Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
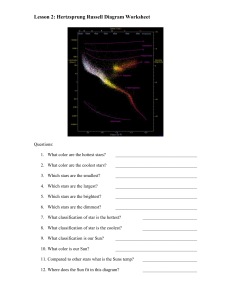
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
Apparent Magnitude
... In 125 B.C., a famous astronomer of that time, named Hipparchus, was making a star map of the “celestial sphere”. Hipparchus not only wanted to locate each star’s position on his map, but also to indicate the brightness of each star. To do this Hipparchus invented the concept of stellar magnitude. H ...
... In 125 B.C., a famous astronomer of that time, named Hipparchus, was making a star map of the “celestial sphere”. Hipparchus not only wanted to locate each star’s position on his map, but also to indicate the brightness of each star. To do this Hipparchus invented the concept of stellar magnitude. H ...
Morning Announcements
... how bright it appears at its true location. Betelgeuse has an absolute magnitude (M) of –5.5, which tells us how bright it would appear if we could move it to a distance of 10 parsecs (about 33 light-years). 11) Where would Betelgeuse appear brighter, in its true location or if it were at a distance ...
... how bright it appears at its true location. Betelgeuse has an absolute magnitude (M) of –5.5, which tells us how bright it would appear if we could move it to a distance of 10 parsecs (about 33 light-years). 11) Where would Betelgeuse appear brighter, in its true location or if it were at a distance ...
Barred Spiral Galaxy
... • Large amounts of electrically charged gas are ejected suddenly from the Sun’s corona. ...
... • Large amounts of electrically charged gas are ejected suddenly from the Sun’s corona. ...
The Family of Stars
... that a star would have if it were at a distance of 10 pc. If we know a star’s absolute magnitude, we can infer its distance by comparing absolute and apparent magnitudes. ...
... that a star would have if it were at a distance of 10 pc. If we know a star’s absolute magnitude, we can infer its distance by comparing absolute and apparent magnitudes. ...
The Magnitude Scale
... from a given source (energy per unit area per unit time per unit bandwidth), then the apparent magnitude of the object is defined by Fν m = −2.5 log10 0 Fν where Fν is the flux per unit frequency received from the source, and F ν0 is a normalising constant. The normalising constants have been calibr ...
... from a given source (energy per unit area per unit time per unit bandwidth), then the apparent magnitude of the object is defined by Fν m = −2.5 log10 0 Fν where Fν is the flux per unit frequency received from the source, and F ν0 is a normalising constant. The normalising constants have been calibr ...
Measuring the Stars pages 813-820
... The age, like the age of Aquarius is the house that the axis of the Earth is pointing to for about the next 2,000 years. The Earth has a wobble, and the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be north. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a c ...
... The age, like the age of Aquarius is the house that the axis of the Earth is pointing to for about the next 2,000 years. The Earth has a wobble, and the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be north. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a c ...
Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
Lab 1-2 : Vocabulary
... in the universe was compressed into an extremely small volume that suddenly began expanding in all directions billions of years ago. ...
... in the universe was compressed into an extremely small volume that suddenly began expanding in all directions billions of years ago. ...
LIfe of a Star
... Can shine for billions of years before they extinguish Observe life of a star (link) ...
... Can shine for billions of years before they extinguish Observe life of a star (link) ...
Ch. 27 Stars & Galaxies
... • Supergiant Stars that run out of helium contract with much higher forces. ...
... • Supergiant Stars that run out of helium contract with much higher forces. ...
Constellation
... pearls' surrounding an Exploding Star Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. This image shows the entire region around the supernova. The most prominent feature in the image is a ring with dozens of bright spots. A shock wave of material unl ...
... pearls' surrounding an Exploding Star Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. This image shows the entire region around the supernova. The most prominent feature in the image is a ring with dozens of bright spots. A shock wave of material unl ...
Astronomy 242: Review Questions #1 Distributed: February 10
... 12. You observe a sample of Cepheid variable stars in a nearby galaxy. Plotting the average apparent K-band magnitude of each one against the period of pulsation yields Fig. 3. The straight line, a least-squares fit to the data, has the equation mK = 16.40 − 3.53 log(P/day). (a) Does it seem reasona ...
... 12. You observe a sample of Cepheid variable stars in a nearby galaxy. Plotting the average apparent K-band magnitude of each one against the period of pulsation yields Fig. 3. The straight line, a least-squares fit to the data, has the equation mK = 16.40 − 3.53 log(P/day). (a) Does it seem reasona ...
Making H-R Diagrams - PLC-METS
... Making an H-R Diagram BACKGOUND INFORMATION: Stars in the sky are not created equal and are composed of different materials, different temperatures, different brightness, different sizes, and different distances from Earth. A star’s mass dictates how bright it will be, how long it will live, its tem ...
