Allison McGraw - WordPress.com
... Orionis (β Ori, β Orionis), is the brightest star in the constellation Orion and the seventh brightest star in the night sky, with visual magnitude 0.13. The star as seen from Earth is actually a triple star system, with the primary star (Rigel A) a bluewhite supergiant of absolute magnitude −7.84 a ...
... Orionis (β Ori, β Orionis), is the brightest star in the constellation Orion and the seventh brightest star in the night sky, with visual magnitude 0.13. The star as seen from Earth is actually a triple star system, with the primary star (Rigel A) a bluewhite supergiant of absolute magnitude −7.84 a ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
Astronomy word grid
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
Structure of the Universe
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
File
... 24) What shape is the Milky Way? 25) What is the local group? 26) How many stars are in the Milky Way? 27) Approximately how big is the Milky Way 28) The largest known galaxy is what type of galaxy? 29) What is a light year? Section 4 30) What is cosmology? 31) How old is the universe? 32) What is t ...
... 24) What shape is the Milky Way? 25) What is the local group? 26) How many stars are in the Milky Way? 27) Approximately how big is the Milky Way 28) The largest known galaxy is what type of galaxy? 29) What is a light year? Section 4 30) What is cosmology? 31) How old is the universe? 32) What is t ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Classification • H-R diagram • Absolute magnitude vs. temperature • For most stars the brightness increases as surface temp increases • Main sequence stars are band in center ...
... Classification • H-R diagram • Absolute magnitude vs. temperature • For most stars the brightness increases as surface temp increases • Main sequence stars are band in center ...
Use this form to take notes in class about stars
... Stars of Spectral Classes B to M 9. What color is our sun? ___________what class is it in? ...
... Stars of Spectral Classes B to M 9. What color is our sun? ___________what class is it in? ...
Physical properties of stars
... Physical properties of stars Magnitude- the brightness of a star Absolute magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star Apparent magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their appar ...
... Physical properties of stars Magnitude- the brightness of a star Absolute magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star Apparent magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their appar ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
Constellations
... Imagine you are standing at the North Pole and see a star directly overhead. Where do you think the star would be if you were standing at the equator? ...
... Imagine you are standing at the North Pole and see a star directly overhead. Where do you think the star would be if you were standing at the equator? ...
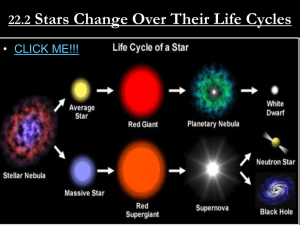
22.2 Stars Change Over Their Life Cycles
... position of an object when viewed from different locations. • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
... position of an object when viewed from different locations. • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
observingopenclusters-2-2-1
... Canis Major, Minor and Monoceros M41, M46 and M47 Locate brightest star Sirius (Canis Major - underneath Orion) Note: reason for its brightness is both its intrinsic luminosity and closeness to the Sun Slide your scope or binoculars parallel to the dog’s back and then move west of that line. You wi ...
... Canis Major, Minor and Monoceros M41, M46 and M47 Locate brightest star Sirius (Canis Major - underneath Orion) Note: reason for its brightness is both its intrinsic luminosity and closeness to the Sun Slide your scope or binoculars parallel to the dog’s back and then move west of that line. You wi ...
Ch 28 Fact Sheet
... Name _______________________________________________________ Date ____________ Per ______ Ch 28 Fact Sheet ________________ 1. The two lenses of a refracting telescope. ________________ ________________ 2. Type of constellation Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Draco & Cepheus are because they go counter cloc ...
... Name _______________________________________________________ Date ____________ Per ______ Ch 28 Fact Sheet ________________ 1. The two lenses of a refracting telescope. ________________ ________________ 2. Type of constellation Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Draco & Cepheus are because they go counter cloc ...
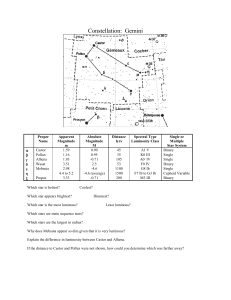
Gemini
... cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), it is of intermediate age, and contains some post-main sequence stars (including several yellow and ora ...
... cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), it is of intermediate age, and contains some post-main sequence stars (including several yellow and ora ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
astronomy 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... 6. What does the lifetime of a star depend on? IT’S MASS. 7. What is a supernova? EXPLOSION OF A HIGH MASS STAR. 8. What is a star system? A GROUP OF TWO OR MORE STARS. 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What ...
... 6. What does the lifetime of a star depend on? IT’S MASS. 7. What is a supernova? EXPLOSION OF A HIGH MASS STAR. 8. What is a star system? A GROUP OF TWO OR MORE STARS. 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What ...
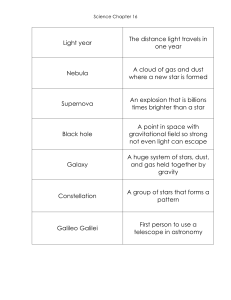
Light year The distance light travels in one year Nebula A cloud of
... The distance light travels in one year ...
... The distance light travels in one year ...
Review_game_and_answers
... Each team will discuss and answer each question Scoring sheets are handed in at the end. 5 points to winning team ...
... Each team will discuss and answer each question Scoring sheets are handed in at the end. 5 points to winning team ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... Observations for September 14th Star Party SSG Coordinators will be at the very dark Icehouse Observing Park (IHOP) observing site, accessed from Highway 50, at 7:30 pm to assist observers with basic telescope setup procedures, Newtonian mirror collimation, and basic polar alignment questions. IHOP ...
... Observations for September 14th Star Party SSG Coordinators will be at the very dark Icehouse Observing Park (IHOP) observing site, accessed from Highway 50, at 7:30 pm to assist observers with basic telescope setup procedures, Newtonian mirror collimation, and basic polar alignment questions. IHOP ...
J tieutifit meti(au.
... est to the earth on October 19th and farthest from it on the governing factor in traction systems for city n�p, North of Andromeda the eye is caught by a zigzag October 7th. but suddenly it was found electricity was destined to rowof stars resembling the letter" W;"these mark the ...
... est to the earth on October 19th and farthest from it on the governing factor in traction systems for city n�p, North of Andromeda the eye is caught by a zigzag October 7th. but suddenly it was found electricity was destined to rowof stars resembling the letter" W;"these mark the ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.