Sydney Observatory night sky map January 2014
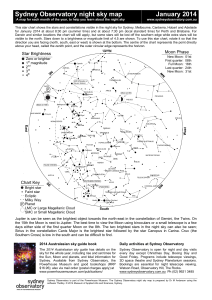
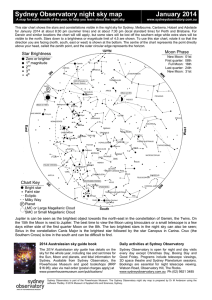
... Jupiter is can be seen as the brightest object towards the north-east in the constellation of Gemini, the Twins. On the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brigh ...
... Jupiter is can be seen as the brightest object towards the north-east in the constellation of Gemini, the Twins. On the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brigh ...
your star chart here - Australasian Science Magazine
... Jupiter is can be seen as the brightest object towards the north-east in the constellation of Gemini, the Twins. On the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brigh ...
... Jupiter is can be seen as the brightest object towards the north-east in the constellation of Gemini, the Twins. On the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brigh ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • may contain millions of stars • Old stars • Great tool to study stellar life cycle ...
... • may contain millions of stars • Old stars • Great tool to study stellar life cycle ...
Physics 1025: Lecture 18 Stellar Magnitudes, Absolute Magnitudes
... For example, consider two stars differing in magnitude by 13 magnitudes (e.g. m 1 = 20 and m2 = 7) magnitude diff. Δm = 13 = 5 + 5 +3 so brightness ratio = (100) x (100) x 16 = 160,000 and thus the m = 7 star is 160,000 times brighter than the m = 20 star. Now there are problems with visual magnitud ...
... For example, consider two stars differing in magnitude by 13 magnitudes (e.g. m 1 = 20 and m2 = 7) magnitude diff. Δm = 13 = 5 + 5 +3 so brightness ratio = (100) x (100) x 16 = 160,000 and thus the m = 7 star is 160,000 times brighter than the m = 20 star. Now there are problems with visual magnitud ...
What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle School
... Stars are giant spheres of glowing gases. A star is powered by nuclear fusion. This is a process whereby hydrogen atoms are fused together to create helium atoms. In the process a tremendous amount of energy is given off in the form of electromagnetic waves and heat. There are billions of stars in a ...
... Stars are giant spheres of glowing gases. A star is powered by nuclear fusion. This is a process whereby hydrogen atoms are fused together to create helium atoms. In the process a tremendous amount of energy is given off in the form of electromagnetic waves and heat. There are billions of stars in a ...
the life cycle of stars
... • A main sequence star with a mass of more than about 10 Suns experiences a spectacular end. • It swells into a red supergiant with cooling, expanding outer layers. • Eventually its core collapses, causing a huge explosion known as a ...
... • A main sequence star with a mass of more than about 10 Suns experiences a spectacular end. • It swells into a red supergiant with cooling, expanding outer layers. • Eventually its core collapses, causing a huge explosion known as a ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... between brightness and temp. Hotter things are brighter Hotter temp = more energy is radiated. Bigger stars are brighter. Bigger surface area = more energy radiated. ...
... between brightness and temp. Hotter things are brighter Hotter temp = more energy is radiated. Bigger stars are brighter. Bigger surface area = more energy radiated. ...
Useful Things to Study (#2)
... main sequence, main sequence, giant phase, lifetime of planetary nebula, white dwarf What is the CNO cycle? It is the principal energy generation mechanism for which kind of stars? What’s the minimum temperature to run the proton-proton cycle in a star’s core? Why are Cepheids and RR Lyrae stars imp ...
... main sequence, main sequence, giant phase, lifetime of planetary nebula, white dwarf What is the CNO cycle? It is the principal energy generation mechanism for which kind of stars? What’s the minimum temperature to run the proton-proton cycle in a star’s core? Why are Cepheids and RR Lyrae stars imp ...
A Star is a ball of matter that is pulled together by gravity, and that
... 4. Measuring the Distance to Stars: we measure the distance between objects in space using ___________. –Parallax is the apparent change in _______________of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. The ______________a star is, the ________________its paralla ...
... 4. Measuring the Distance to Stars: we measure the distance between objects in space using ___________. –Parallax is the apparent change in _______________of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. The ______________a star is, the ________________its paralla ...
Star Properties and Stellar Evolution
... What is the size of stars? Vary from the size of Earth to 2,000 times the size of the ...
... What is the size of stars? Vary from the size of Earth to 2,000 times the size of the ...
Word
... a. In the following Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram every dot corresponds to a different star in our galaxy. What is the total range in absolute magnitude and also in brightness? Using your knowledge of magnitudes, describe why a star with color index of B-V=1.5 would appear red to the human eye. [HINT: ...
... a. In the following Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram every dot corresponds to a different star in our galaxy. What is the total range in absolute magnitude and also in brightness? Using your knowledge of magnitudes, describe why a star with color index of B-V=1.5 would appear red to the human eye. [HINT: ...
Big bang and Stars
... Energy released from nuclear fusion counteracts inward force of gravity. Throughout its life, these two forces determine the stages of a star’s life. ...
... Energy released from nuclear fusion counteracts inward force of gravity. Throughout its life, these two forces determine the stages of a star’s life. ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... 1. Why is it difficult to find out how common the most luminous stars are ? The least luminous stars ? (Chapt. 9, Review Question 13) See p 186 of your text. It is difficult to count the most luminous stars in a known volume of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least lu ...
... 1. Why is it difficult to find out how common the most luminous stars are ? The least luminous stars ? (Chapt. 9, Review Question 13) See p 186 of your text. It is difficult to count the most luminous stars in a known volume of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least lu ...
12.4 Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun
... • Helium begins to fuse in the core, as a helium flash. The star expands into a red giant as the core continues to collapse. The envelope blows off, leaving a white dwarf to gradually cool. • Nova results from material accreting onto a white dwarf from a companion star ...
... • Helium begins to fuse in the core, as a helium flash. The star expands into a red giant as the core continues to collapse. The envelope blows off, leaving a white dwarf to gradually cool. • Nova results from material accreting onto a white dwarf from a companion star ...
The Sun . . .
... where it expands and grows cooler and more luminous. Its final stage is white dwarf, after it collapses upon itself and only the hot, dense core will remain. ...
... where it expands and grows cooler and more luminous. Its final stage is white dwarf, after it collapses upon itself and only the hot, dense core will remain. ...
Calculating_Main_Sequence_Lifetimes_StudentGuide
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
Planetarium Activity 1 Learning to measure brightness and Limiting
... 3. The second time the lights are raised, number the stars (on your worksheet) in the order of their disappearance. This step will be repeated several times if you are unsure of differences between stars of similar brightness. 4. Assign Greek Letters to the stars in each constellation in the order o ...
... 3. The second time the lights are raised, number the stars (on your worksheet) in the order of their disappearance. This step will be repeated several times if you are unsure of differences between stars of similar brightness. 4. Assign Greek Letters to the stars in each constellation in the order o ...
parallax in arc seconds
... member of a triple star system called the Alpha Centauri System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
... member of a triple star system called the Alpha Centauri System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.