proposed october viewing list
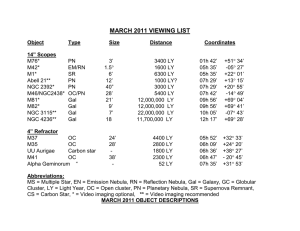
... CS = Carbon Star, * = Video imaging optional, ** = Video imaging recommended ...
... CS = Carbon Star, * = Video imaging optional, ** = Video imaging recommended ...
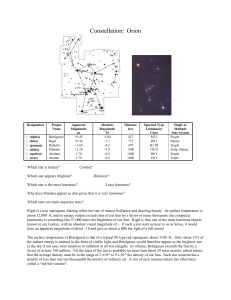
Orion
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
There's more than one way to make a Blue Straggler 1
... The more massive star in this double-star system cannibalizes its partner, creating a single, even more massive star. ...
... The more massive star in this double-star system cannibalizes its partner, creating a single, even more massive star. ...
File
... the equator so that day and night are of equal length around the world (March 21 and September 22 – 23) 3. Apollo 11 - the 1st manned landing on the moon 4. galaxy - billions of stars grouped together 5. stellar evolution - the stages of development and duration of stars, some of which appear on the ...
... the equator so that day and night are of equal length around the world (March 21 and September 22 – 23) 3. Apollo 11 - the 1st manned landing on the moon 4. galaxy - billions of stars grouped together 5. stellar evolution - the stages of development and duration of stars, some of which appear on the ...
The Constellation Microscopium, the Microscope Microscopium is a
... Piscis Austrinus and Grus to the west, Sagittarius to the east, Indus to the south, and touching on Telescopium to the southeast. The recommended three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted Seen in the 1824 star chart set Urania's Mirror (lower left) by the International Astronomical ...
... Piscis Austrinus and Grus to the west, Sagittarius to the east, Indus to the south, and touching on Telescopium to the southeast. The recommended three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted Seen in the 1824 star chart set Urania's Mirror (lower left) by the International Astronomical ...
STARS and GALAXIES
... • Absolute Luminosity (brightness)Measures how bright a star is in relation to the sun, if all the stars were the same distance from the Earth. ...
... • Absolute Luminosity (brightness)Measures how bright a star is in relation to the sun, if all the stars were the same distance from the Earth. ...
labex7
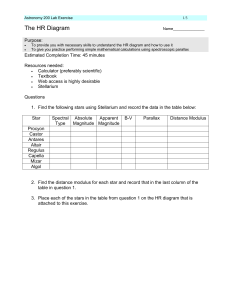
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... D. T-Tauri stars E. white dwarfs 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR ...
... D. T-Tauri stars E. white dwarfs 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR ...
Life and Death of a Star – video questions
... 3. Each contracting cloud can produce a few dozen to __________________ of stars. 4. What is the temperature in the middle of a dust disc? __________________ 5. A star’s biggest opponent is ________________ that wants to crush the star. 6. What holds up the star from gravity? ...
... 3. Each contracting cloud can produce a few dozen to __________________ of stars. 4. What is the temperature in the middle of a dust disc? __________________ 5. A star’s biggest opponent is ________________ that wants to crush the star. 6. What holds up the star from gravity? ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will ...
... Two stars in orbit about their common center of mass Various types of binary stars. Doppler shifts give velocity Orbital mechanics give the masses of the two stars Eclipses allow determination of individual stellar radii See Studio Laboratory this Friday ...
... Two stars in orbit about their common center of mass Various types of binary stars. Doppler shifts give velocity Orbital mechanics give the masses of the two stars Eclipses allow determination of individual stellar radii See Studio Laboratory this Friday ...
After Dark in Allenspark
... closest it will be all year and up all night. You can spot it, shining brightly, low in the East in the evening sky. January 29: New moon. And, as I promised, a way to find Capella, the 6th brightest star in the sky, by "star hopping," or going step by step from the easier stars to the tougher ones. ...
... closest it will be all year and up all night. You can spot it, shining brightly, low in the East in the evening sky. January 29: New moon. And, as I promised, a way to find Capella, the 6th brightest star in the sky, by "star hopping," or going step by step from the easier stars to the tougher ones. ...
Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star
... Exit Slip: Stars 1. What 5 characteristics are used to classify stars? 2. What can the color of a star tell you about it? ...
... Exit Slip: Stars 1. What 5 characteristics are used to classify stars? 2. What can the color of a star tell you about it? ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... The luminosity of a star is accurately known but measurement of its apparent brightness is made difficult by the presence of dust in the interstellar medium. Suggest the effect this has on the measured distance to the star. ...
... The luminosity of a star is accurately known but measurement of its apparent brightness is made difficult by the presence of dust in the interstellar medium. Suggest the effect this has on the measured distance to the star. ...
Cetus and Lepus
... chained to a rock by the sea but was saved by the hero Perseus, who used the head of Medusa to turn the monster into stone. ...
... chained to a rock by the sea but was saved by the hero Perseus, who used the head of Medusa to turn the monster into stone. ...
Astronomy Chapter 13 Name
... K. The law stating that the apparent brightness of a body decreases inversely as the square of its distance L. A star whose luminosity changes in time M. The region in the H-R diagram in which most stars are located N. A dense star whose radius is approximately equal to Earth’s but whose mass is com ...
... K. The law stating that the apparent brightness of a body decreases inversely as the square of its distance L. A star whose luminosity changes in time M. The region in the H-R diagram in which most stars are located N. A dense star whose radius is approximately equal to Earth’s but whose mass is com ...
Stars - Denbigh Baptist Christian School
... Sizes and Distances of Stars Dwarfs – small and medium Our Sun has diameter of 865,000 miles (1,400,000 km) This size makes it a medium-sized yellow star. Giant stars – 10’s – 100’s of times larger and 100’s times more luminous. Supergiants – 100’s times larger and 1000’s times more luminous. Next c ...
... Sizes and Distances of Stars Dwarfs – small and medium Our Sun has diameter of 865,000 miles (1,400,000 km) This size makes it a medium-sized yellow star. Giant stars – 10’s – 100’s of times larger and 100’s times more luminous. Supergiants – 100’s times larger and 1000’s times more luminous. Next c ...
22 October: The Formation of Stars
... • When we see massive main sequence stars (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
... • When we see massive main sequence stars (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
... by 17". Mag 1.5 Adhara has a Mag 7.5 double just 7.5" due south. Adhara is a main sequence star that shines 9,000 times as brightly as our own sun. Good thing it's 432 lightyears away. ...
... by 17". Mag 1.5 Adhara has a Mag 7.5 double just 7.5" due south. Adhara is a main sequence star that shines 9,000 times as brightly as our own sun. Good thing it's 432 lightyears away. ...
Slide 1 - Fort Bend ISD
... • Betelgeuse fairly cool, but big. Shines brightly • Rigel is a lot smaller than Betelgeuse, but it’s hot, so it also shines brightly ...
... • Betelgeuse fairly cool, but big. Shines brightly • Rigel is a lot smaller than Betelgeuse, but it’s hot, so it also shines brightly ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.