Some Basic Principles from Astronomy
... understand the fundamental nature of the sources the apparent magnitude is not as useful. • Consider an example: the brightest star in the sky is Sirius (α CMa), with an apparent magnitude m = −1.47. The second brightest is the star Canopus (α Car) in the southern constellation Carina, has an appare ...
... understand the fundamental nature of the sources the apparent magnitude is not as useful. • Consider an example: the brightest star in the sky is Sirius (α CMa), with an apparent magnitude m = −1.47. The second brightest is the star Canopus (α Car) in the southern constellation Carina, has an appare ...
Bluffing your way in Astronomy: Taurus
... It’s a old star too, being much further through its lifecycle than the Sun, having exhausted its supply of hydrogen it is now generating energy by fusing atoms of helium into carbon. In other words, it isn’t too well and is on the stellar equivalent of life support. Aldebaran is orbited by a dim red ...
... It’s a old star too, being much further through its lifecycle than the Sun, having exhausted its supply of hydrogen it is now generating energy by fusing atoms of helium into carbon. In other words, it isn’t too well and is on the stellar equivalent of life support. Aldebaran is orbited by a dim red ...
star a
... are a measure of the star’s surface temperature. Spectral Types: Stars are classified into spectral types (subdivisions of the spectral classes O, B, A, F, G, K, and M), based on the major patterns of spectral lines in their spectra. The spectral class and type of a star is directly related to its s ...
... are a measure of the star’s surface temperature. Spectral Types: Stars are classified into spectral types (subdivisions of the spectral classes O, B, A, F, G, K, and M), based on the major patterns of spectral lines in their spectra. The spectral class and type of a star is directly related to its s ...
Packet 3
... 12. How come when you go outside on an October night you see different stars than on an April night? 13. The Earth moves in 2 different ways thus the, 2 apparent motions of stars are caused by the earth’s R________________________ & R_________________________. 15. Describe blue shift: 14. The 3 actu ...
... 12. How come when you go outside on an October night you see different stars than on an April night? 13. The Earth moves in 2 different ways thus the, 2 apparent motions of stars are caused by the earth’s R________________________ & R_________________________. 15. Describe blue shift: 14. The 3 actu ...
Notes - Bill Wolf
... preserved the original magnitude scale, though it is worthy of note that since 2.5125 ≈ 100, a magnitude difference of 5 yields a brightness ratio of 100. What do we mean by “brightness,” anyway? It’s exactly what we talked about in Astro 1: it’s the flux that reaches our eyes here at earth. Absolut ...
... preserved the original magnitude scale, though it is worthy of note that since 2.5125 ≈ 100, a magnitude difference of 5 yields a brightness ratio of 100. What do we mean by “brightness,” anyway? It’s exactly what we talked about in Astro 1: it’s the flux that reaches our eyes here at earth. Absolut ...
Spectra of Star Clusters
... • How are stars classified into spectral types? • Stars are classified according to their spectra, with different spectral types generally corresponding to different temperatures. In order from hottest to coolest, the major spectral types are O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. These are subdivided into num ...
... • How are stars classified into spectral types? • Stars are classified according to their spectra, with different spectral types generally corresponding to different temperatures. In order from hottest to coolest, the major spectral types are O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. These are subdivided into num ...
PPTX
... • Associations are arbitrary, man-made, culture-specific. • Not natural groupings: stars are not necessarily close in 3D space. Shapes are specific to Earth's present location in galaxy. • Fainter stars don't participate in pattern • Constellations are transient because stars are all moving with res ...
... • Associations are arbitrary, man-made, culture-specific. • Not natural groupings: stars are not necessarily close in 3D space. Shapes are specific to Earth's present location in galaxy. • Fainter stars don't participate in pattern • Constellations are transient because stars are all moving with res ...
Astrophysics E1. This question is about stars.
... Option E — Astrophysics E1. This question is about the relative population density of stars and galaxies. The number of stars around the Sun, within a distance of 17 ly, is 75. The number of galaxies in the local group, within a distance of 4.0 x 106 ly from the Sun, is 26. (a) Calculate the average ...
... Option E — Astrophysics E1. This question is about the relative population density of stars and galaxies. The number of stars around the Sun, within a distance of 17 ly, is 75. The number of galaxies in the local group, within a distance of 4.0 x 106 ly from the Sun, is 26. (a) Calculate the average ...
