File
... Supergiants are the largest and brightest stars in the galaxy. Red supergiants are larger than blue ones, but less hot. When a large star runs out of hydrogen to fuse, it expands to become a red giant. When it reaches the stage of burning helium to carbon, it expands and become a red supergiant. Thr ...
... Supergiants are the largest and brightest stars in the galaxy. Red supergiants are larger than blue ones, but less hot. When a large star runs out of hydrogen to fuse, it expands to become a red giant. When it reaches the stage of burning helium to carbon, it expands and become a red supergiant. Thr ...
Society News - Bristol Astronomical Society
... (Algieba), this is a great double for small telescopes. The primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow Gclass star. The pair are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. Just to the west of Leo lies the faint constellation of Cancer, which is home to one o ...
... (Algieba), this is a great double for small telescopes. The primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow Gclass star. The pair are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. Just to the west of Leo lies the faint constellation of Cancer, which is home to one o ...
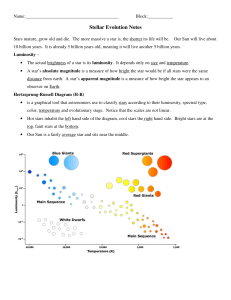
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Lecture 5: Light as a tool
... Apparent magnitude tells us nothing about the luminosity of the objects, but it tell us how difficult it is to see the objects in the sky. Absolute magnitude, on the other hand, is directly related to the luminosity of the object. But it does not tell us how bright they appear in the sky. ...
... Apparent magnitude tells us nothing about the luminosity of the objects, but it tell us how difficult it is to see the objects in the sky. Absolute magnitude, on the other hand, is directly related to the luminosity of the object. But it does not tell us how bright they appear in the sky. ...
Volume 20 Number 10 September 2012
... Now, some of the deceased star's glowing remains whirl around the black hole and emit x-rays and reveal the black hole’s mass. Satellites discovered that the x-rays fluctuate in strength every 200 seconds. Assuming this is the orbital period of hot gas revolving near the black hole, the astronomers ...
... Now, some of the deceased star's glowing remains whirl around the black hole and emit x-rays and reveal the black hole’s mass. Satellites discovered that the x-rays fluctuate in strength every 200 seconds. Assuming this is the orbital period of hot gas revolving near the black hole, the astronomers ...
Activity: Stellar Evolution Scavenger Hunt - Chandra X
... 1. HORESEHEAD NEBULA— active starforming nebula 2. PLEIADES—maasive, blue main sequence stars ...
... 1. HORESEHEAD NEBULA— active starforming nebula 2. PLEIADES—maasive, blue main sequence stars ...
File
... 10. The region of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram that most stars fall within is the ______________________ . 11. A graph of stars showing surface temperature on the x-axis and absolute brightness on the y-axis is a(n) ________________________ . 12. ______________________ is often used to determine ...
... 10. The region of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram that most stars fall within is the ______________________ . 11. A graph of stars showing surface temperature on the x-axis and absolute brightness on the y-axis is a(n) ________________________ . 12. ______________________ is often used to determine ...
Name_______________________Period_________Date
... Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains 2. What is the difference between a constellation, binary star, and a star cluster? Binary Star •Cluster •Constellation Group of stars that form Group o ...
... Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains 2. What is the difference between a constellation, binary star, and a star cluster? Binary Star •Cluster •Constellation Group of stars that form Group o ...
Learning Objectives Weeks 9-11 . 1. Know that star birth can begin
... 11. High-mass stars create heavy elements in their cores. A star of 8 or more solar masses evolves into a supergiant 100 times (or more) larger than the Sun. 12. High-mass stars violently blow apart in supernova explosions. By forming a dense core of iron, a massive star sows the seeds of its own de ...
... 11. High-mass stars create heavy elements in their cores. A star of 8 or more solar masses evolves into a supergiant 100 times (or more) larger than the Sun. 12. High-mass stars violently blow apart in supernova explosions. By forming a dense core of iron, a massive star sows the seeds of its own de ...