... Making an H-R Diagram BACKGOUND INFORMATION: Stars in the sky are not created equal and are composed of different materials, different temperatures, different brightness, different sizes, and different distances from Earth. A star’s mass dictates how bright it will be, how long it will live, its tem ...
the fixed stars - The Witches` Almanac
... while others are negative, even sinister. The fixed stars have been important since astrology’s earliest days. Fixed is something of a misnomer. The stars do move ever so slightly; however, the distance traveled over a century is barely perceptible. Alpheratz is a purplishwhite double star of the ...
... while others are negative, even sinister. The fixed stars have been important since astrology’s earliest days. Fixed is something of a misnomer. The stars do move ever so slightly; however, the distance traveled over a century is barely perceptible. Alpheratz is a purplishwhite double star of the ...
a geolocation. Obtain the information related to certain star.
... An amateur astronomer is searching for a star in the field. She forgot her star charts or they don't have the exact information she is looking for.... ...
... An amateur astronomer is searching for a star in the field. She forgot her star charts or they don't have the exact information she is looking for.... ...
How it works:
... On the reverse of this sheet are four constellations, all of which can be seen on summer nights in Colorado. Each constellation has five stars. For every book read, fill in one star. Each time you complete a constellation, bring this sheet to the teenseen to receive a prize and a raffle ticket for a ...
... On the reverse of this sheet are four constellations, all of which can be seen on summer nights in Colorado. Each constellation has five stars. For every book read, fill in one star. Each time you complete a constellation, bring this sheet to the teenseen to receive a prize and a raffle ticket for a ...
Constellation Information
... Gemini. Cancers chief attraction is the huge star cluster labeled M44. Its bright enough to see with the naked eye as a dim, fuzzy patch if you have a clear, moonless evening at an observing site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-pow ...
... Gemini. Cancers chief attraction is the huge star cluster labeled M44. Its bright enough to see with the naked eye as a dim, fuzzy patch if you have a clear, moonless evening at an observing site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-pow ...
constellations - Otterbein University
... - constellation shapes and names - star names and position in constellation - deep sky objects’ names and position • Quiz: You will be asked to find these objects on a star map. ...
... - constellation shapes and names - star names and position in constellation - deep sky objects’ names and position • Quiz: You will be asked to find these objects on a star map. ...
Stars, H-R and Life Cycle of Star
... Two astronomers discovered a relationship between the absolute magnitude (real brightness) of a star and its surface temperature. They plotted the data on a graph. ...
... Two astronomers discovered a relationship between the absolute magnitude (real brightness) of a star and its surface temperature. They plotted the data on a graph. ...
Abs-Apar Mag
... • 1856 proposal to standardize • standard ratio of 2.512 between magnitudes. • 5 magnitude steps correspond to 100x factor brightness change • The Star Vega selected as baseline (magnitude 0.0) – 5th brightest star, 2nd in North hemisphere – Is now magnitude 0.03, by redefined baseline scale ...
... • 1856 proposal to standardize • standard ratio of 2.512 between magnitudes. • 5 magnitude steps correspond to 100x factor brightness change • The Star Vega selected as baseline (magnitude 0.0) – 5th brightest star, 2nd in North hemisphere – Is now magnitude 0.03, by redefined baseline scale ...
HR DIAGRAM REPORT FORM
... 4. How many of the stars in table 10.1 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ How many of the stars in table 10.2 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ 5. Based on ...
... 4. How many of the stars in table 10.1 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ How many of the stars in table 10.2 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ 5. Based on ...
The Danger of Deadly Cosmic Explosions
... • Across galaxy, maybe 50,000 light years away. • Rotating neutron star, fantastic magnetic field. • Spectacular, but not lethally dangerous – well, except for astronauts maybe. ...
... • Across galaxy, maybe 50,000 light years away. • Rotating neutron star, fantastic magnetic field. • Spectacular, but not lethally dangerous – well, except for astronauts maybe. ...
Bright stars and faint stars: the stellar magnitude system Magnitudes
... • Imagine moving it to a distance of 10 parsecs • The apparent magnitude it would have is its absolute magnitude • The absolute magnitude is a distanceindependent quantity • Look at Appendix 12 and Appendix 13 (the brightest stars) and think about the meaning of the absolute magnitudes ...
... • Imagine moving it to a distance of 10 parsecs • The apparent magnitude it would have is its absolute magnitude • The absolute magnitude is a distanceindependent quantity • Look at Appendix 12 and Appendix 13 (the brightest stars) and think about the meaning of the absolute magnitudes ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.























