coordinates. The stars that make up the co ...
... is in the state of New York, we specify for example that Betelgeuse is in Orion. However, there are also reasons why we use right ascension and declination (i.e., exact coordinates) as you will find out. Actually, professional astronomers only use the exact coordinates. The stars that make up the co ...
chapter 2
... to attack the myths regarding these objects was a Greek scientist Thales (640 B:C). According to his theory the earth is flat. It floats on the ocean like a ship. The sun, the moon and the stars are balls of fire revolving around this flat earth. The idea of a flat earth was rejected by the great ph ...
... to attack the myths regarding these objects was a Greek scientist Thales (640 B:C). According to his theory the earth is flat. It floats on the ocean like a ship. The sun, the moon and the stars are balls of fire revolving around this flat earth. The idea of a flat earth was rejected by the great ph ...
STAR UNIT FLASH BACKS
... 2. How long would it take for an F-22 Raptor jet flying at top speed (1,500 miles per hour) to fly from the earth to the sun? a.) 8 minutes b.) 1 year c.) 7 years 1. TRUE OR FALSE: The Andromeda Galaxy will most likely eat (aka combine with) our Milky Way Galaxy in about 4 billion years. ...
... 2. How long would it take for an F-22 Raptor jet flying at top speed (1,500 miles per hour) to fly from the earth to the sun? a.) 8 minutes b.) 1 year c.) 7 years 1. TRUE OR FALSE: The Andromeda Galaxy will most likely eat (aka combine with) our Milky Way Galaxy in about 4 billion years. ...
Investigate Stars and Galaxies - American Museum of Natural History
... Lower Level (40 minutes) Using their student worksheets, have students visit the following two locations to collect evidence about stars. They can explore individually, in pairs, or in small groups. ...
... Lower Level (40 minutes) Using their student worksheets, have students visit the following two locations to collect evidence about stars. They can explore individually, in pairs, or in small groups. ...
notes
... Discovered by E.E. Barnard in 1884, NGC 6822 is also known as Barnard's Galaxy. It is located 1.6 million light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius. In this image, taken by the 4-meter Blanco Telescope in Chile, the galaxy glows blue with the light of countless massive, hot stars. Pinkish bu ...
... Discovered by E.E. Barnard in 1884, NGC 6822 is also known as Barnard's Galaxy. It is located 1.6 million light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius. In this image, taken by the 4-meter Blanco Telescope in Chile, the galaxy glows blue with the light of countless massive, hot stars. Pinkish bu ...
Ch 28 Class Notes
... 2. An important class of pulsating stars are called _____________________________. These are yellow supergiants whose cycles of brightness range from about 1 day to 50 days (5 is average). The absolute magnitude of a Cepheid is related to the length of time between its periods of maximum brightness ...
... 2. An important class of pulsating stars are called _____________________________. These are yellow supergiants whose cycles of brightness range from about 1 day to 50 days (5 is average). The absolute magnitude of a Cepheid is related to the length of time between its periods of maximum brightness ...
New York City Disciple Code - EarthSpaceScience-Keller
... included for most star missing completely Waiter has the ability to know when we want tostages check Most stages include athem Most are missing a description of the description of their core in and when core we want to be left alone. All orders are correct. ...
... included for most star missing completely Waiter has the ability to know when we want tostages check Most stages include athem Most are missing a description of the description of their core in and when core we want to be left alone. All orders are correct. ...
What is a Hertzsprung
... • As it expands, the ionized helium cools, and becomes less ionized and therefore more transparent, allowing the radiation to escape cooling the star and slowing the fusion rate. • Then the expansion stops, and reverses due to the star's gravitational attraction. • The process then repeats. ...
... • As it expands, the ionized helium cools, and becomes less ionized and therefore more transparent, allowing the radiation to escape cooling the star and slowing the fusion rate. • Then the expansion stops, and reverses due to the star's gravitational attraction. • The process then repeats. ...
ABSOLUTE AND APPARENT MAGNITUDES
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
charts_set_7
... (logarithmic) scale. A difference of 5 magnitudes = 100 x in brightness. Astronomers also refer to a star’s absolute magnitude, which is related to its luminosity. The visible stars have magnitudes less than about 6. ...
... (logarithmic) scale. A difference of 5 magnitudes = 100 x in brightness. Astronomers also refer to a star’s absolute magnitude, which is related to its luminosity. The visible stars have magnitudes less than about 6. ...
Document
... Neutron Stars • Neutron stars are compact objects that are created in the cores of massive stars during supernova explosions. The core of the star collapses, and crushes together every proton with a corresponding electron turning each electron-proton pair into a neutron. The neutrons, however, can ...
... Neutron Stars • Neutron stars are compact objects that are created in the cores of massive stars during supernova explosions. The core of the star collapses, and crushes together every proton with a corresponding electron turning each electron-proton pair into a neutron. The neutrons, however, can ...
Small images
... they were handed down through the Greeks and Arabs. Few pictorial records of the ancient constellation figures have survived, but in the Almagest AD 150, Ptolemy catalogued the positions of 1,022 of the brightest stars both in terms of celestial latitude and longitude, and of their places in 48 cons ...
... they were handed down through the Greeks and Arabs. Few pictorial records of the ancient constellation figures have survived, but in the Almagest AD 150, Ptolemy catalogued the positions of 1,022 of the brightest stars both in terms of celestial latitude and longitude, and of their places in 48 cons ...
OBAFGKM(LT) extra credit due today. Mid
... Last Time: Stars “Luminosity class” is added to the spectral type, telling you if it’s main-sequence (a “dwarf”, V), giant (III), or super-giant star (I). The sun is a G2 V. Stars occur in smaller “open” and giant “globular” clusters, with hundreds to millions of stars. Stars in clusters born at th ...
... Last Time: Stars “Luminosity class” is added to the spectral type, telling you if it’s main-sequence (a “dwarf”, V), giant (III), or super-giant star (I). The sun is a G2 V. Stars occur in smaller “open” and giant “globular” clusters, with hundreds to millions of stars. Stars in clusters born at th ...