General Astrophysical Concepts: Astronomical length scales
... to the black hole’s mass The event horizon or Schwarzschild radius of a black hole, the region over which it is capable of trapping light (radiation), is proportional to the black hole’s mass “A black hole has no hair” is a statement that describes the loss of identity of matter when it is swallowed ...
... to the black hole’s mass The event horizon or Schwarzschild radius of a black hole, the region over which it is capable of trapping light (radiation), is proportional to the black hole’s mass “A black hole has no hair” is a statement that describes the loss of identity of matter when it is swallowed ...
Life of a star - bahringcarthnoians
... enough to swallow the inner planets, up to Earth. But don’t panic, because this won’t happen for about 4.5 billion years. ...
... enough to swallow the inner planets, up to Earth. But don’t panic, because this won’t happen for about 4.5 billion years. ...
Patterns in the Night Sky Constellation: a grouping of stars, as
... geographical coordinates of their location. Geostationary Orbit Satellites: Directly above the equator; appear motionless in the sky, which makes them useful for communications and other commercial industries because they can be linked to antennas on Earth. Communication industries use geostationary ...
... geographical coordinates of their location. Geostationary Orbit Satellites: Directly above the equator; appear motionless in the sky, which makes them useful for communications and other commercial industries because they can be linked to antennas on Earth. Communication industries use geostationary ...
Virtual Sky II (Rev 10/11)
... Name of brightest star _______________ (Size of star on chart related to brightness but look at magnitude in data panel to be sure. Lowest magnitude is brightest) Name of a double star ____________ (Click on brighter stars. If it is double there will be a components tab on the data panel) Name and n ...
... Name of brightest star _______________ (Size of star on chart related to brightness but look at magnitude in data panel to be sure. Lowest magnitude is brightest) Name of a double star ____________ (Click on brighter stars. If it is double there will be a components tab on the data panel) Name and n ...
Document
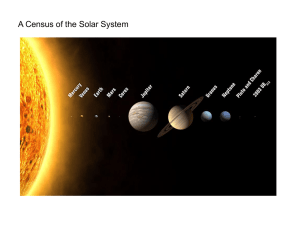
... including 58 residing in life-friendly orbits around their parent stars. The census, collected by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope after just four months of work, shows that small planets like Earth are much more prevalent than Jupiter-sized worlds and that multiple-planet systems are ...
... including 58 residing in life-friendly orbits around their parent stars. The census, collected by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope after just four months of work, shows that small planets like Earth are much more prevalent than Jupiter-sized worlds and that multiple-planet systems are ...
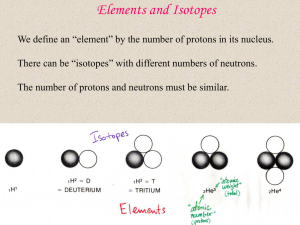
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
... The most common elements are : H (90%) , He (10%), C,N,O (0.1%) They are made by stars… Hydrogen burning in high mass stars The “CNO” cycle Start here ...
... The most common elements are : H (90%) , He (10%), C,N,O (0.1%) They are made by stars… Hydrogen burning in high mass stars The “CNO” cycle Start here ...
Stars
... Stars have different sizes. White dwarf stars are about the size of Earth. Supergiant stars can be wider than 300 million miles. That is more than one thousand times the distance from Earth to the Moon. Stars can be different colors such as blue, yellow, orange, red, white, and black. ...
... Stars have different sizes. White dwarf stars are about the size of Earth. Supergiant stars can be wider than 300 million miles. That is more than one thousand times the distance from Earth to the Moon. Stars can be different colors such as blue, yellow, orange, red, white, and black. ...
Astronomy Study Guide #2
... 10. What do you have to do in order to find the absolute magnitude of a star? What is apparent magnitude? 11. Which stars which contribute most to the chemical enrichment of the interstellar medium? 12. What is a light year? ...
