IV International Astronomy Olympiad
... at 2000 A? Which one emits more radiation at 10000 A? What is the ratio of the total radiation emitted by the two stars? Consider the stars as black bodies. 2. Engineers from the Simferopol University describe a new method to utilize old military ships: to construct very small black holes from their ...
... at 2000 A? Which one emits more radiation at 10000 A? What is the ratio of the total radiation emitted by the two stars? Consider the stars as black bodies. 2. Engineers from the Simferopol University describe a new method to utilize old military ships: to construct very small black holes from their ...
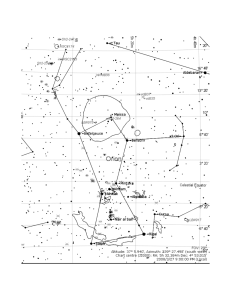
CONSTELLATION DELPHINUS, THE DOLPHIN
... 1873, divisible in only large amateur telescopes. To the unaided eye, it appears to be a white star of magnitude 3.6. It has a period of 27 years and is 97 light-years from Earth. • Gamma Delphini is a celebrated binary star among amateur astronomers. The primary is a gold-colored star of magnitude ...
... 1873, divisible in only large amateur telescopes. To the unaided eye, it appears to be a white star of magnitude 3.6. It has a period of 27 years and is 97 light-years from Earth. • Gamma Delphini is a celebrated binary star among amateur astronomers. The primary is a gold-colored star of magnitude ...
Lecture Note
... Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by parallax, the apparent shift of a star against the background stars observed as the Earth moves along its orbit ...
... Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by parallax, the apparent shift of a star against the background stars observed as the Earth moves along its orbit ...
lesson 5-8 quiz.show.pps
... It is the shortest day of the year. The sun is the farthest from the equator. It occurs on or around November 21st every year in the northern hemisphere. ...
... It is the shortest day of the year. The sun is the farthest from the equator. It occurs on or around November 21st every year in the northern hemisphere. ...
24-2 Characteristics of Stars
... • Light year – distance that light travels in one year (9.5 million million km) ...
... • Light year – distance that light travels in one year (9.5 million million km) ...
Stars - Quia
... when a nearby object is seen against a distant backdrop from two different perspectives ...
... when a nearby object is seen against a distant backdrop from two different perspectives ...
May - RASC St. John`s Centre
... very bright stars about 60º away. One is Vega in Lyra, The Lyre, which Appolo, the god of music as well as the Sun, gave his son Orpheus with which he played the most enchanting music. Arcing slightly in the direction of Polaris along this line finds Deneb in Cygnus, The Swan, also known as the Nort ...
... very bright stars about 60º away. One is Vega in Lyra, The Lyre, which Appolo, the god of music as well as the Sun, gave his son Orpheus with which he played the most enchanting music. Arcing slightly in the direction of Polaris along this line finds Deneb in Cygnus, The Swan, also known as the Nort ...
Stars Unit 1-2: Stars
... • Brightness is the perceived strength of the star’s light when observed from earth. – This is more commonly called apparent magnitude. ...
... • Brightness is the perceived strength of the star’s light when observed from earth. – This is more commonly called apparent magnitude. ...
Stars
... E0102-72 is a supernova remnant in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. This galaxy is 190,000 light years from Earth. E0102 -72, which is approximately a thousand years old, is believed to have resulted from the explosion of a massive star. Stretching across forty light ...
... E0102-72 is a supernova remnant in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. This galaxy is 190,000 light years from Earth. E0102 -72, which is approximately a thousand years old, is believed to have resulted from the explosion of a massive star. Stretching across forty light ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... Students know the Sun is a medium-sized star located in the Milky Way Galaxy, part of which can be seen as a glowing band of light spanning the clear night sky. W/S Answers to Sample Test Questions 2. C, DOK level 1 3. B, DOK level 1 4. C, DOK level 1 5. D, DOK level 1 6. A, DOK level 2 7. B, DOK le ...
... Students know the Sun is a medium-sized star located in the Milky Way Galaxy, part of which can be seen as a glowing band of light spanning the clear night sky. W/S Answers to Sample Test Questions 2. C, DOK level 1 3. B, DOK level 1 4. C, DOK level 1 5. D, DOK level 1 6. A, DOK level 2 7. B, DOK le ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2005
... NGC2903 (8.9) sg. A spiral galaxy inclined to our line of sight. One of the brightest galaxies in Leo it is surprisingly not a Messier object. NGC3190 (11.0) sg and NGC3193 (10.9) eg. Pair of galaxies located mid-way between and . NGC3226 (11.4) and NGC3227 (10.8) about 1o east of form a close ...
... NGC2903 (8.9) sg. A spiral galaxy inclined to our line of sight. One of the brightest galaxies in Leo it is surprisingly not a Messier object. NGC3190 (11.0) sg and NGC3193 (10.9) eg. Pair of galaxies located mid-way between and . NGC3226 (11.4) and NGC3227 (10.8) about 1o east of form a close ...
