RFS_multiple_choice_Dec8_Key
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #16
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
Sky Notes - April 2012 - North Devon Astronomical Society
... dwarf companion, and current estimates place the pair at a distance of around 50 light-years from us. Interestingly, Gamma Cephei will be the pole star between 3000 and 5200 AD. Cep Delta Cephei - the first Cepheid variable. Unlike eclipsing binaries, where the light from a star is dimmed by ...
... dwarf companion, and current estimates place the pair at a distance of around 50 light-years from us. Interestingly, Gamma Cephei will be the pole star between 3000 and 5200 AD. Cep Delta Cephei - the first Cepheid variable. Unlike eclipsing binaries, where the light from a star is dimmed by ...
Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ Stars Study Guide (Ch. 21)
... 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
... 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
Main Sequence Stars
... The rst classi cation of stars was suggested by Einar Hertzsprung in Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate bein ...
... The rst classi cation of stars was suggested by Einar Hertzsprung in Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate bein ...
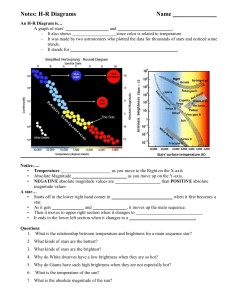
H-R Diagram Notes
... An H-R Diagram is… A graph of stars’ ___________________ and ________________________. – It also shows ___________________ since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. – It stands for _____________________ ...
... An H-R Diagram is… A graph of stars’ ___________________ and ________________________. – It also shows ___________________ since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. – It stands for _____________________ ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
September Evening Skies
... mid-September 2005. At chart time 7 objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Altair, Antares, Fomalhaut, and Deneb. Our usual monthly maps are designed for stargazers just beginning to find their way around the sky. This month’s ma ...
... mid-September 2005. At chart time 7 objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Altair, Antares, Fomalhaut, and Deneb. Our usual monthly maps are designed for stargazers just beginning to find their way around the sky. This month’s ma ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of ___hydrogen___ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of ___hydrogen___ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
Life Cycle of Stars Flipbook Assignment
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
Surface Environments of the Planets o+ our Solar System
... characteristics of stars. You will also be asked to locate and identify some non-stellar objects. You may begin by trying the website at http://www.stellar-database.com/ ...
... characteristics of stars. You will also be asked to locate and identify some non-stellar objects. You may begin by trying the website at http://www.stellar-database.com/ ...
Stars
... The number of stars visible to the naked eye from earth has been estimated to total 8000, of which 4000 are visible from the northern hemisphere and 4000 from the southern hemisphere. At any one time in either hemisphere, only about 2000 stars are visible. The other 2000 are located in the daytime s ...
... The number of stars visible to the naked eye from earth has been estimated to total 8000, of which 4000 are visible from the northern hemisphere and 4000 from the southern hemisphere. At any one time in either hemisphere, only about 2000 stars are visible. The other 2000 are located in the daytime s ...
Characteristics of Stars
... • Absolute Magnitude: the “Real” brightness of the star. How much light it really gives off.(Need to know the distance to the Star) • Apparent Magnitude: How bright the star appears to be. ...
... • Absolute Magnitude: the “Real” brightness of the star. How much light it really gives off.(Need to know the distance to the Star) • Apparent Magnitude: How bright the star appears to be. ...
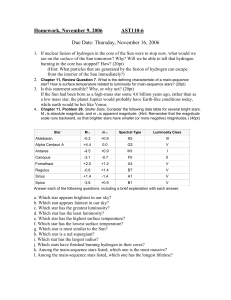
Homework, August 29, 2002 AST110-6
... burning in the core has stopped? How? (20pt) (Hint: What particles that are generated by the fusion of hydrogen can escape from the interior of the Sun immediately?) 2. Chapter 11, Review Question 7. What is the defining characteristic of a main-sequence star? How is surface temperature related to l ...
... burning in the core has stopped? How? (20pt) (Hint: What particles that are generated by the fusion of hydrogen can escape from the interior of the Sun immediately?) 2. Chapter 11, Review Question 7. What is the defining characteristic of a main-sequence star? How is surface temperature related to l ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... Stars differ in composition, age, and size. *young stars are rich in hydrogen *older stars use up hydrogen to produce more helium ...
... Stars differ in composition, age, and size. *young stars are rich in hydrogen *older stars use up hydrogen to produce more helium ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.