6th Grade Science Chapter 19 Jeopardy Game
... they are very similar to early galaxies. b. Distant galaxies share many characteristics with early galaxies. c. Distant galaxies have not changed as much as close galaxies, so they are most similar to early galaxies. d. Because it takes a long time for light to travel through space, looking at dista ...
... they are very similar to early galaxies. b. Distant galaxies share many characteristics with early galaxies. c. Distant galaxies have not changed as much as close galaxies, so they are most similar to early galaxies. d. Because it takes a long time for light to travel through space, looking at dista ...
Solution Key
... where we can determine AV from the amount of reddening, that is AV = 3 (0.8 - 0) = 2.4 which leads to d = 738 pc (for MV = + 0.6). ...
... where we can determine AV from the amount of reddening, that is AV = 3 (0.8 - 0) = 2.4 which leads to d = 738 pc (for MV = + 0.6). ...
canopus e.g procyon
... Proxima Centauri is a faint red star that orbits Alpha-Centauri A and B with a period of about one million years. Proxima Centauri is 4.22 light years from the Earth (now) and about 0.24 light years from Alpha-Centauri A and B. • Alpha-Centauri A and B – a double star system with a period of about ...
... Proxima Centauri is a faint red star that orbits Alpha-Centauri A and B with a period of about one million years. Proxima Centauri is 4.22 light years from the Earth (now) and about 0.24 light years from Alpha-Centauri A and B. • Alpha-Centauri A and B – a double star system with a period of about ...
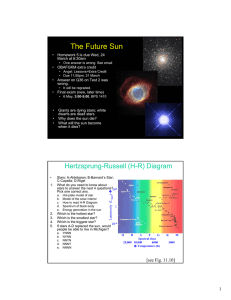
Teacher Sheet 1. What variables does the HR Diagram compare
... Although they are cool [red], they are very luminous, and therefore bright. In the Main Sequence, stars that are cool are not as luminous. 13. How do white dwarf stars differ from stars in the Main Sequence? White dwarf stars are very hot [blue], but dim because they are so small. 14. Describe stars ...
... Although they are cool [red], they are very luminous, and therefore bright. In the Main Sequence, stars that are cool are not as luminous. 13. How do white dwarf stars differ from stars in the Main Sequence? White dwarf stars are very hot [blue], but dim because they are so small. 14. Describe stars ...
The Future Sun • Homework 5 is due Wed, 24 March at 6:30am
... • Formation time is the collapse time of the cluster, which is very short. ...
... • Formation time is the collapse time of the cluster, which is very short. ...
Sample Midterm - IUPUI Physics
... Note: It is possible for a question to have more than one correct answer. You just have to pick one of the possible correct answers if that happens. 1) What is the remnant of a star twice the mass of our sun at the end of its lifetime? A) White Dwarf B) Neutron Star C) Black Hole D) Nothing (it comp ...
... Note: It is possible for a question to have more than one correct answer. You just have to pick one of the possible correct answers if that happens. 1) What is the remnant of a star twice the mass of our sun at the end of its lifetime? A) White Dwarf B) Neutron Star C) Black Hole D) Nothing (it comp ...
Testing Your Sky
... a hindrance when it comes to observing the night. Under brightly lit conditions you'll not be able to view the fainter objects of the night. What follows is an exercise for determining darkness of the sky, a condition that might affect your viewing. Be sure to make the observation only after your ey ...
... a hindrance when it comes to observing the night. Under brightly lit conditions you'll not be able to view the fainter objects of the night. What follows is an exercise for determining darkness of the sky, a condition that might affect your viewing. Be sure to make the observation only after your ey ...
Module 6: “The Message of Starlight Assignment 9: Parallax, stellar
... At this point there is no way to avoid the units that astronomers use: we have mentioned magnitude already, which is a brightness scale in which very bright stars are roughly magnitude 0, faint stars are magnitude 5, and really faint stars have larger and larger magnitudes. These are further divide ...
... At this point there is no way to avoid the units that astronomers use: we have mentioned magnitude already, which is a brightness scale in which very bright stars are roughly magnitude 0, faint stars are magnitude 5, and really faint stars have larger and larger magnitudes. These are further divide ...
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 13
... 2. A pulsating variable star has a period of 10 days. About how many times more luminous is it than the Sun? Refer to Fig. 15.12 in the textbook. It is about 3000 times more luminous than the Sun. Once you know the star’s luminosity L, you can calculate its distance r from the measured apparent bri ...
... 2. A pulsating variable star has a period of 10 days. About how many times more luminous is it than the Sun? Refer to Fig. 15.12 in the textbook. It is about 3000 times more luminous than the Sun. Once you know the star’s luminosity L, you can calculate its distance r from the measured apparent bri ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... How do spiral galaxies form? A protogalactic cloud forms a disk because of available gas. For this to happen, the cloud must not be so dense that stars quickly form. The disk is formed because of conservation of angular momentum. The spiral arms form when gas clouds are squeezed, trigging star forma ...
... How do spiral galaxies form? A protogalactic cloud forms a disk because of available gas. For this to happen, the cloud must not be so dense that stars quickly form. The disk is formed because of conservation of angular momentum. The spiral arms form when gas clouds are squeezed, trigging star forma ...
Evolution of Stars and Galaxies
... Unusual: Sun is not part of a multiple star system or cluster (only 1 star near us!) ...
