Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
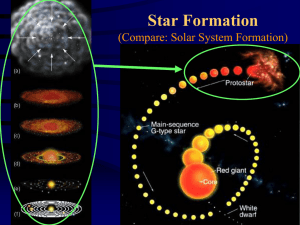
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
Document
... • Betelgeuse is the only star big enough to directly see its surface with a normal telescope. ...
... • Betelgeuse is the only star big enough to directly see its surface with a normal telescope. ...
Stars and Galaxies – Notes
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are doublestar systems in which two stars revolve around each ...
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are doublestar systems in which two stars revolve around each ...
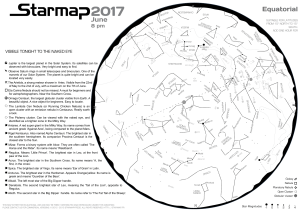
22 pm - Starmap
... rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the nights when the Moon is too bright as its light would make the observation of faint objects ...
... rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the nights when the Moon is too bright as its light would make the observation of faint objects ...
Stars - Independence High School
... • Seasonal- Orbit equator and can only be seen during certain times of the year ...
... • Seasonal- Orbit equator and can only be seen during certain times of the year ...
Luminosity
... The Nearest Stars • If the sun were a golf ball the nearest star would be in Comox • αCentauri is nearest star at 4light years then Barnard’s star ...
... The Nearest Stars • If the sun were a golf ball the nearest star would be in Comox • αCentauri is nearest star at 4light years then Barnard’s star ...
Ast 405, Pulsating Stars The following is based Chapter 14 of the
... • 11. Hence the luminosity changes of a pulsating star are caused by surface temperature and radius changes. Of these the temperature variation is more important. ...
... • 11. Hence the luminosity changes of a pulsating star are caused by surface temperature and radius changes. Of these the temperature variation is more important. ...
20 pm - Starmap
... The objects listed on the first page can be observed with naked eyes, in clear skies, with moderate light pollution. Close your eyes one minute and let them adapt to darkness. You will be surprised how many more details will be apparent. Using binoculars, preferably with a tripod, will considerably ...
... The objects listed on the first page can be observed with naked eyes, in clear skies, with moderate light pollution. Close your eyes one minute and let them adapt to darkness. You will be surprised how many more details will be apparent. Using binoculars, preferably with a tripod, will considerably ...
Quiz Questions
... 3. The major source of energy in the early, pre-main sequence life of the Sun was A. nuclear fusion C. chemical burning of carbon atoms B. nuclear fission D. heat from gravitational contraction 4. Why does hydrogen fusion only occur in the deep interiors of the Sun (and other stars)? A. because this ...
... 3. The major source of energy in the early, pre-main sequence life of the Sun was A. nuclear fusion C. chemical burning of carbon atoms B. nuclear fission D. heat from gravitational contraction 4. Why does hydrogen fusion only occur in the deep interiors of the Sun (and other stars)? A. because this ...
constellations - Otterbein University
... - constellation shapes and names - star names and position in constellation - deep sky objects’ names and position • Quiz: You will be asked to find these objects on a star map. ...
... - constellation shapes and names - star names and position in constellation - deep sky objects’ names and position • Quiz: You will be asked to find these objects on a star map. ...
9ol.ASTRONOMY 1 ... Identify Terms - Matching (20 @ 1 point each =...
... 28. .Radioactive dating techniques have revealed that our Earth and Moon are approximately how old? 29. According to our theory of solar system formation, what three major changes occurred in the solar nebula as it shrank in size? 30. According to our present theory of solar system formation, why w ...
... 28. .Radioactive dating techniques have revealed that our Earth and Moon are approximately how old? 29. According to our theory of solar system formation, what three major changes occurred in the solar nebula as it shrank in size? 30. According to our present theory of solar system formation, why w ...
The Big Dipper is a
... If your astrological sign is Aries, the Sun should be in the constellation Aries on your birthday. The dates, according to astrological tradition, during which the Sun is in the constellation Aries are: March 21 to April 20th. In which constellation is the Sun actually in, during this time period? a ...
... If your astrological sign is Aries, the Sun should be in the constellation Aries on your birthday. The dates, according to astrological tradition, during which the Sun is in the constellation Aries are: March 21 to April 20th. In which constellation is the Sun actually in, during this time period? a ...
Stars
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Beauty and the beast - University of Wyoming
... misconception is that the North Star is the brightest star in the sky. Polaris is the North Star because it is the only star that does not move throughout the night. All of the other stars trace circles around it. Observers will always find it in the same spot – north and 41° above the horizon (for ...
... misconception is that the North Star is the brightest star in the sky. Polaris is the North Star because it is the only star that does not move throughout the night. All of the other stars trace circles around it. Observers will always find it in the same spot – north and 41° above the horizon (for ...
Test#3
... a) rotation rate, b) temperature, c) distance, d) age 2. How much brighter would a star be if an observer moved from 3 to 1 parsec from the star? a) 3 times, b) 9 times, c) 27 times, d) 81 times 3. The difference between the apparent and absolute magnitudes of a star is a measure of the star's a) lu ...
... a) rotation rate, b) temperature, c) distance, d) age 2. How much brighter would a star be if an observer moved from 3 to 1 parsec from the star? a) 3 times, b) 9 times, c) 27 times, d) 81 times 3. The difference between the apparent and absolute magnitudes of a star is a measure of the star's a) lu ...
stars
... huge explosion. • This huge explosion was known as The Big Bang. • Scientist believe that this huge explosion gave birth to the stars and planets ...
... huge explosion. • This huge explosion was known as The Big Bang. • Scientist believe that this huge explosion gave birth to the stars and planets ...
Lab 2: The Planisphere
... and direction of the Milky Way across the sky. Looking north from Cygnus, there are other constellations that appear to lie in, or partially in, the plane of the Milky Way. Name two of these constellations. ...
... and direction of the Milky Way across the sky. Looking north from Cygnus, there are other constellations that appear to lie in, or partially in, the plane of the Milky Way. Name two of these constellations. ...
Chapter #10 Question #27: (c) Four individual protons. During
... The final result is an iron core which is released to the interstellar space during a high mass star supernova. A massive star supernova that blew up before the formation of the solar system would have released iron into the surrounding space which was used up by our solar system during its formatio ...
... The final result is an iron core which is released to the interstellar space during a high mass star supernova. A massive star supernova that blew up before the formation of the solar system would have released iron into the surrounding space which was used up by our solar system during its formatio ...
Hertzsprung Russell diagram
... main sequence stars – the Sun is a main sequence star. In a way stars that lie on the main sequence are ‘normal’ stars while those that lie to one side or other of this area are ‘unusual’ stars – these stars such as white dwarfs, red giants and supergiants. Notice that supergiant stars can be either ...
... main sequence stars – the Sun is a main sequence star. In a way stars that lie on the main sequence are ‘normal’ stars while those that lie to one side or other of this area are ‘unusual’ stars – these stars such as white dwarfs, red giants and supergiants. Notice that supergiant stars can be either ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.