* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download constellations - Otterbein University
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
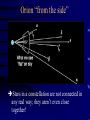
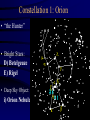
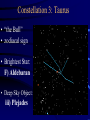
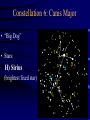
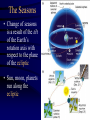
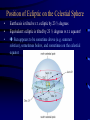
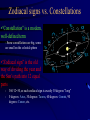
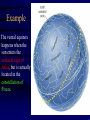
Constellation Quiz Workshop • Learn the data on the Constellation Quiz Data Sheet: - constellation shapes and names - star names and position in constellation - deep sky objects’ names and position • Quiz: You will be asked to find these objects on a star map. Constellations of Stars • About 5000 stars visible with naked eye • About 3500 of them from the northern hemisphere • Stars that appear to be close are grouped together into constellations since antiquity • Officially 88 constellations (with strict boundaries for classification of objects) • Names range from mythological (Perseus, Cassiopeia) to technical (Air Pump, Compass) Constellation 1: Orion Orion as seen at night Orion as imagined by men Orion “from the side” Stars in a constellation are not connected in any real way; they aren’t even close together! Constellation 1: Orion • “the Hunter” • Bright Stars: D) Betelgeuze E) Rigel • Deep Sky Object: i) Orion Nebula Constellation 2: Gemini • “the Twins” • zodiacal sign • Brightest Stars: I) Castor J=K) Pollux Constellation 3: Taurus • “the Bull” • zodiacal sign • Brightest Star: F) Aldebaran • Deep Sky Object: iii) Plejades Constellation 4: Ursa Major • Other name: Big Dipper • Stars: B) Dubhe C) Merak • Navigation: go 5 times the distance from Merak to Dubhe and you are at Polaris. Constellation 5: Ursa Minor • Other name: Little Dipper • α Ursa Minoris is Polaris [A], the pole star Constellation 6: Canis Major • “Big Dog” • Stars: H) Sirius (brightest fixed star) Constellation 7: Cancer • “Crab” • No bright Stars Constellation 8: Leo • “the Lion” • zodiacal sign • Brightest Star: G) Regulus Constellation 9: Cassiopeia • Greek mythological figure: mother of Andromeda • the big “W” in the sky • No bright stars Constellation 10: Pisces • “the Fishes” • Zodiacal sign • No bright stars Constellation 11: Pegasus • Greek mythological figure: the winged horse • big rectangle in the sky • No bright stars Constellation 12: Andromeda • Greek mythological figure: Daughter of Queen Cassiopeia and King Cepheus rescued from Cetus by Perseus • Deep Sky Object: Andromeda Galaxy The Seasons • Change of seasons is a result of the tilt of the Earth’s rotation axis with respect to the plane of the ecliptic • Sun, moon, planets run along the ecliptic Position of Ecliptic on the Celestial Sphere • • • Earth axis is tilted w.r.t. ecliptic by 23 ½ degrees Equivalent: ecliptic is tilted by 23 ½ degrees w.r.t. equator! Sun appears to be sometime above (e.g. summer solstice), sometimes below, and sometimes on the celestial equator Zodiacal signs vs. Constellations •“Constellation” is a modern, well-defined term - Some constellations are big, some are small on the celestial sphere •“Zodiacal sign” is the old way of dividing the year and the Sun’s path into 12 equal parts - 360/12=30, so each zodiacal sign is exactly 30 degrees “long” 0 degrees: Aries, 30 degrees: Taurus, 60 degrees: Gemini, 90 degrees: Cancer, etc. Example The vernal equinox happens when the sun enters the zodiacal sign of Aries, but is actually located in the constellation of Pisces.