Stars - TeacherWeb
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
SNC1PL Celestial Objects and Constellations
... Ion tail is created by solar wind reacting with material on the comet to produce a tail that is directed away from the comet ...
... Ion tail is created by solar wind reacting with material on the comet to produce a tail that is directed away from the comet ...
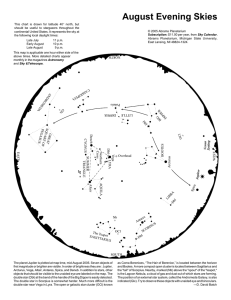
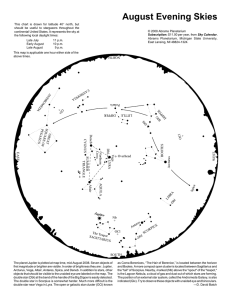
August Evening Skies
... double star near Vega in Lyra. The open or galactic star cluster (OCl) known ...
... double star near Vega in Lyra. The open or galactic star cluster (OCl) known ...
red shift blue shift
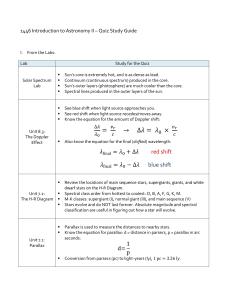
... Review the locations of main sequence stars, supergiants, giants, and white dwarf stars on the H-R Diagram. Spectral class order from hottest to coolest: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. M-K classes: supergiant (I), normal giant (III), and main sequence (V) Stars evolve and do NOT last forever. Absolute magnitu ...
... Review the locations of main sequence stars, supergiants, giants, and white dwarf stars on the H-R Diagram. Spectral class order from hottest to coolest: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. M-K classes: supergiant (I), normal giant (III), and main sequence (V) Stars evolve and do NOT last forever. Absolute magnitu ...
Chapter 24 Test:Stars/Galaxies
... Although it has a greater _____ than Sirius, Rigel does NOT look as bright in the night sky. (a) black hole, (b) parallax, (c) apparent magnitude, (d) absolute magnitude. ...
... Although it has a greater _____ than Sirius, Rigel does NOT look as bright in the night sky. (a) black hole, (b) parallax, (c) apparent magnitude, (d) absolute magnitude. ...
Variable and Binary Stars
... – 75% of O-type stars seem to have a companion – If Jupiter had been ~100 times more massive, the Sun would have a companion star ...
... – 75% of O-type stars seem to have a companion – If Jupiter had been ~100 times more massive, the Sun would have a companion star ...
chapter 18
... Astronomers measure stellar distances in three different units. The smallest of these is a) the light-year. b) the absolute magnitude. c) the astronomical unit. d) the parsec. ...
... Astronomers measure stellar distances in three different units. The smallest of these is a) the light-year. b) the absolute magnitude. c) the astronomical unit. d) the parsec. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears
... Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the observer. The absolute magnitude of stars is measured on a Scale ...
... Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the observer. The absolute magnitude of stars is measured on a Scale ...
The IC 348 surface density in the Perseus molecular cloud L. Cambrésy Observatoire de Strasbourg, France
... Embedded clusters toward the North America Nebula ...
... Embedded clusters toward the North America Nebula ...
Stars
... Apparent magnitude: brightness as seen from Earth Absolute magnitude: brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth ...
... Apparent magnitude: brightness as seen from Earth Absolute magnitude: brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Measuring distances to stars • Measure parallax – the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. • Knowing the angle that the star’s position changes and the size of Earth’s orbit, astronomers can calculate the distance of the star from earth. ...
... Measuring distances to stars • Measure parallax – the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. • Knowing the angle that the star’s position changes and the size of Earth’s orbit, astronomers can calculate the distance of the star from earth. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Define main sequence stars: • Major grouping of stars • Form a narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
... Define main sequence stars: • Major grouping of stars • Form a narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
Maui Stargazing April Observing List DEEP SPACE OBJECTS
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
chap17_f03_phints
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64X greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? HINT: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found ...
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64X greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? HINT: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.