Constellations
... The first on the list of Heracles' jobs was the task of killing the Nemean Lion, a giant beast that roamed the hills and the streets of the Peloponnesian villages, devouring whomever it met. The animal's skin was immune to iron, bronze, and stone and Heracles' arrows bounced off the lion. So Heracle ...
... The first on the list of Heracles' jobs was the task of killing the Nemean Lion, a giant beast that roamed the hills and the streets of the Peloponnesian villages, devouring whomever it met. The animal's skin was immune to iron, bronze, and stone and Heracles' arrows bounced off the lion. So Heracle ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE STARS AND CONSTELLATIONS
... equator intersect at two points. The planes containing the two great circles are actually tilted by 23.5 degrees, the same angle by which the earth's axis of rotation is tilted away from the line perpendicular to its orbital plane about the sun. ...
... equator intersect at two points. The planes containing the two great circles are actually tilted by 23.5 degrees, the same angle by which the earth's axis of rotation is tilted away from the line perpendicular to its orbital plane about the sun. ...
January 2016 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... down to live the longest stage of their lives as normal ‘Main Sequence’ stars. Our Sun is about 4.3 billion years old and approaching half way through its main sequence. We can see many stars at this stage in Orion and others older and many much younger. There is another factor that affects the life ...
... down to live the longest stage of their lives as normal ‘Main Sequence’ stars. Our Sun is about 4.3 billion years old and approaching half way through its main sequence. We can see many stars at this stage in Orion and others older and many much younger. There is another factor that affects the life ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... 13. How do the magnitudes of stars C and D in problem 4 compare? (Problem 4 synopsis: Stars C and D are the same distance from us, but star D is 10,000 times more luminous.) To answer this problem you need to use the rule regarding magnitudes and brightness’s: if two stars differ in magnitude by 5 m ...
... 13. How do the magnitudes of stars C and D in problem 4 compare? (Problem 4 synopsis: Stars C and D are the same distance from us, but star D is 10,000 times more luminous.) To answer this problem you need to use the rule regarding magnitudes and brightness’s: if two stars differ in magnitude by 5 m ...
Crux The Southern Cross
... locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not interact then we call this an optical double. It is possible, but rarer for 4 or 6 stars to be grouped into Computer simulati ...
... locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not interact then we call this an optical double. It is possible, but rarer for 4 or 6 stars to be grouped into Computer simulati ...
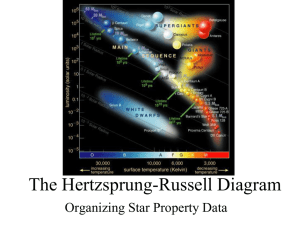
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
supplemental educational materials PDF
... • Students may incorrectly identify the Big Dipper or the Pleiades as constellations, but they are “asterisms” – subsets or supersets of constellations. For example, the Big Dipper is part of the constellation Ursa Major and the Pleiades are found in Taurus. • Different constellations are visible at ...
... • Students may incorrectly identify the Big Dipper or the Pleiades as constellations, but they are “asterisms” – subsets or supersets of constellations. For example, the Big Dipper is part of the constellation Ursa Major and the Pleiades are found in Taurus. • Different constellations are visible at ...
Phys133 Sample MidTerm #2 Covers Chs.10
... 4) What happens when a star exhausts its core hydrogen supply? A) It contracts, becoming hotter and brighter. B) Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger but cooler and therefore remains at the same brightness. C) It expands, becoming bigger but dimmer. D) It contr ...
... 4) What happens when a star exhausts its core hydrogen supply? A) It contracts, becoming hotter and brighter. B) Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger but cooler and therefore remains at the same brightness. C) It expands, becoming bigger but dimmer. D) It contr ...
Apparent Brightness, Parallax and the Distance to Sirius
... • The measured flux of light from Sirius is 1.2 X 10 – 4 ergs/ cm2 sec. From this, calculate how far away Sirius would be based on our assumption. Give your answer in cm, but then convert ...
... • The measured flux of light from Sirius is 1.2 X 10 – 4 ergs/ cm2 sec. From this, calculate how far away Sirius would be based on our assumption. Give your answer in cm, but then convert ...
