Universe and Star Formation - White Plains Public Schools
... AIM: Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for Ancient characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature • Color is a clue to a star’s Temperature. Red is Cooler…………….Blue – Hotter Yellow to White – in ...
... AIM: Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for Ancient characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature • Color is a clue to a star’s Temperature. Red is Cooler…………….Blue – Hotter Yellow to White – in ...
Krupp (1999) broadly defines the interdisciplinary field
... brightest corresponds to smaller numbers.) However, these conditions rarely exist on Rapa Nui, even in pre-historic times. It seems unlikely that magnitude 5 and 6 stars would have been rendered, without especially compelling reasons for doing so. One documented exception to this is aboriginal peopl ...
... brightest corresponds to smaller numbers.) However, these conditions rarely exist on Rapa Nui, even in pre-historic times. It seems unlikely that magnitude 5 and 6 stars would have been rendered, without especially compelling reasons for doing so. One documented exception to this is aboriginal peopl ...
The Night Sky This Month - Usk Astronomical Society
... legs and seat of his throne make a rough square, which at this time looks like an upside down house (or throne); the back of the seat comes to a point. As legend suggests, Cepheus is a fairly innocuous constellation and its brightest star, Alderamin, has a magnitude of only 2.4. The name seems to de ...
... legs and seat of his throne make a rough square, which at this time looks like an upside down house (or throne); the back of the seat comes to a point. As legend suggests, Cepheus is a fairly innocuous constellation and its brightest star, Alderamin, has a magnitude of only 2.4. The name seems to de ...
Lecture 24 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightness from the sun at '-26' magnitude to the faintest objects seen a ...
... from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightness from the sun at '-26' magnitude to the faintest objects seen a ...
Astrophysics
... Certain spectral lines appeared consistently at certain temperatures and disappeared at others Different lines appear with different degrees of ionisation – which results from different temperatures ...
... Certain spectral lines appeared consistently at certain temperatures and disappeared at others Different lines appear with different degrees of ionisation – which results from different temperatures ...
Astronomy Power Point
... Brightness of stars • Brightness = the amount of light stars give off – This depends on its size and temperature – How bright it looks from Earth depends on distance and actual brightness • Apparent magnitude • Absolute magnitude ...
... Brightness of stars • Brightness = the amount of light stars give off – This depends on its size and temperature – How bright it looks from Earth depends on distance and actual brightness • Apparent magnitude • Absolute magnitude ...
powerpoint - Physics @ IUPUI
... period of pulsation and their absolute brightness. • The longer the period, the bigger the star is, and the brighter it is (sort of like a bigger bell has a larger period of vibration). • This allows us to measure distances (especially since these are very bright stars which can be seen a LONG dista ...
... period of pulsation and their absolute brightness. • The longer the period, the bigger the star is, and the brighter it is (sort of like a bigger bell has a larger period of vibration). • This allows us to measure distances (especially since these are very bright stars which can be seen a LONG dista ...
here in Powerpoint format
... bA is the apparent brightness of star A bB is the apparent brightness of star B mA is the apparent magnitude of star A mB is the apparent magnitude of star B ...
... bA is the apparent brightness of star A bB is the apparent brightness of star B mA is the apparent magnitude of star A mB is the apparent magnitude of star B ...
Document
... 5. The teacher asked the class to list various items from the chart in order from brightest to dimmest apparent magnitude. Which object should Anthony list first? A. B. C. D. ...
... 5. The teacher asked the class to list various items from the chart in order from brightest to dimmest apparent magnitude. Which object should Anthony list first? A. B. C. D. ...
Camelopardalis-Better-Know-A-Constellation
... Can be seen in binoculars from country skies, sometimes fools comet hunters. NGC 2403 possesses about 100 emission regions as well as 27 variable stars. Larger instruments will reveal many of these regions that seem to take on likeliness to M33. Three supernovae have been spotted in this galaxy, one ...
... Can be seen in binoculars from country skies, sometimes fools comet hunters. NGC 2403 possesses about 100 emission regions as well as 27 variable stars. Larger instruments will reveal many of these regions that seem to take on likeliness to M33. Three supernovae have been spotted in this galaxy, one ...
Toys Watch the Sky - The Sun is a close star
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
Galaxy Far Far Away ppt
... By looking at the radial velocities of surrounding stars, we can estimate the Sun’s velocity to be about 220 km/s. It takes about 240 million years for the Sun to orbit the center of the galaxy! ...
... By looking at the radial velocities of surrounding stars, we can estimate the Sun’s velocity to be about 220 km/s. It takes about 240 million years for the Sun to orbit the center of the galaxy! ...
