ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... http://library.thinkquest.org/26220/stars/formation.html What is a nebula (click on protostars)? ...
... http://library.thinkquest.org/26220/stars/formation.html What is a nebula (click on protostars)? ...
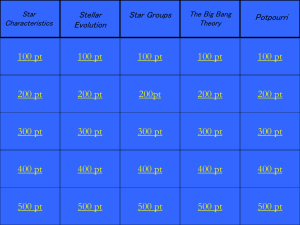
The HR Diagram
... • Where are stars most of their lives? • Where are they when they begin to die? • What are they after they use up their ...
... • Where are stars most of their lives? • Where are they when they begin to die? • What are they after they use up their ...
February - Bristol Astronomical Society
... Batista Hodierna around 1654, it was probably quite well known to ancient astronomers. Charles Messier, was one of many people who later rediscovered the cluster. He added it to his famous catalogue on January 16, 1765 ...
... Batista Hodierna around 1654, it was probably quite well known to ancient astronomers. Charles Messier, was one of many people who later rediscovered the cluster. He added it to his famous catalogue on January 16, 1765 ...
Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ Stars Study Guide (Ch. 21)
... Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
... Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
Stars and Constellations
... then able to make its own heat and light. • The life of the star then depends on its mass. ...
... then able to make its own heat and light. • The life of the star then depends on its mass. ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... clusters situated about 7,300 light years away. With visual magnitudes of 5.3 and 6.1 respectively, the pair was labeled as Caldwell 14 by Sir Patrick Moore, but somehow missed a Messier designation. While either cluster could stand alone as a noteworthy object, the pair, spanning two full Moon diam ...
... clusters situated about 7,300 light years away. With visual magnitudes of 5.3 and 6.1 respectively, the pair was labeled as Caldwell 14 by Sir Patrick Moore, but somehow missed a Messier designation. While either cluster could stand alone as a noteworthy object, the pair, spanning two full Moon diam ...
STEPHAN`S QUINTET
... These galaxies are of interest because of their violent collisions. Four of the five galaxies in Stephan´s Quintet form a physical association, Hickson Compact Group 92, and are involved in a cosmic dance that most likely will end with the galaxies merging. Also of interest, NGC 7320 indicates a sma ...
... These galaxies are of interest because of their violent collisions. Four of the five galaxies in Stephan´s Quintet form a physical association, Hickson Compact Group 92, and are involved in a cosmic dance that most likely will end with the galaxies merging. Also of interest, NGC 7320 indicates a sma ...
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
May
... NGC4656 is a type SBm barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici (KAY-neez- vë-NAT-ih-si). Popularly known as the Hockey Stick Galaxy, the key features are the angled tilt of the disk and the apparent offset of the core. If observing at low magnification look in the same field of view ...
... NGC4656 is a type SBm barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici (KAY-neez- vë-NAT-ih-si). Popularly known as the Hockey Stick Galaxy, the key features are the angled tilt of the disk and the apparent offset of the core. If observing at low magnification look in the same field of view ...
Properties of Stars
... with temperatures between 5000 and 6000 K appear yellow • Binary Stars – pairs of stars, pulled together by gravity, that orbit each other • Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate – its mass • The mass of a body can be calculated if it is attached by gravity ...
... with temperatures between 5000 and 6000 K appear yellow • Binary Stars – pairs of stars, pulled together by gravity, that orbit each other • Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate – its mass • The mass of a body can be calculated if it is attached by gravity ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. June 2005. A
... NGC6205 (M13) (5.9) gc. Arguably one of the outstanding objects in the northern hemisphere. Just visible to the naked eye from dark sites it appears as a fuzzy blob in binoculars. It stands high power well and the outer edges begin to resolve into individual stars in a 4" (100mm) telescope. Increasi ...
... NGC6205 (M13) (5.9) gc. Arguably one of the outstanding objects in the northern hemisphere. Just visible to the naked eye from dark sites it appears as a fuzzy blob in binoculars. It stands high power well and the outer edges begin to resolve into individual stars in a 4" (100mm) telescope. Increasi ...
d 2
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
Monday, April 15
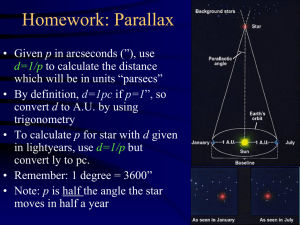
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
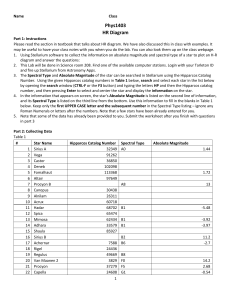
Astronomy 162 Lab 4: Stars
... Magnitude is measured so that the smaller numbers correspond to the brightest objects. The Sun is by far the brightest object in the sky and has an Apparent Magnitude of about -30. The Apparent Magnitude of any object is determined by two things: the object's intrinsic brightness, and the object's d ...
... Magnitude is measured so that the smaller numbers correspond to the brightest objects. The Sun is by far the brightest object in the sky and has an Apparent Magnitude of about -30. The Apparent Magnitude of any object is determined by two things: the object's intrinsic brightness, and the object's d ...
ppt
... • From there we can calculate how much further away the star must be than the Sun to make it the brightness we see from Earth • Delta Cephei shows has a period of about 5 days • This is a reasonably bright star in the constellation of Cepheus • Cepheids are in other galaxies also, and used similarly ...
... • From there we can calculate how much further away the star must be than the Sun to make it the brightness we see from Earth • Delta Cephei shows has a period of about 5 days • This is a reasonably bright star in the constellation of Cepheus • Cepheids are in other galaxies also, and used similarly ...
Study Guide: Use your notes and handouts to
... 35. What is a Hertzsprung Russell Diagram? 36. What is on the X axis of a HR Diagram? 37. What is on the Y axis of the HR Diagram? 38. What is used to determine luminosity? 39. How are main sequence stars represented on a HR Diagram? 40. Where would you find the white dwarf stars on a HR Diagram? 41 ...
... 35. What is a Hertzsprung Russell Diagram? 36. What is on the X axis of a HR Diagram? 37. What is on the Y axis of the HR Diagram? 38. What is used to determine luminosity? 39. How are main sequence stars represented on a HR Diagram? 40. Where would you find the white dwarf stars on a HR Diagram? 41 ...
Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
... Starlight Brightness • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star appears to be from earth when viewed with the unaided eye. Distance can cause a dimmer star to appear to be brighter than a brighter star that is farther away. • Absolute Magnitude: The amount of light (brightness) a star actually has. Th ...
... Starlight Brightness • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star appears to be from earth when viewed with the unaided eye. Distance can cause a dimmer star to appear to be brighter than a brighter star that is farther away. • Absolute Magnitude: The amount of light (brightness) a star actually has. Th ...
HS-ESS1-2 - Trimble County Schools
... A. What are Binary Stars? 1) How do most of them appear from Earth? 2) How are Astonomers able to identify them? B. What are Doppler Shifts? 1) Compare/Contrast blueshift and redshift. 2) How does speed affect it? C. What are two units of measure for long stellar distances? D Describe the apparent s ...
... A. What are Binary Stars? 1) How do most of them appear from Earth? 2) How are Astonomers able to identify them? B. What are Doppler Shifts? 1) Compare/Contrast blueshift and redshift. 2) How does speed affect it? C. What are two units of measure for long stellar distances? D Describe the apparent s ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.