09astrophysics_2007Nov
... •Absolute Magnitude: how bright the would be if viewed at standard distance •Standard Distance: is 10 parsecs •Sun is M=+4.83 •Star with 100 Solar Luminosities (100 x brighter than sun) would be 5 magnitudes brighter, or have absolute magnitude of M= -0.17 ...
... •Absolute Magnitude: how bright the would be if viewed at standard distance •Standard Distance: is 10 parsecs •Sun is M=+4.83 •Star with 100 Solar Luminosities (100 x brighter than sun) would be 5 magnitudes brighter, or have absolute magnitude of M= -0.17 ...
Stellar evolution, I
... Stars, like people, spend a certain fraction of their history with negative lifetime. ...
... Stars, like people, spend a certain fraction of their history with negative lifetime. ...
Objects Beyond our Solar System
... it would have a mass of millions of kilograms. These stars are very small, just a few km across but they still have a mass that is as great as the sun. The gravity of these stars are incredible; if you dropped a marshmallow onto the surface of a neutron star it would have as much energy as a nuc ...
... it would have a mass of millions of kilograms. These stars are very small, just a few km across but they still have a mass that is as great as the sun. The gravity of these stars are incredible; if you dropped a marshmallow onto the surface of a neutron star it would have as much energy as a nuc ...
Sky Watching Talk
... of stars all in roughly the same direction from Earth, BUT …. Each has its own different distance from the Earth – Therefore, NOT grouped together is space ...
... of stars all in roughly the same direction from Earth, BUT …. Each has its own different distance from the Earth – Therefore, NOT grouped together is space ...
STARS - AN INTRODUCTION
... Stars are balls of burning gas. Different types of gases make the star burn. They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
... Stars are balls of burning gas. Different types of gases make the star burn. They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
1 - Alice Pevyhouse
... 4. The scientist who first made astronomical observations that showed the validity of the heliocentric model of the solar system was 5. The most important observation made to validate(show it was true) the heliocentric model was: ...
... 4. The scientist who first made astronomical observations that showed the validity of the heliocentric model of the solar system was 5. The most important observation made to validate(show it was true) the heliocentric model was: ...
File
... 11. What famous stars are often confused as constellations and what are they really? Big dipper and Little dipper – they are actually asterisms - prominent patterns or groups of stars, typically having a popular name but smaller than a constellation 12. Explain precession and what it means in the fu ...
... 11. What famous stars are often confused as constellations and what are they really? Big dipper and Little dipper – they are actually asterisms - prominent patterns or groups of stars, typically having a popular name but smaller than a constellation 12. Explain precession and what it means in the fu ...
Lecture 12
... • How do we measure stellar luminosities? • How do we measure stellar temperatures? • How do we measure stellar masses? ...
... • How do we measure stellar luminosities? • How do we measure stellar temperatures? • How do we measure stellar masses? ...
Definitions
... Spectroscopy – is the systematic study of spectra and spectral lines Blackbody – is a hypothetical body that is a perfect absorber and emitter of EMR C spectrum – consists of a continuous range of frequencies w/o either bright or dark lines, appearing as a continuous range of colours E spectrum – co ...
... Spectroscopy – is the systematic study of spectra and spectral lines Blackbody – is a hypothetical body that is a perfect absorber and emitter of EMR C spectrum – consists of a continuous range of frequencies w/o either bright or dark lines, appearing as a continuous range of colours E spectrum – co ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 1 ...
... Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 1 ...
Mr. Scharff
... Introduction. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the ...
... Introduction. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... This constellation is best located by looking southward to the familiar scorpion shape, then locating the bright red star, Antares. This red supergiant represents the heart of the easy-to-recognize scorpion. Messier 4 is a 5th magnitude globular cluster that may be seen in the same FoV with Antares ...
... This constellation is best located by looking southward to the familiar scorpion shape, then locating the bright red star, Antares. This red supergiant represents the heart of the easy-to-recognize scorpion. Messier 4 is a 5th magnitude globular cluster that may be seen in the same FoV with Antares ...
How many stars are visible to the naked eye in the night sky?
... Currently there are two active Canadian Astronauts. They are: LieutenantColonel Jeremy Hansen and Dr. David SaintJacques. ...
... Currently there are two active Canadian Astronauts. They are: LieutenantColonel Jeremy Hansen and Dr. David SaintJacques. ...
Core Theme 2: Constellations
... the first evidence of atmospheric water vapor beyond the solar system, while extrasolar planets orbiting the star HR 8799 also in Pegasus are the first to be directly imaged. ...
... the first evidence of atmospheric water vapor beyond the solar system, while extrasolar planets orbiting the star HR 8799 also in Pegasus are the first to be directly imaged. ...
Stars
... • Our sun shows absorption lines for hydrogen (marked with an H) and other heavier elements. ...
... • Our sun shows absorption lines for hydrogen (marked with an H) and other heavier elements. ...
bYTEBoss lesson 3 life of star
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
"Stars" Power Point notes
... • 90% of stars fall on a diagonal, curved line, called the main sequence. • The remaining stars fall into one of three other groups. - Red giants - Supergiants - White dwarfs ...
... • 90% of stars fall on a diagonal, curved line, called the main sequence. • The remaining stars fall into one of three other groups. - Red giants - Supergiants - White dwarfs ...
File
... force of fusion is = to the inward pull of gravity. • When a star reaches equilibrium it will be found in the main sequence of the H-R diagram. • Stars spend most of their lives in equilibrium (main ...
... force of fusion is = to the inward pull of gravity. • When a star reaches equilibrium it will be found in the main sequence of the H-R diagram. • Stars spend most of their lives in equilibrium (main ...
- MrKowalik.com
... 4. If Earth and another celestial object were coming closer together, the electromagnetic waves are bunched together resulting in _____________________________________ 5. If Earth and another celestial object were moving apart, the electromagnetic waves are spread out causing a _____________________ ...
... 4. If Earth and another celestial object were coming closer together, the electromagnetic waves are bunched together resulting in _____________________________________ 5. If Earth and another celestial object were moving apart, the electromagnetic waves are spread out causing a _____________________ ...
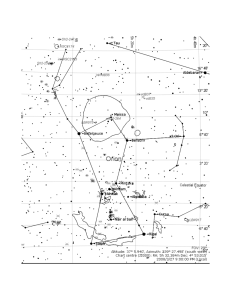
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.