star
... Contains two (or sometimes more) stars which orbit around their common center of mass. Importance - only when a star is in a binary system that we have the possibility of deriving its true mass. The period – watching the system for many years. The more unequal the masses are, the The distance betwe ...
... Contains two (or sometimes more) stars which orbit around their common center of mass. Importance - only when a star is in a binary system that we have the possibility of deriving its true mass. The period – watching the system for many years. The more unequal the masses are, the The distance betwe ...
Signs of the Zodiac: Capricorn
... Secunda Giedi (Alpha-2 Capricorni), which are separated by 0.11 degrees in the sky. Nashira γ Capricorni (Gamma Capricorni) is a blue-white A-type giant, approximately 139 light years distant. Its name is derived from the Arabic phrase for “bearer of good news.” It has an apparent magnitude of 3.69 ...
... Secunda Giedi (Alpha-2 Capricorni), which are separated by 0.11 degrees in the sky. Nashira γ Capricorni (Gamma Capricorni) is a blue-white A-type giant, approximately 139 light years distant. Its name is derived from the Arabic phrase for “bearer of good news.” It has an apparent magnitude of 3.69 ...
What have we learned?
... • What are the three major types of galaxies? – The major types are spiral galaxies, elliptical galaxies, and irregular galaxies. – Spirals have both disk and spheroidal components; ellipticals have no disk. ...
... • What are the three major types of galaxies? – The major types are spiral galaxies, elliptical galaxies, and irregular galaxies. – Spirals have both disk and spheroidal components; ellipticals have no disk. ...
Study Island
... climate. He waters them more often, but they do not improve. Which of the following scientific questions should he ask next to find out what is wrong with his roses? A. Which rose bush has larger, more colorful blooms? B. Does temperature affect the growth of the rose bushes? C. How much do rose bus ...
... climate. He waters them more often, but they do not improve. Which of the following scientific questions should he ask next to find out what is wrong with his roses? A. Which rose bush has larger, more colorful blooms? B. Does temperature affect the growth of the rose bushes? C. How much do rose bus ...
The winter sky over Bosham
... In the southeast sky in the early evening is the hourglass shape of Orion, the hunter, one of the most recognisable constellations in the night sky. Unlike most constellations, which are mostly random groupings of stars that happen to appear together in the sky, the stars of Orion are almost all rel ...
... In the southeast sky in the early evening is the hourglass shape of Orion, the hunter, one of the most recognisable constellations in the night sky. Unlike most constellations, which are mostly random groupings of stars that happen to appear together in the sky, the stars of Orion are almost all rel ...
Introduction to Stars ppt
... M-Sun star has 30 times more H than the Sun, but burns it with a luminosity that is 30,000 times greater. It’s lifetime is 30/30,000 = 1/10,000 as long as the Sun – corresponding to a lifetime of only a few million years. This is a very short time, cosmically speaking. This is one reason why massive ...
... M-Sun star has 30 times more H than the Sun, but burns it with a luminosity that is 30,000 times greater. It’s lifetime is 30/30,000 = 1/10,000 as long as the Sun – corresponding to a lifetime of only a few million years. This is a very short time, cosmically speaking. This is one reason why massive ...
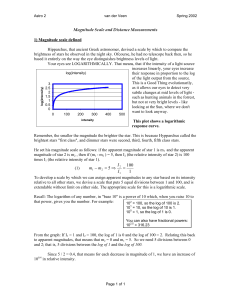
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... Hipparchus, that ancient Greek astronomer, devised a scale by which to compare the brightness of stars he observed in the night sky. Ofcourse, he had no telescope back then, so he based it entirely on the way the eye distinguishes brightness levels of light. Your eyes see LOGARITHMICALLY. That means ...
... Hipparchus, that ancient Greek astronomer, devised a scale by which to compare the brightness of stars he observed in the night sky. Ofcourse, he had no telescope back then, so he based it entirely on the way the eye distinguishes brightness levels of light. Your eyes see LOGARITHMICALLY. That means ...
LESSON 4, STARS
... form pictures, as we look at them from Earth. If we looked at the same stars from outside our ...
... form pictures, as we look at them from Earth. If we looked at the same stars from outside our ...
The Night Sky
... Annual motion of the stars The same stars are not visible all year long. Any given non-circumpolar star will set 4 minutes early each day until it becomes lost in the glare of the setting Sun. ...
... Annual motion of the stars The same stars are not visible all year long. Any given non-circumpolar star will set 4 minutes early each day until it becomes lost in the glare of the setting Sun. ...
HW #4 (due March 27)
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
TYPES OF STARS
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
HW6 due - Yale Astronomy
... The sun will collide with another star of the same size (radius = 1 Rsun) if it comes within a distance of 2Rsun of that star. (Their edges will just touch if they come within a distance ...
... The sun will collide with another star of the same size (radius = 1 Rsun) if it comes within a distance of 2Rsun of that star. (Their edges will just touch if they come within a distance ...
~Crowfoot
... a) arises from the Balmer γ transition. b) is due to preferential scattering of blue light as in Earth’s sky. c) is the light from an embedded blue star. 3)2 The “Pillars of Creation” on this image Eagle Nebula a) show the destruction of a nebula by a supernova explosion b) are the jets from a young ...