... 10. What do you have to do in order to find the absolute magnitude of a star? What is apparent magnitude? 11. Which stars which contribute most to the chemical enrichment of the interstellar medium? 12. What is a light year? ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... If p is in arcsec and d is in parsecs A star with a parallax of 1 arcsec is 1 parsec distant ...
... If p is in arcsec and d is in parsecs A star with a parallax of 1 arcsec is 1 parsec distant ...
Stars - Mc Guckin Science
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Oct 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer than these three but they are phases every 29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes, 3 seconds. too faint to be seen with the naked eye. It is 2,160 miles in diameter and averages 239,000 miles from Earth. A New Moon is not visible in the ...
... Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer than these three but they are phases every 29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes, 3 seconds. too faint to be seen with the naked eye. It is 2,160 miles in diameter and averages 239,000 miles from Earth. A New Moon is not visible in the ...
Solutions2
... d) Do you think you might be able to resolve its disk with the U of A telescope? Why or why not (show a calculation)? The U of A telescope has an aperture of 12 inches (0.33 m), and therefore an angular resolution (in V band, 550 nm) of θ = 1.22 ∗ (5.5 × 10−7 m/0.33m) = 2.0 × 10−6 radians, or 0.4”. ...
... d) Do you think you might be able to resolve its disk with the U of A telescope? Why or why not (show a calculation)? The U of A telescope has an aperture of 12 inches (0.33 m), and therefore an angular resolution (in V band, 550 nm) of θ = 1.22 ∗ (5.5 × 10−7 m/0.33m) = 2.0 × 10−6 radians, or 0.4”. ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... 16) Which of the following terms is given to a pair of stars that appear to change positions in the sky, indicating that they are orbiting one another? A) visual binary B) eclipsing binary C) double star D) spectroscopic binary E) none of the above ...
... 16) Which of the following terms is given to a pair of stars that appear to change positions in the sky, indicating that they are orbiting one another? A) visual binary B) eclipsing binary C) double star D) spectroscopic binary E) none of the above ...
Life Cycle of a Star Notes
... together to form heavier elements such as helium and release energy. If enough matter is left behind, this may be so dense, and its gravitational field so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is then called a black hole. We cannot see ...
... together to form heavier elements such as helium and release energy. If enough matter is left behind, this may be so dense, and its gravitational field so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is then called a black hole. We cannot see ...
Messier Galaxies of #202541
... was incorrectly plotting M91. With all these distant smudges, he confusingly misplaced M91 by triangulating on his map from M58 instead of the correct M89. So, it’s quite understandable about observer’s trepidation when galaxy hunting in this area. But don’t let that stop you--you have better maps a ...
... was incorrectly plotting M91. With all these distant smudges, he confusingly misplaced M91 by triangulating on his map from M58 instead of the correct M89. So, it’s quite understandable about observer’s trepidation when galaxy hunting in this area. But don’t let that stop you--you have better maps a ...
Chapter 25 - Notes Super Size
... Stars & Galaxies Stars Constellations • _________________ of stars representing mythological characters, animals, or familiar objects. • Most constellations come from the _________________. • The stars in a constellation may appear close, however each star can be _________________ of light-years awa ...
... Stars & Galaxies Stars Constellations • _________________ of stars representing mythological characters, animals, or familiar objects. • Most constellations come from the _________________. • The stars in a constellation may appear close, however each star can be _________________ of light-years awa ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
... lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
Astro 10 Practice Test 3
... b. The helium in their cores has all been used up, which means they’ve started buring hydrogen for the first time. c. They have been ejected from the cluster by gravitational encounters with other stars. d. They’ve run out of hydrogen to burn in their cores, and have evolved into red giants. ...
... b. The helium in their cores has all been used up, which means they’ve started buring hydrogen for the first time. c. They have been ejected from the cluster by gravitational encounters with other stars. d. They’ve run out of hydrogen to burn in their cores, and have evolved into red giants. ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.