Astronomy of the Northern Sky—
... The Cat’s Eye Nebulae, NGC 6543, in Draco is among the brightest anywhere, magnitude 8.1 (17:59 +66º 38’). On the way from β to γ Ursa Majoris (and slightly outside this line which makes the bottom of the Big Dipper’s Bowl), near the point of a thin north-pointing triangle, is the Owl Nebula, M97, a ...
... The Cat’s Eye Nebulae, NGC 6543, in Draco is among the brightest anywhere, magnitude 8.1 (17:59 +66º 38’). On the way from β to γ Ursa Majoris (and slightly outside this line which makes the bottom of the Big Dipper’s Bowl), near the point of a thin north-pointing triangle, is the Owl Nebula, M97, a ...
Properties of Stars - Mr. Carter`s Earth
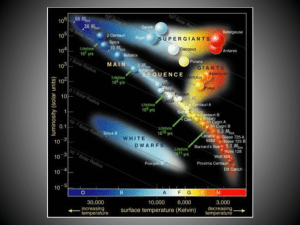
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
galaxy_physics
... Quasar and Galaxy Evolution • Quasar/Starburst/Galaxy evolution related ? • Major mergers – Extreme star formation rates – Elliptical/bulge formation – BH formation and feeding = QSO ...
... Quasar and Galaxy Evolution • Quasar/Starburst/Galaxy evolution related ? • Major mergers – Extreme star formation rates – Elliptical/bulge formation – BH formation and feeding = QSO ...
Branches of Earth Science Tools Used to Study Stars Constellations
... o SPECTRUM: the band of colors that forms as light passes through a prism o Used to see if galaxies are moving away or toward the earth Telescopes: device that makes distant objects appear closer Types of Telescopes o Optical o Radio o X-Ray o U-V o Infrared ...
... o SPECTRUM: the band of colors that forms as light passes through a prism o Used to see if galaxies are moving away or toward the earth Telescopes: device that makes distant objects appear closer Types of Telescopes o Optical o Radio o X-Ray o U-V o Infrared ...
Lecture02-ASTA01 - University of Toronto
... Asterisms • In addition to the 88 official constellations, the sky contains a number of less formally defined groupings known as asterisms. • For example, the Big Dipper is an asterism you probably recognize that is part of the constellation Ursa Major (the Great Bear) ...
... Asterisms • In addition to the 88 official constellations, the sky contains a number of less formally defined groupings known as asterisms. • For example, the Big Dipper is an asterism you probably recognize that is part of the constellation Ursa Major (the Great Bear) ...
Astrological Forecasts: 1999-2000
... The constellation of Krittika runs in the sidereal zodiac from 26° 40’ Aries up to 10° Taurus. It becomes activated especially when major outer planets transit through its territory. The symbol for Krittika is the razor, and that which burns. It is capable of cutting off what was previously consider ...
... The constellation of Krittika runs in the sidereal zodiac from 26° 40’ Aries up to 10° Taurus. It becomes activated especially when major outer planets transit through its territory. The symbol for Krittika is the razor, and that which burns. It is capable of cutting off what was previously consider ...
TYPES OF STARS
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. How do they make sense of all these stars? The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines (cal ...
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. How do they make sense of all these stars? The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines (cal ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
... is that Sirius is actually a double star. Sirius B is a challenging target, just 5" from Sirius and quite dim at Mag 8.5. It requires excellent optics but, if you can nail it, it's surely a feather in your cap. A little to the west of Sirius is a three star asterism, with the central star, V1, being ...
... is that Sirius is actually a double star. Sirius B is a challenging target, just 5" from Sirius and quite dim at Mag 8.5. It requires excellent optics but, if you can nail it, it's surely a feather in your cap. A little to the west of Sirius is a three star asterism, with the central star, V1, being ...
Conceptobasico.pdf
... The star closest to this point, Polaris, is often called the North Star. A similar extension from the South Pole marks the South Celestial Pole. The Celestial Equator is the projection of the Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere. All points along the celestial equator are equidistant from the n ...
... The star closest to this point, Polaris, is often called the North Star. A similar extension from the South Pole marks the South Celestial Pole. The Celestial Equator is the projection of the Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere. All points along the celestial equator are equidistant from the n ...
Conceptual Physics
... 3. In a random sample of stars in the Sun’s neighborhood, you would expect about 90% of them: a. To be red giants b. To be white dwarfs c. To be main sequence stars d. To have just been born e. To be older than the Sun 4. A star near the top of the main sequence has a mass about: a. Twice the Sun’s ...
... 3. In a random sample of stars in the Sun’s neighborhood, you would expect about 90% of them: a. To be red giants b. To be white dwarfs c. To be main sequence stars d. To have just been born e. To be older than the Sun 4. A star near the top of the main sequence has a mass about: a. Twice the Sun’s ...
August Newsletter
... of the most spectacular and well-known objects in the sky. The centre of our Milky Way galaxy is located in the direction of Sagittarius and because of this Sagittarius contains more deep sky objects than any other constellation. There are no less than 15 Messier objects found in this constellation, ...
... of the most spectacular and well-known objects in the sky. The centre of our Milky Way galaxy is located in the direction of Sagittarius and because of this Sagittarius contains more deep sky objects than any other constellation. There are no less than 15 Messier objects found in this constellation, ...
Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics
... Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and brightness. ...
... Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and brightness. ...
The Milky Way
... the fastest speed there is. So remember, when you're feeling very small and insecure, How amazingly unlikely is your birth, And pray that there's intelligent life somewhere up in space, 'Cause there's bugger all down here on Earth. ...
... the fastest speed there is. So remember, when you're feeling very small and insecure, How amazingly unlikely is your birth, And pray that there's intelligent life somewhere up in space, 'Cause there's bugger all down here on Earth. ...
Galaxies
... Stars are grouped in clusters and galaxies Galaxies are grouped in clusters. Even clusters of galaxies are ...
... Stars are grouped in clusters and galaxies Galaxies are grouped in clusters. Even clusters of galaxies are ...
Citizen Sky Epsilon Aurigae Script for Fulldome Planetariums
... Our own solar system may have formed from a disk similar to this. What can Epsilon Aurigae teach us about our own origins? To answer our questions, we need more observations. From a distance, we cannot see the details of the Epsilon Aurigae system. Instead, it reveals itself as only a single point o ...
... Our own solar system may have formed from a disk similar to this. What can Epsilon Aurigae teach us about our own origins? To answer our questions, we need more observations. From a distance, we cannot see the details of the Epsilon Aurigae system. Instead, it reveals itself as only a single point o ...
Signs of the Zodiac, Cancer
... Cancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as such. Its astrological symbol is . Cancer is relatively small among the constellations with an area of only 505 square degrees and its stars are rather faint; in fact it is the dimm ...
... Cancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as such. Its astrological symbol is . Cancer is relatively small among the constellations with an area of only 505 square degrees and its stars are rather faint; in fact it is the dimm ...
celestial equator
... If we draw a line from the zenith through a celestial object and extend that line to the horizon, we obtain the azimuth angle of the object. By convention, the north point on the horizon has azimuth 0 degrees, the east point has azimuth 90 degrees, the south point has azimuth 180 degrees, and the w ...
... If we draw a line from the zenith through a celestial object and extend that line to the horizon, we obtain the azimuth angle of the object. By convention, the north point on the horizon has azimuth 0 degrees, the east point has azimuth 90 degrees, the south point has azimuth 180 degrees, and the w ...
Today`s Class: Measuring temperatures of stars Astronomer`s
... Absorption lines in star’s spectrum tell us ionization level ...
... Absorption lines in star’s spectrum tell us ionization level ...
Constellations - Mayo Dark Sky Park
... knows what stories are ancestors here created when they saw this giant in the night sky? Let your imagination wander as you learn about the patterns of stars forming constellations and the legends and myths that have been attached to them over thousands of years. ...
... knows what stories are ancestors here created when they saw this giant in the night sky? Let your imagination wander as you learn about the patterns of stars forming constellations and the legends and myths that have been attached to them over thousands of years. ...
Background Information - Eu-Hou
... temperature of a star and its luminosity. If all stars were alike, those with the same luminosity would have equal temperature and hotter stars would be brighter than cooler ones. In 1911, Ejnar Hertzsprung (Denmark), plotted a graph of star’s magnitudes against their colour. Independently in 1913, ...
... temperature of a star and its luminosity. If all stars were alike, those with the same luminosity would have equal temperature and hotter stars would be brighter than cooler ones. In 1911, Ejnar Hertzsprung (Denmark), plotted a graph of star’s magnitudes against their colour. Independently in 1913, ...
ref H-R Spectral types
... weaker still, neutral metal dominant lines most ionised prominent Calcium lines ...
... weaker still, neutral metal dominant lines most ionised prominent Calcium lines ...
- National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... 1496 was found to lie at a distance of 1.4 x 103 parsecs (4600 light years) from Earth. In addition, the cluster, which contains no evident spectral class O or B stars, is approximately 400 million years old. INTRODUCTION An open cluster is a group of gravitationally-bound stars that formed in a sin ...
... 1496 was found to lie at a distance of 1.4 x 103 parsecs (4600 light years) from Earth. In addition, the cluster, which contains no evident spectral class O or B stars, is approximately 400 million years old. INTRODUCTION An open cluster is a group of gravitationally-bound stars that formed in a sin ...
PDF version (two pages, including the full text)
... Alphard, heart of the serpent, high in the northwest. Above and to the left of the Crow, for an observer facing east, is the Cup. Alphard is an Arabic name meaning the ‘solitary one’, as there are no other bright stars near it. At about 40 times the diameter of the sun and 400 times as bright, Alpha ...
... Alphard, heart of the serpent, high in the northwest. Above and to the left of the Crow, for an observer facing east, is the Cup. Alphard is an Arabic name meaning the ‘solitary one’, as there are no other bright stars near it. At about 40 times the diameter of the sun and 400 times as bright, Alpha ...
star
... Contains two (or sometimes more) stars which orbit around their common center of mass. Importance - only when a star is in a binary system that we have the possibility of deriving its true mass. The period – watching the system for many years. The more unequal the masses are, the The distance betwe ...
... Contains two (or sometimes more) stars which orbit around their common center of mass. Importance - only when a star is in a binary system that we have the possibility of deriving its true mass. The period – watching the system for many years. The more unequal the masses are, the The distance betwe ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.