Chapter 30 Section 2 Handout
... Main-sequence stars that are more massive than the sun and become larger than regular giant stars. ...
... Main-sequence stars that are more massive than the sun and become larger than regular giant stars. ...
W > 1 - The Open University
... Unlike the gradual disappearance of a planet (small disc) a star vanishes instantly demonstrating that it is a point source of light as viewed from the Earth. For all occultation events start observing 10 to 15 minutes before the predicted time to identify the required star and to allow for slightly ...
... Unlike the gradual disappearance of a planet (small disc) a star vanishes instantly demonstrating that it is a point source of light as viewed from the Earth. For all occultation events start observing 10 to 15 minutes before the predicted time to identify the required star and to allow for slightly ...
coSmoS in youR PockET
... The Universe is everything that exists: all planets, stars, galaxies and all of the other objects in space. A galaxy is a large collection of stars, along with gas, dust and other stuff. The galaxy that we live in is called the Milky Way. A Star is a massive ball of luminous hot gas, held together ...
... The Universe is everything that exists: all planets, stars, galaxies and all of the other objects in space. A galaxy is a large collection of stars, along with gas, dust and other stuff. The galaxy that we live in is called the Milky Way. A Star is a massive ball of luminous hot gas, held together ...
Unit 1
... • Recall that the velocity necessary to • Also recall that nothing can travel avoid being gravitationally drawn faster than the speed of light, c, or back from an object (the escape 3108 m/s velocity) is: ...
... • Recall that the velocity necessary to • Also recall that nothing can travel avoid being gravitationally drawn faster than the speed of light, c, or back from an object (the escape 3108 m/s velocity) is: ...
+(J - cloudfront.net
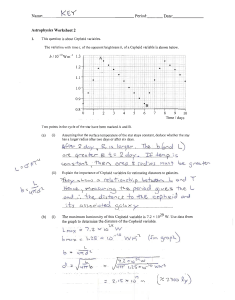
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
Startalk
... A big glowing ball of gas! Contains mainly H and He They have a core that is dense and super hot! Nuclear fusion is the source of their energy! ...
... A big glowing ball of gas! Contains mainly H and He They have a core that is dense and super hot! Nuclear fusion is the source of their energy! ...
Astronomy Notes
... 1. ________________________ - stars begin as a large dust and gas cloud in space. 2. ________________________ - occurs nearby and shoots matter and energy into the nebula, “seeds” it with elements not originally present and causes it to spin 3. ________________________ - because of gravity the nebul ...
... 1. ________________________ - stars begin as a large dust and gas cloud in space. 2. ________________________ - occurs nearby and shoots matter and energy into the nebula, “seeds” it with elements not originally present and causes it to spin 3. ________________________ - because of gravity the nebul ...
G030485-00 - DCC
... LIGO’s interest LIGO will study the early history of our creation by detecting the remnant ghosts, neutron stars and black holes LIGO-G030485-00-D ...
... LIGO’s interest LIGO will study the early history of our creation by detecting the remnant ghosts, neutron stars and black holes LIGO-G030485-00-D ...
Astronomy pt. 2
... c)No more H(very little), He turns into C More energy HHe and HeC, gravity cant hold on ahhh! ...
... c)No more H(very little), He turns into C More energy HHe and HeC, gravity cant hold on ahhh! ...
SE 1.0 - Edquest
... Constellations are groupings of stars that we see as patterns. The International Astronomical Union recognizes 88 officially. There are other patterns that are unofficially recognized, such as The Big Dipper, and are known as … A. anomalies B. asterisms C. asteroids D. aspergummies ...
... Constellations are groupings of stars that we see as patterns. The International Astronomical Union recognizes 88 officially. There are other patterns that are unofficially recognized, such as The Big Dipper, and are known as … A. anomalies B. asterisms C. asteroids D. aspergummies ...
Size Color and Temperature
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
Stars - Haag
... Star’s are also classified according to their brightness. Luminosity is the amount of energy emitted by a star each second ...
... Star’s are also classified according to their brightness. Luminosity is the amount of energy emitted by a star each second ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... NGC4559 (10.5) sg. Bright oval smudge. Mottled appearance in large telescopes. NGC4565 (10.5) sg. One of the finest "edge-on" spiral galaxies. Appears as a thin needle of light with the hint of a central bulge. Moderate apertures begin to show a dark dust lane. The North Galactic Pole is located a f ...
