PHYS 175 (2014) Final Examination Name: ___SOLUTION_____
... 11. When hydrogen fusion in the core of the Sun ends, the Sun will move off the main sequence. As a result, the surface temperature of the Sun will ______ and the diameter of the Sun will ______. ...
... 11. When hydrogen fusion in the core of the Sun ends, the Sun will move off the main sequence. As a result, the surface temperature of the Sun will ______ and the diameter of the Sun will ______. ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 13. (2 pts.) In the TV show Star Trek, the fastest the Enterprise can travel is warp 9 (1516 times the speed of light). How long would it take to travel from one end of the galaxy to the other moving at warp 9? What about from our solar system to the Galactic center? (Express your answers in the mos ...
... 13. (2 pts.) In the TV show Star Trek, the fastest the Enterprise can travel is warp 9 (1516 times the speed of light). How long would it take to travel from one end of the galaxy to the other moving at warp 9? What about from our solar system to the Galactic center? (Express your answers in the mos ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Shapley’s model Globular clusters must orbit around the center of mass of the galaxy! Thus, assuming the clusters are distributed uniformly around the galaxy, he measured the 3D distribution of clusters (using Cepheid variables) and then assumed that the center of that distribution was where the cen ...
... Shapley’s model Globular clusters must orbit around the center of mass of the galaxy! Thus, assuming the clusters are distributed uniformly around the galaxy, he measured the 3D distribution of clusters (using Cepheid variables) and then assumed that the center of that distribution was where the cen ...
Document
... structure, some nebulae might actually be entire separate galaxies or island universes 1774-1781 - Messier catalog compiled (109 objects in Northern sky) including Andromeda galaxy - M31 ...
... structure, some nebulae might actually be entire separate galaxies or island universes 1774-1781 - Messier catalog compiled (109 objects in Northern sky) including Andromeda galaxy - M31 ...
Chapter 16 - "The Universe"
... 500 million years. • The red giant has helium fusion reactions occurring in the core and hydrogen fusion reactions occurring in the shell. • The radius and luminosity decrease and the star moves backward to a main sequence star. ...
... 500 million years. • The red giant has helium fusion reactions occurring in the core and hydrogen fusion reactions occurring in the shell. • The radius and luminosity decrease and the star moves backward to a main sequence star. ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
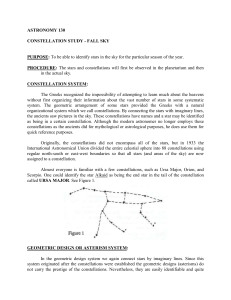
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
Lesson 4, Stars
... viewed from two locations is called parallax. Astronomers use parallax to find the distance ...
... viewed from two locations is called parallax. Astronomers use parallax to find the distance ...
Characteristics of Stars
... nuclear fusion is happening at their cores… they create their own light • Have different characteristics which allow many different ‘varieties’ of stars to exist ...
... nuclear fusion is happening at their cores… they create their own light • Have different characteristics which allow many different ‘varieties’ of stars to exist ...
PowerPoint
... Some Reasons for the great abundance of Low-Mass stars… 1) Obviously requires less material to make (many!) Low-Mass Stars, than High-Mass ones; 2) Even though High-Mass stars have more “fuel” (Hydrogen)… ...
... Some Reasons for the great abundance of Low-Mass stars… 1) Obviously requires less material to make (many!) Low-Mass Stars, than High-Mass ones; 2) Even though High-Mass stars have more “fuel” (Hydrogen)… ...
chapter8
... intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): L ...
... intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): L ...
AstrologicalPredicti.. - Saptarishis Astrology
... early degree of Sagittarius and the last degree of Scorpio. The nodes travel backwards and around the time close to the eclipses they remain around the same degree for 3-4 months. This is occurring now around the area of 0 degrees of Sagittarius and 29 Scorpio. There is indecision between these two ...
... early degree of Sagittarius and the last degree of Scorpio. The nodes travel backwards and around the time close to the eclipses they remain around the same degree for 3-4 months. This is occurring now around the area of 0 degrees of Sagittarius and 29 Scorpio. There is indecision between these two ...
AstrologicalPredicti.. - Saptarishis Astrology
... early degree of Sagittarius and the last degree of Scorpio. The nodes travel backwards and around the time close to the eclipses they remain around the same degree for 3-4 months. This is occurring now around the area of 0 degrees of Sagittarius and 29 Scorpio. There is indecision between these two ...
