PPT - University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
Theoretical Modeling of Massive Stars Mr. Russell University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
Morning Announcements
... The reason is that there is a connection between temperature and total energy output, which is described by the Stefan-Boltzmann law. There are two important aspects to remember: • The total amount of light energy that a star emits — called the luminosity (L), and measured by the absolute magnitude ...
... The reason is that there is a connection between temperature and total energy output, which is described by the Stefan-Boltzmann law. There are two important aspects to remember: • The total amount of light energy that a star emits — called the luminosity (L), and measured by the absolute magnitude ...
Stars - St. Mary School
... 1. Compare and contrast Ursa Major and the Milky Way. Both Ursa Major and the Milky Way are of stars. Ursa Major is a constellation that ancient people thought contained a pattern of stars that looked like a bear. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy containing billions of stars held together by gravity ...
... 1. Compare and contrast Ursa Major and the Milky Way. Both Ursa Major and the Milky Way are of stars. Ursa Major is a constellation that ancient people thought contained a pattern of stars that looked like a bear. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy containing billions of stars held together by gravity ...
Life Cycle of Stars - Faulkes Telescope Project
... It is this cycle of stellar evolution that produces all of the heavy elements required for life. Our Solar System formed from such a second or third generation nebula, leaving an abundance of heavy elements here on Earth and throughout the Solar System. This means that we are all made of star stuff ...
... It is this cycle of stellar evolution that produces all of the heavy elements required for life. Our Solar System formed from such a second or third generation nebula, leaving an abundance of heavy elements here on Earth and throughout the Solar System. This means that we are all made of star stuff ...
Create a HR Diagram - EarthSpaceScience
... Use that Table of stars and plot them on the Empty H-R diagram based on Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. Stars: Star Name ...
... Use that Table of stars and plot them on the Empty H-R diagram based on Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. Stars: Star Name ...
Astronomy
... Red shift: as a source of visible light moves away from the observer, the wavelengths increase, creating a shift toward the red end of the visible spectrum. Star: a fixed luminous point in the night sky that is a large, remote incandescent body like the sun. Solar System: includes our Sun, the nine ...
... Red shift: as a source of visible light moves away from the observer, the wavelengths increase, creating a shift toward the red end of the visible spectrum. Star: a fixed luminous point in the night sky that is a large, remote incandescent body like the sun. Solar System: includes our Sun, the nine ...
ď - Google Sites
... 2. What is the general relationship between temperature and star brightness? ...
... 2. What is the general relationship between temperature and star brightness? ...
Stars - Moodle
... • Its size, temperature, and color are relatively ________________________ • During this time it burns up its supply of _____________________ ...
... • Its size, temperature, and color are relatively ________________________ • During this time it burns up its supply of _____________________ ...
HR Diagram (Temperature Versus Absolute Magnitude)
... • This distance is one Astronomical Unit (AU) • Astronomical units can be used to measure distances within our solar systems ...
... • This distance is one Astronomical Unit (AU) • Astronomical units can be used to measure distances within our solar systems ...
handout
... C. The distance between two stars on the celestial sphere can only be given as the difference between the _____________________ in which we see the stars. i. Therefore, distances on the celestial sphere are measured as ______________ (degrees, arc minutes, arc _______________) IV. Apparent Motion o ...
... C. The distance between two stars on the celestial sphere can only be given as the difference between the _____________________ in which we see the stars. i. Therefore, distances on the celestial sphere are measured as ______________ (degrees, arc minutes, arc _______________) IV. Apparent Motion o ...
H-R Diagram - SFA Physics
... stars in the night sky. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 onto Figure 2. ...
... stars in the night sky. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 onto Figure 2. ...
Document
... • Nebula: New stars form in a cloud of gas and dust. The gas and dust are pulled together by gravity in a ball and gets very dense. Temperature increases, and nuclear fusion begins and the ball of gas and dust starts to glow. • Stars don’t live forever. Stars expand as it grows old. After the hydrog ...
... • Nebula: New stars form in a cloud of gas and dust. The gas and dust are pulled together by gravity in a ball and gets very dense. Temperature increases, and nuclear fusion begins and the ball of gas and dust starts to glow. • Stars don’t live forever. Stars expand as it grows old. After the hydrog ...
Slide 1 - Typepad
... Auriga contains an nteresting variety: many open clusters and nebulous regions simply because the Milky Way runs through it. 3 Open clusters in/out of pentagon of Constellation Auriga south of Capella. M37 the richest cluster containing over 500 stars spread across 20 arcminutes and is the brightest ...
... Auriga contains an nteresting variety: many open clusters and nebulous regions simply because the Milky Way runs through it. 3 Open clusters in/out of pentagon of Constellation Auriga south of Capella. M37 the richest cluster containing over 500 stars spread across 20 arcminutes and is the brightest ...
The Life of a Star
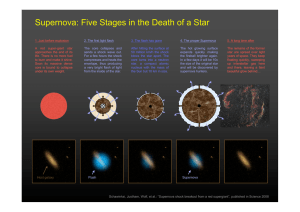
... life of a low-mass star and that of a star 10 times the Sun’s mass. Low-mass stars cool down and swell up into a red giant. Outer layers drift away and the star shrinks to become a white dwarf which will cool and fade away. High-mass stars swells into a red supergiant which undergoes a supernova. Th ...
... life of a low-mass star and that of a star 10 times the Sun’s mass. Low-mass stars cool down and swell up into a red giant. Outer layers drift away and the star shrinks to become a white dwarf which will cool and fade away. High-mass stars swells into a red supergiant which undergoes a supernova. Th ...
Study Guide - Universe Exam key 2014-15 v2
... Gas and dust for a nebula and if there is enough mass, then gravity will pull the particles together and fusion will begin. The majority of the gas is in the form of hydrogen. (H) ...
... Gas and dust for a nebula and if there is enough mass, then gravity will pull the particles together and fusion will begin. The majority of the gas is in the form of hydrogen. (H) ...
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM (H
... There are other lines (diagonal lines) shown on the graph marked “solar radii” (radii is plural for radius) on the righthand side. These lines are used to represent the physical size of stars on the diagram. Using the diagonal solar radii lines, give the solar radius (size) of the sun. ...
... There are other lines (diagonal lines) shown on the graph marked “solar radii” (radii is plural for radius) on the righthand side. These lines are used to represent the physical size of stars on the diagram. Using the diagonal solar radii lines, give the solar radius (size) of the sun. ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.