... NGC4559 (10.5) sg. Bright oval smudge. Mottled appearance in large telescopes. NGC4565 (10.5) sg. One of the finest "edge-on" spiral galaxies. Appears as a thin needle of light with the hint of a central bulge. Moderate apertures begin to show a dark dust lane. The North Galactic Pole is located a f ...
Nights of the Heavenly G With
... "hooked" on the "G!" Stand under the stars and with your arm outstretched trace a sweeping arc, starting at Capella and moving to Castor, to Pollux, to Procyon, to Sirius, to Rigel in Orion, sweeping to Aldebaran in the Bull, and then cutting back down to Orion's belt. You will have learned most of ...
... "hooked" on the "G!" Stand under the stars and with your arm outstretched trace a sweeping arc, starting at Capella and moving to Castor, to Pollux, to Procyon, to Sirius, to Rigel in Orion, sweeping to Aldebaran in the Bull, and then cutting back down to Orion's belt. You will have learned most of ...
HW2 due - Yale Astronomy
... (express your answer as a ratio, i.e. calculate the radius of the star divided by the radius of the earth) ...
... (express your answer as a ratio, i.e. calculate the radius of the star divided by the radius of the earth) ...
Patterns in the night sky - Laureate International College
... whole night they appear to move from east to west (as sun does during day). But the stars are not actually moving across the celestial sphere – Earth’s rotation causes the illusion of movement. The stars appear to rotate around a single point in the sky – the North Star – Polaris - which seems to st ...
... whole night they appear to move from east to west (as sun does during day). But the stars are not actually moving across the celestial sphere – Earth’s rotation causes the illusion of movement. The stars appear to rotate around a single point in the sky – the North Star – Polaris - which seems to st ...
d - Haus der Astronomie
... LIGHT YEAR is NOT a unit of measurament of time. It is correct to say that the image of celestial body, which is far a certain number of light years, shows us that celestial body as it was the same number of years ago, and not at this time. ...
... LIGHT YEAR is NOT a unit of measurament of time. It is correct to say that the image of celestial body, which is far a certain number of light years, shows us that celestial body as it was the same number of years ago, and not at this time. ...
Chapter 15 Stars, Galaxies
... 10. a 11. c 12. a. Protostar b. Supergiant c. Supernova d. Black Hole e. Stars that are the most massive become black holes. Stars that are less massive but still high-mass stars become neutron stars. f. They all start out as a part of nebulas that contract to form protostars. g. Low-mass and medium ...
... 10. a 11. c 12. a. Protostar b. Supergiant c. Supernova d. Black Hole e. Stars that are the most massive become black holes. Stars that are less massive but still high-mass stars become neutron stars. f. They all start out as a part of nebulas that contract to form protostars. g. Low-mass and medium ...
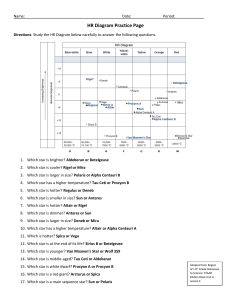
HR Diagram Practice Page
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
Homework PHY121 (Astronomy
... particular object, animal or person to the people in ancient cultures. Most stars in such groupings, however, only seem to be related to each other. In reality, they have very different distances to us. If one would look at a given constellation, say Cassiopeia, which forms a big “W” on our sky, fro ...
... particular object, animal or person to the people in ancient cultures. Most stars in such groupings, however, only seem to be related to each other. In reality, they have very different distances to us. If one would look at a given constellation, say Cassiopeia, which forms a big “W” on our sky, fro ...
Document
... 3. Using Stellarium to help you find the names of the zodiacal constellations and their brightest stars, fill in the chart on the reverse side. The circle is the ecliptic going through the twelve constellations indicated by big arrows. Label each big arrow with the name of the constellation and try ...
... 3. Using Stellarium to help you find the names of the zodiacal constellations and their brightest stars, fill in the chart on the reverse side. The circle is the ecliptic going through the twelve constellations indicated by big arrows. Label each big arrow with the name of the constellation and try ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.