... early degree of Sagittarius and the last degree of Scorpio. The nodes travel backwards and around the time close to the eclipses they remain around the same degree for 3-4 months. This is occurring now around the area of 0 degrees of Sagittarius and 29 Scorpio. There is indecision between these two ...
neutron star - Livonia Public Schools
... • A white dwarf is a star that has exhausted most or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size, believed to be near its final stage of evolution. • The sun begins as a nebula, spends much of its life as a main-sequence star, and then becomes a red giant, a planetary nebula, a wh ...
... • A white dwarf is a star that has exhausted most or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size, believed to be near its final stage of evolution. • The sun begins as a nebula, spends much of its life as a main-sequence star, and then becomes a red giant, a planetary nebula, a wh ...
08 September: How far away are the closest stars?
... Arcturus … 36 light years Vega … 26 light years Altair … 17 light years Beta Canum Venaticorum .. 27 light years (a star like the Sun) • Lambda Serpentis … 38 light years (***) • 72 Herculis … 47 light years (***) • 18 Scorpii … 46 light years (the “Solar Twin”) ...
... Arcturus … 36 light years Vega … 26 light years Altair … 17 light years Beta Canum Venaticorum .. 27 light years (a star like the Sun) • Lambda Serpentis … 38 light years (***) • 72 Herculis … 47 light years (***) • 18 Scorpii … 46 light years (the “Solar Twin”) ...
Lecture notes -- pdf file - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... in 1838 (Friedrich Bessel) • Closest star is Alpha Centauri, p=0.75 arcseconds, d=1.33 parsecs= 4.35 light years • Nearest stars are a few to many parsecs, 5 - 20 light years ...
... in 1838 (Friedrich Bessel) • Closest star is Alpha Centauri, p=0.75 arcseconds, d=1.33 parsecs= 4.35 light years • Nearest stars are a few to many parsecs, 5 - 20 light years ...
Chapter 9 “The Family of Stars “
... No, the parallax of the star is never measured. The first step in determining the distance to a star using spectroscopic parallax is to obtain a spectrum of the star from which its spectral type and luminosity class can be determined. The absorption lines that are present can be used to determine th ...
... No, the parallax of the star is never measured. The first step in determining the distance to a star using spectroscopic parallax is to obtain a spectrum of the star from which its spectral type and luminosity class can be determined. The absorption lines that are present can be used to determine th ...
The Life of a Star - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster • A stellar association is a group ...
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster • A stellar association is a group ...
May 2017 - Museums Wellington
... constellation of Virgo, and below, just above the horizon is orange coloured Arcturus, the brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere and the 4th brightest in the night sky. Arcturus has a similar mass to the Sun, but has already expanded to become a red giant, with 25 times the diameter an ...
... constellation of Virgo, and below, just above the horizon is orange coloured Arcturus, the brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere and the 4th brightest in the night sky. Arcturus has a similar mass to the Sun, but has already expanded to become a red giant, with 25 times the diameter an ...
Astronomy Webquest _2 STARS
... From Earth, there are a number of things that we can observe about stars. One of the easiest things to measure is the star's brightness, or magnitude. There are a number of things that make stars appear brighter on Earth. One factor is the distance between Earth and the star. Even though our sun is ...
... From Earth, there are a number of things that we can observe about stars. One of the easiest things to measure is the star's brightness, or magnitude. There are a number of things that make stars appear brighter on Earth. One factor is the distance between Earth and the star. Even though our sun is ...
Properties of Stars
... Some stars are just being born in their nebulas. Some have turned into black holes or supergiants, etc. If you graph all of the stars in our universe according to their brightness (absolute magnitude) and their temperature, they all fit into specific places on the graph based on what type of star th ...
... Some stars are just being born in their nebulas. Some have turned into black holes or supergiants, etc. If you graph all of the stars in our universe according to their brightness (absolute magnitude) and their temperature, they all fit into specific places on the graph based on what type of star th ...
Finding Constellations From Orion
... The second constellation that El Nath belongs to is Taurus (TOR-us), the Bull. Taurus is easily located by following a line from Betelgeuse through Orion’s head. This takes you to the eye of the Bull, Aldebaran (al-DEB-a-ron), the 14th brightest star. The Hyades, a V-shaped cluster of bout 200 stars ...
... The second constellation that El Nath belongs to is Taurus (TOR-us), the Bull. Taurus is easily located by following a line from Betelgeuse through Orion’s head. This takes you to the eye of the Bull, Aldebaran (al-DEB-a-ron), the 14th brightest star. The Hyades, a V-shaped cluster of bout 200 stars ...
Order of Magnitude Icebreaker
... ★ Use your physical intuition, not google! ★ Remember: Multiple approaches possible! ...
... ★ Use your physical intuition, not google! ★ Remember: Multiple approaches possible! ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.