"Stars" Power Point notes
... • Apparent magnitude is the apparent brightness of a star as measured on Earth. - Apparent magnitude depends on the star’s actual brightness and distance. - The smaller the magnitude number, the brighter the star. (http://spaceweather.com/flybys ) ...
... • Apparent magnitude is the apparent brightness of a star as measured on Earth. - Apparent magnitude depends on the star’s actual brightness and distance. - The smaller the magnitude number, the brighter the star. (http://spaceweather.com/flybys ) ...
Night Sky Checklist July–August–September Unaided Eye Astronomy
... the Big Dipper and the North Star. Its brightest star, Thuban, was the North Star when the Egyptian pyramids were built. Scorpius, the Scorpion, is a very large, easily located constellation just above the southern horizon. It’s one of the few really striking ecliptic constellations. Polynesians pic ...
... the Big Dipper and the North Star. Its brightest star, Thuban, was the North Star when the Egyptian pyramids were built. Scorpius, the Scorpion, is a very large, easily located constellation just above the southern horizon. It’s one of the few really striking ecliptic constellations. Polynesians pic ...
Lab 2: The Planisphere
... RA-Dec coordinates are only good for storing the location of stars in reference books. This coordinate system, called the equatorial system, tells us nothing about how to actually find something in the sky when we go outside. The altitude-azimuth coordinate system, called the horizon system, fulfill ...
... RA-Dec coordinates are only good for storing the location of stars in reference books. This coordinate system, called the equatorial system, tells us nothing about how to actually find something in the sky when we go outside. The altitude-azimuth coordinate system, called the horizon system, fulfill ...
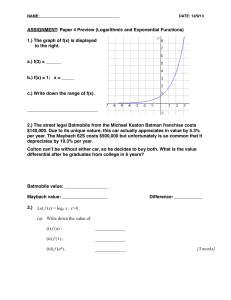
Let f (x) = log x , Let f (x) = loga x , x>0 . (a) Write down the value of (i
... Answer: ________!! ...
... Answer: ________!! ...
An introduction to the HR diagram File
... have high absolute magnitude). However they are much cooler than would be expected for stars of large radius. White dwarf stars White dwarfs are high temperature stars but their small radius (some around the size of Earth) is abnormal for such high temperatures ...
... have high absolute magnitude). However they are much cooler than would be expected for stars of large radius. White dwarf stars White dwarfs are high temperature stars but their small radius (some around the size of Earth) is abnormal for such high temperatures ...
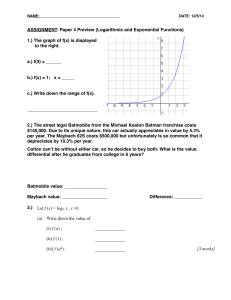
Let f (x) = log x , Let f (x) = loga x , x>0 . (a) Write down the value of (i
... Answer: ________!! ...
... Answer: ________!! ...
Galaxy Powerpoint
... A. Galaxies are very large groups of stars. B. Most contain 100s of billions of stars! C. They are classified by shape. 1. Spiral: a) “Nucleus with Arms” b) The center is full of many yellow stars, which makes it look like a nucleus. c) Many spiral arms come out of the nucleus. ...
... A. Galaxies are very large groups of stars. B. Most contain 100s of billions of stars! C. They are classified by shape. 1. Spiral: a) “Nucleus with Arms” b) The center is full of many yellow stars, which makes it look like a nucleus. c) Many spiral arms come out of the nucleus. ...
Grand Tour Worksheet - School District of La Crosse
... 8. Where is Betelgeuse in its life? 9. What happened with the Ring Nebula? 10. How fast are the gases receding from the Ring Nebula? ...
... 8. Where is Betelgeuse in its life? 9. What happened with the Ring Nebula? 10. How fast are the gases receding from the Ring Nebula? ...
DSLR photometry - British Astronomical Association
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons that were captured is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons that were captured is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
Properties of Stars in general
... Blue stars – very hot ~ 20,000K White stars - hot ~ 10,000k Sun-like stars – yellow ~ 6,000K Orange stars ~ 4500k Red stars ~ 3000K Temperature has a major effect on the spectral lines seen in the atmosphere of a star ...
... Blue stars – very hot ~ 20,000K White stars - hot ~ 10,000k Sun-like stars – yellow ~ 6,000K Orange stars ~ 4500k Red stars ~ 3000K Temperature has a major effect on the spectral lines seen in the atmosphere of a star ...
Stars
... heat and light from nuclear reactions (fusion) within its core. • Stars are classified by color, temperature, size, composition, and brightness. ...
... heat and light from nuclear reactions (fusion) within its core. • Stars are classified by color, temperature, size, composition, and brightness. ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.