The Temperature of Stars
... Stars vary in size and mass. Stars such as the sun are considered medium-sized stars. The sun has a diameter of 1,390,000 km. Most stars visible from Earth are mediumsized stars. Many stars also have about the same mass as the sun, however some stars may be more or less massive. ...
... Stars vary in size and mass. Stars such as the sun are considered medium-sized stars. The sun has a diameter of 1,390,000 km. Most stars visible from Earth are mediumsized stars. Many stars also have about the same mass as the sun, however some stars may be more or less massive. ...
Document
... D • A is incorrect because star A has a negative apparent magnitude, which means it is a brighter star. • B is incorrect because even though star B has a big apparent magnitude, it does not have the biggest apparent magnitude of the stars listed. • C is incorrect because stars that have smaller appa ...
... D • A is incorrect because star A has a negative apparent magnitude, which means it is a brighter star. • B is incorrect because even though star B has a big apparent magnitude, it does not have the biggest apparent magnitude of the stars listed. • C is incorrect because stars that have smaller appa ...
Stars - Academic Computer Center
... • At this distance it takes light 4.3 years to travel from this star. In other words the star is 4.3 light years away. • The space shuttle travels 17,500 miles/hour, at this ...
... • At this distance it takes light 4.3 years to travel from this star. In other words the star is 4.3 light years away. • The space shuttle travels 17,500 miles/hour, at this ...
Binocular Universe: Summer`s Swan Song
... but he did spot a small clump of starlight a little less than 2° south-southeast of Sadr. Noting its position, he added it as the 29th entry in his famous catalog. Though not one of Messier’s best, M29 is visible through small, hand-supported binoculars as a tiny, rectangular patch of light, with pe ...
... but he did spot a small clump of starlight a little less than 2° south-southeast of Sadr. Noting its position, he added it as the 29th entry in his famous catalog. Though not one of Messier’s best, M29 is visible through small, hand-supported binoculars as a tiny, rectangular patch of light, with pe ...
Lecture 9: Stellar Spectra
... Lines get broader as the pressure increases. Larger stars are puffier, which means lower pressure, so that Larger Stars have Narrower Lines Since larger stars are brighter at a given temperature, this measures relative stellar luminosity for stars of the same temperature. See Figure 19-15 ...
... Lines get broader as the pressure increases. Larger stars are puffier, which means lower pressure, so that Larger Stars have Narrower Lines Since larger stars are brighter at a given temperature, this measures relative stellar luminosity for stars of the same temperature. See Figure 19-15 ...
antarctic and associated exploration book collection
... (1.3 light years ((LY)). Isaac Newton adopted a more philosophical approach, arguing (1686) that Sirius and Saturn had about the same apparent brightness (!) and thus, by adopting appropriate values for planet size, distance and ...
... (1.3 light years ((LY)). Isaac Newton adopted a more philosophical approach, arguing (1686) that Sirius and Saturn had about the same apparent brightness (!) and thus, by adopting appropriate values for planet size, distance and ...
Part 2 - Aryabhat
... on this list. Like Alpha Centauri it appears so bright only because at 11.4 light-years, it is relatively close. Procyon is an example of a main sequence "sub giant" star, one that is beginning the death process by converting its remaining core hydrogen into helium. Procyon is currently twice the di ...
... on this list. Like Alpha Centauri it appears so bright only because at 11.4 light-years, it is relatively close. Procyon is an example of a main sequence "sub giant" star, one that is beginning the death process by converting its remaining core hydrogen into helium. Procyon is currently twice the di ...
Week 10
... On Earth, the parallax angle measured for the star Procyon is 0.29 arcseconds. If you were to measure Procyon’s parallax angle from Venus, what would the parallax angle be? (Note: Venus’ orbit is smaller than Earth’s orbit.) A. More than 0.29 arcseconds B. 0.29 arcseconds C. Less than 0.29 arcsecond ...
... On Earth, the parallax angle measured for the star Procyon is 0.29 arcseconds. If you were to measure Procyon’s parallax angle from Venus, what would the parallax angle be? (Note: Venus’ orbit is smaller than Earth’s orbit.) A. More than 0.29 arcseconds B. 0.29 arcseconds C. Less than 0.29 arcsecond ...