Sun, Stars, HR Diagram
... white dwarf B) to shrink to a white dwarf then eventually expand to a red giant C) become hotter and expand into a blue supergiant D) to become a black hole 17. By using a spectroscope an astronomer can A) B) C) D) ...
... white dwarf B) to shrink to a white dwarf then eventually expand to a red giant C) become hotter and expand into a blue supergiant D) to become a black hole 17. By using a spectroscope an astronomer can A) B) C) D) ...
Unit 49-59 Review
... a. Its radius has increased b. Its temperature has increased c. Its temp or its radius has increased d. Its temp and its radius has increased e. None of the above 25. A star that is very hot and not very luminous must have a. a very large radius b. a very small radius c. a very small mass d. a very ...
... a. Its radius has increased b. Its temperature has increased c. Its temp or its radius has increased d. Its temp and its radius has increased e. None of the above 25. A star that is very hot and not very luminous must have a. a very large radius b. a very small radius c. a very small mass d. a very ...
Stars
... Life span of a star depends on its size and mass. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size and mass. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • increasing temperature at core slows contraction – Luminosity about 1000 times that of the sun – Duration ~ 1 million years – Temperature ~ 1 million K at core, 3,000 K at surface • Still too cool for nuclear fusion! ...
... • increasing temperature at core slows contraction – Luminosity about 1000 times that of the sun – Duration ~ 1 million years – Temperature ~ 1 million K at core, 3,000 K at surface • Still too cool for nuclear fusion! ...
Final Review Sheet - Astronomy Part 2
... 2. What is the difference between a constellation, binary star, and a star cluster? ...
... 2. What is the difference between a constellation, binary star, and a star cluster? ...
PISGAH Dr. Bob Hayward ASTRONOMICAL Astronomer/Educator
... planets (after Venus, now our “Morning Star”), we could call Jupiter our “Evening Star.” Keep an eye on it and particularly note it on Saturday evening when it is just to the north of the still nearly full moon. Mars follows Jupiter by rising a few minutes before 1 a.m. It is getting brighter as we ...
... planets (after Venus, now our “Morning Star”), we could call Jupiter our “Evening Star.” Keep an eye on it and particularly note it on Saturday evening when it is just to the north of the still nearly full moon. Mars follows Jupiter by rising a few minutes before 1 a.m. It is getting brighter as we ...
Document
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
PPT - University of Delaware
... of comes from stars, their winds, and their deaths. WR wind bubble NGC 2359 ...
... of comes from stars, their winds, and their deaths. WR wind bubble NGC 2359 ...
Science 9 – Space Exploration
... 10. When measuring the diameter of the sun, we use an indirect method, so that we can determine the diameter without actually measuring it directly. To calculate the accuracy of your measured value, this is calculated to show how far from the real value your measured value is … A. actual error B. e ...
... 10. When measuring the diameter of the sun, we use an indirect method, so that we can determine the diameter without actually measuring it directly. To calculate the accuracy of your measured value, this is calculated to show how far from the real value your measured value is … A. actual error B. e ...
chapter 28 pages 747-752
... • 1. nebula- cloud of gas and dust • 2. Rotation causes formation of protostar • 3. Once it is hot enough for H to fuse into He, main sequence stage occurs • This is the longest stage of a stars life. • 4. In medium sized stars, once all H has been fused into He, He then starts to fuse into C during ...
... • 1. nebula- cloud of gas and dust • 2. Rotation causes formation of protostar • 3. Once it is hot enough for H to fuse into He, main sequence stage occurs • This is the longest stage of a stars life. • 4. In medium sized stars, once all H has been fused into He, He then starts to fuse into C during ...
Lesson 10 Red Shift
... vibrate faster have higher amounts of energy, and those that vibrate slower have lower amounts of energy). Although the electromagnetic spectrum comprises wavelengths from ultra high energy (and dangerous) gamma rays to ultra low energy radio waves, the only part that we can see is the very limited ...
... vibrate faster have higher amounts of energy, and those that vibrate slower have lower amounts of energy). Although the electromagnetic spectrum comprises wavelengths from ultra high energy (and dangerous) gamma rays to ultra low energy radio waves, the only part that we can see is the very limited ...
Thursday October 1 - Montana State University
... • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
... • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.