The Brightness of Stars
... Quantifying the brightness of stars started with Hipparchus (2nd C. BC) and his magnitude scale He designated the brightest star he could see as a “1” magnitude and the dimmest a “6” magnitude Astronomers still labor under a more quantified version of this system One tragic consequence is that ...
... Quantifying the brightness of stars started with Hipparchus (2nd C. BC) and his magnitude scale He designated the brightest star he could see as a “1” magnitude and the dimmest a “6” magnitude Astronomers still labor under a more quantified version of this system One tragic consequence is that ...
RFS_multiple_choice_Dec8_Key
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
Lecture 6: Properties of Stars The Constellations The Constellations
... o Distant stars used as reference points. Closer star appears to move relative to distant stars during Earth’s orbit about Sun. o Parallax angle: p ~ 1 AU / d => d = ~ 1 AU / p ...
... o Distant stars used as reference points. Closer star appears to move relative to distant stars during Earth’s orbit about Sun. o Parallax angle: p ~ 1 AU / d => d = ~ 1 AU / p ...
Astronomy – Studying the Stars & Space
... use their hydrogen quickly and may light cannot escape explode in a huge its gravity bright flash • Gas or dust that sink • Can be brighter than into black hole from a an entire galaxy for star form x-ray light several days which may indicate a • A collapsed star can black holes’ existence become a ...
... use their hydrogen quickly and may light cannot escape explode in a huge its gravity bright flash • Gas or dust that sink • Can be brighter than into black hole from a an entire galaxy for star form x-ray light several days which may indicate a • A collapsed star can black holes’ existence become a ...
Characteristics of Stars Stars Analyzing Starlight Star Characteristics
... by analyzing the spectra of the light that a star emits ...
... by analyzing the spectra of the light that a star emits ...
properties of stars 2012
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
65008_StarFinderPart2
... When would be a good DATE to see a blue star (Rigel) if you wanted to star gaze at 10 P.M.? Hint: there are multiple possible answers here, give a Date. ...
... When would be a good DATE to see a blue star (Rigel) if you wanted to star gaze at 10 P.M.? Hint: there are multiple possible answers here, give a Date. ...
Friday, August 28 - Otterbein University
... locate the pole star. It is 17 degrees above the northern horizon. What is your latitude? ...
... locate the pole star. It is 17 degrees above the northern horizon. What is your latitude? ...
August Skies
... lopsided house or, if someone insisted that it represent a primate type figure, I’d make it a gnome with a big pointy hat and name him Gulcifer. Given the ...
... lopsided house or, if someone insisted that it represent a primate type figure, I’d make it a gnome with a big pointy hat and name him Gulcifer. Given the ...
Astronomy Review
... 52. A(n) _____________________________ is a large group of stars, dust, and gases held together by gravity. 53. Circle the letter of the type of galaxy that the Milky Way is. a. Spiral galaxy ...
... 52. A(n) _____________________________ is a large group of stars, dust, and gases held together by gravity. 53. Circle the letter of the type of galaxy that the Milky Way is. a. Spiral galaxy ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... long wrinkle ridge known as the Dorsa Smirnov. This is a very prominent feature and can be seen with large binoculars or a small telescope. Midway along the ridge is the small crater Very; a bowl shaped crater with high walls and a rounded floor. At just 5 km (3 miles) wide, a telescope of at least ...
... long wrinkle ridge known as the Dorsa Smirnov. This is a very prominent feature and can be seen with large binoculars or a small telescope. Midway along the ridge is the small crater Very; a bowl shaped crater with high walls and a rounded floor. At just 5 km (3 miles) wide, a telescope of at least ...
Stars and their Properties
... o The Moving Cluster Method – Stars converge to a central point if you are moving backwards in space at very high speed – Used to 1,000 parsecs Sun is not in a star cluster Convergent Point – Point at which the cluster of stars are converging (coming together) Convergent point can be outside t ...
... o The Moving Cluster Method – Stars converge to a central point if you are moving backwards in space at very high speed – Used to 1,000 parsecs Sun is not in a star cluster Convergent Point – Point at which the cluster of stars are converging (coming together) Convergent point can be outside t ...
SGL 9 NGC Galaxy magnitude 9/10 observing challenge Up for
... This group NGC3605 / NGC 3607 and NGC 3608 are part of the Leo II group of galaxies. NGC 3605 is however in the background and NGC 3607/8 (both magnitude 9) are interacting around 65 million light years away. How many can you see? Two or Three? Object 4 – NGC 3521 (Taki page 74) Down again, under Le ...
... This group NGC3605 / NGC 3607 and NGC 3608 are part of the Leo II group of galaxies. NGC 3605 is however in the background and NGC 3607/8 (both magnitude 9) are interacting around 65 million light years away. How many can you see? Two or Three? Object 4 – NGC 3521 (Taki page 74) Down again, under Le ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.