... Unusual: Sun is not part of a multiple star system or cluster (only 1 star near us!) ...
Summary: Nuclear burning in stars
... • Spiral arms have higher density than space between arms • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
... • Spiral arms have higher density than space between arms • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
What`s Up - April 2016
... name meaning the ‘solitary one’, as there are no other bright stars near it. At about 40 times the diameter of the sun and 400 times as bright, Alphard is one of the ‘bright giants’ in our neighbourhood. But our ‘neighbourhood’ is rather large. Alphard is 11 million times as far away from us as our ...
... name meaning the ‘solitary one’, as there are no other bright stars near it. At about 40 times the diameter of the sun and 400 times as bright, Alphard is one of the ‘bright giants’ in our neighbourhood. But our ‘neighbourhood’ is rather large. Alphard is 11 million times as far away from us as our ...
Lecture 11 - Stars and Atomic Spectra
... • Up to now, we have been discussing the wavelength of light as determining it color • However, light comes in discrete packets called photons and the energy of each photon is set by its color or wavelength • From Einstein, we known that the photon energy is inversely proportional to its wavelength ...
... • Up to now, we have been discussing the wavelength of light as determining it color • However, light comes in discrete packets called photons and the energy of each photon is set by its color or wavelength • From Einstein, we known that the photon energy is inversely proportional to its wavelength ...
Prep/Review Questions - Faculty Web Sites at the University
... Mark the location on the Earth where people are now experiencing sunset. For these observers, which object, the Moon or Mars, will rise first above the eastern horizon? Draw in on the diagram an arrowhead to show the direction in which the Earth is moving around the Sun. Mark the approximate positio ...
... Mark the location on the Earth where people are now experiencing sunset. For these observers, which object, the Moon or Mars, will rise first above the eastern horizon? Draw in on the diagram an arrowhead to show the direction in which the Earth is moving around the Sun. Mark the approximate positio ...
Summer 2001 Day 07: Intro to Solar System
... circle (i.e. within the confines of this building), the NEAREST next star would be in CORTLAND! (3) A parsec is real big! (4) Miles – km analogy Practice Problem #1 & #2 2) Proper Motion and Radial Velocity A) Stars are not truly fixed in the sky, but move in two ways B) Towards or away from the Sun ...
... circle (i.e. within the confines of this building), the NEAREST next star would be in CORTLAND! (3) A parsec is real big! (4) Miles – km analogy Practice Problem #1 & #2 2) Proper Motion and Radial Velocity A) Stars are not truly fixed in the sky, but move in two ways B) Towards or away from the Sun ...
ASTRONOMY 130
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
and Concept Self-test (1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9)
... Moves 10 arc seconds per year! Only a few stars move even 1 arc second per year; yet, over the course of your lifetime, it will barely move one ...
... Moves 10 arc seconds per year! Only a few stars move even 1 arc second per year; yet, over the course of your lifetime, it will barely move one ...
binary star
... A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature • Color is a clue to a star’s temperature. ...
... A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature • Color is a clue to a star’s temperature. ...
The Milky Way – A Classic Galaxy
... telescope in the 1920’s to image The Andromeda Nebula • Could see the brightest individual stars. Among them, variables of the right color and light variation to show them as Cepheids • Therefore, this was not a nearby nebula around a new star, it was an entire galaxy. • Herschel’s map then could be ...
... telescope in the 1920’s to image The Andromeda Nebula • Could see the brightest individual stars. Among them, variables of the right color and light variation to show them as Cepheids • Therefore, this was not a nearby nebula around a new star, it was an entire galaxy. • Herschel’s map then could be ...
The Big Dipper Constellation
... The Big Dipper What is a Constellation? From very early times, man has been fascinated by the stars. Early stargazers began naming stars. They also noticed patterns of stars that appeared night after night in the sky. These patterns or groupings of stars are called constellations. They also began to ...
... The Big Dipper What is a Constellation? From very early times, man has been fascinated by the stars. Early stargazers began naming stars. They also noticed patterns of stars that appeared night after night in the sky. These patterns or groupings of stars are called constellations. They also began to ...
Comet Lulin - indstate.edu
... Since Comet Lulin will be moving opposite the motion of the Earth, it will appear to approach us and move away especially fast. Beginning in February 2009, Comet Lulin will rise at about midnight local time, and will be about 6th or 7th magnitude. This won't be bright enough to go out and look at ...
... Since Comet Lulin will be moving opposite the motion of the Earth, it will appear to approach us and move away especially fast. Beginning in February 2009, Comet Lulin will rise at about midnight local time, and will be about 6th or 7th magnitude. This won't be bright enough to go out and look at ...
Document
... system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the faint star of an an unresolved binary system comprising a K ...
... system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the faint star of an an unresolved binary system comprising a K ...
STAAR Review – Week Ten
... a. Stars with greater magnitudes tend to have lower temperatures. b. Stars with greater masses tend to have lower temperatures. c. Stars with greater magnitudes tend to have higher temperatures. d. Stars with greater temperatures tend to have lower magnitudes. 19. What do our Sun and the star Vega h ...
... a. Stars with greater magnitudes tend to have lower temperatures. b. Stars with greater masses tend to have lower temperatures. c. Stars with greater magnitudes tend to have higher temperatures. d. Stars with greater temperatures tend to have lower magnitudes. 19. What do our Sun and the star Vega h ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.