* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Studying Space
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
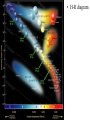
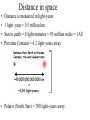
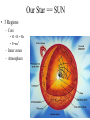
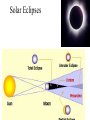
Studying Space SOL version The Universe • How Old? -- 13.7-15 billion years old • How did it begin? – The Big Bang Theory Galaxy • Groups of stars & nebulae • Our galaxy: – Milky Way Galaxy – Spiral • Types: – Spiral galaxy – Elliptical galaxy – Irregular galaxy The Birth of a Star • A nebulae of gas & dust starts to condense • Temp => 10,000,000° C • Fusion begins • 2 Hydrogens 1 Helium Stars • Celestial bodies made up of Hydrogen & Helium • Groups of stars are called Constellations • Star Clusters/Globular Clusters – 100s of stars that move as 1 mass • Binary Stars – pairs of stars that rotate around each other. • H-R diagram Motion of stars • Apparent motion tends to be circumpolar. • There are 3 real motions – 1) rotate on an axis – 2) revolve around another star – 3) move to or away from the earth Distance in space • • • • Distance is measured in light-years 1 light–year = 9.5 trillion km Sun to earth = 8 light-minutes = 93 million miles = 1AU Proxima Centauri = 4.2 light-years away • Polaris (North Star) = 700 light-years away. Parallax of stars • Aids scientists in measuring distance. • It is the apparent shift of a star over a 6 month period. • It is just like when you shut 1 eye & look at an object; then open the other & the object appears to have moved. Our Star == SUN • 3 Regions – Core • H + H = He • E=mc2 – Inner zones – Atmosphere Sunspots • Cooler areas of the Sun • Sunspot Cycle = 11 years • Current cycle low in 1997 HIGH to another low in 2008 Solar Flares • Electrically charged particle are shot out into space • Cause magnetic Storms • Disrupt satellites & ISS Solar Wind • Flow out from the sun • Ions shoot out toward the planets Auroras • Northern/Southern Lights Solar Eclipses Models of the Solar System • Aristotle – Geocentric model – Earth in the middle • Copernicus – Haliocentric model – Sun-centered – Proven by Galileo’s telescope – Identified Retrograde motion Kepler’s Laws of Motion 1st law: planets move in ellipses perihelon: closest to sun aphelion: farthest away Kepler’s • Law of Equal Areas • Planets move fastest when they are closest to the sun. http://csep10.phys.utk. edu/astr162/lect/binari es/visual/kepleroldfra me.html nd 2 law Kepler’s rd 3 • 1 astronomical unit = the distance from the earth to the sun = r • 1 year = period of revolution = p • For any planet: – K r3 = p2 law of motion Newton’s use of Kepler’s Laws • Gravity keeps the stars & planets in motion • G = m1 x m2 d2 Asteroids • Most stay in the Asteroid Belt between Mars & Jupiter • Large rocks left over from the creation of our solar system • Very similar to earth rocks – Silicates – Iron & nickel – Carbon Comets • Orbit the sun in very large ellipses • Oort cloud: origin of most comets – located beyond Pluto Meteroids meteors meteorites Lunar Eclipses