... a) arises from the Balmer γ transition. b) is due to preferential scattering of blue light as in Earth’s sky. c) is the light from an embedded blue star. 3)2 The “Pillars of Creation” on this image Eagle Nebula a) show the destruction of a nebula by a supernova explosion b) are the jets from a young ...
Lesson Plan - ScienceA2Z.com
... The International Astronomical Union (IAU) divides the sky into 88 official constellations with exact boundaries, so that every direction or place in the sky belongs within one constellation. In the northern hemisphere, these are mostly based upon the constellations of the ancient Greek tradition, p ...
... The International Astronomical Union (IAU) divides the sky into 88 official constellations with exact boundaries, so that every direction or place in the sky belongs within one constellation. In the northern hemisphere, these are mostly based upon the constellations of the ancient Greek tradition, p ...
The Family of Stars
... more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the flux received from star A is 5 times less than from star B, so star A ...
... more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the flux received from star A is 5 times less than from star B, so star A ...
Dim Stars - granthamkuehl
... In our study of Stars The students will be able to Determine color, temp., brightness and Size of a star And show what they learned by Interpreting the HR Diagram ...
... In our study of Stars The students will be able to Determine color, temp., brightness and Size of a star And show what they learned by Interpreting the HR Diagram ...
Announcements Evolution of High-Mass Stars: Red Supergiants
... measure distances to stars. • Parallax only works for nearby stars (within ...
... measure distances to stars. • Parallax only works for nearby stars (within ...
Astr604-Ch1
... 1.2.3 Masses and radii of stars The mass of a star can be measured only by its gravitational effect. Under certain conditions, the mass of star that is member of a binary system can calculate based on spectral line shifts. The radii of a number of stars have been found directly from measurement of t ...
... 1.2.3 Masses and radii of stars The mass of a star can be measured only by its gravitational effect. Under certain conditions, the mass of star that is member of a binary system can calculate based on spectral line shifts. The radii of a number of stars have been found directly from measurement of t ...
July - astra
... well liked for its blue & gold colors. Ptolemaeus magnitude +11. The second closest star visible to Alphonsus the naked eye is Sirius at 8.6 ly followed by Epsilon Moon (e) Eridani at 10.5 ly and Procyon at 11.4 ly. There Tycho Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer ...
... well liked for its blue & gold colors. Ptolemaeus magnitude +11. The second closest star visible to Alphonsus the naked eye is Sirius at 8.6 ly followed by Epsilon Moon (e) Eridani at 10.5 ly and Procyon at 11.4 ly. There Tycho Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer ...
Part 1
... Measuring Brightness: History • Photometry - the measure of brightness • Hipparchus (150 B.C.) – catalog of 1000 stars – included position & brightness – Magnitude = brightness • brightest stars were first magnitude • faintest stars were sixth magnitude • estimated by eye (logarithmic response) ...
... Measuring Brightness: History • Photometry - the measure of brightness • Hipparchus (150 B.C.) – catalog of 1000 stars – included position & brightness – Magnitude = brightness • brightest stars were first magnitude • faintest stars were sixth magnitude • estimated by eye (logarithmic response) ...
Stars Study Guide KEY
... *7. Which stars live the longest, high-mass or low-mass? Low Mass Stars live longer. Why? They have less self-gravity which means they burn through their fuel slower. 8. What will happen to our star, the Sun, at the end of its life? The sun will expand in the Red Giant phase, then will release its o ...
... *7. Which stars live the longest, high-mass or low-mass? Low Mass Stars live longer. Why? They have less self-gravity which means they burn through their fuel slower. 8. What will happen to our star, the Sun, at the end of its life? The sun will expand in the Red Giant phase, then will release its o ...
Way Milky the MAPPING
... whether the bulge “puffed up all at once or slowly.” Understanding the distributions of speed, direction, and velocity of the stars in the bar and the bulge might help determine the galaxy’s evolution. “One of the predictions of my model is that there is a sharp difference in the velocity distributi ...
... whether the bulge “puffed up all at once or slowly.” Understanding the distributions of speed, direction, and velocity of the stars in the bar and the bulge might help determine the galaxy’s evolution. “One of the predictions of my model is that there is a sharp difference in the velocity distributi ...
Nov 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... well liked for its blue & gold colors. Ptolemaeus magnitude +11. The second closest star visible to Alphonsus the naked eye is Sirius at 8.6 ly followed by Epsilon Moon (e) Eridani at 10.5 ly and Procyon at 11.4 ly. There Tycho Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer ...
... well liked for its blue & gold colors. Ptolemaeus magnitude +11. The second closest star visible to Alphonsus the naked eye is Sirius at 8.6 ly followed by Epsilon Moon (e) Eridani at 10.5 ly and Procyon at 11.4 ly. There Tycho Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer ...
Stars and Constellations Power Point
... •Black holes of stellar mass are expected to form when very massive stars collapse at the end of their life cycle. •After a black hole has formed it can continue to grow by absorbing mass from its surroundings. •There is general consensus that supermassive black holes exist in the centers of most ga ...
... •Black holes of stellar mass are expected to form when very massive stars collapse at the end of their life cycle. •After a black hole has formed it can continue to grow by absorbing mass from its surroundings. •There is general consensus that supermassive black holes exist in the centers of most ga ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.