* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM (H
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
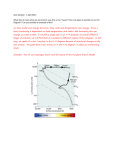
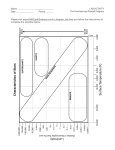
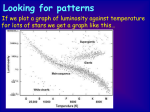
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM (H-R DIAGRAM) 1. NOTE: Absolute Magnitude IS THE SAME THING AS LUMINOSITY ON THE GRAPH DEFINE: absolute magnitude (Pg. 372 if you don’t know) 2. Look at the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram below. What does the vertical (up and down) axis represent? __________________________ What does the horizontal (right to left) axis at the bottom represent? _______________________________ 3. Using the H-R diag. what is the surface temperature of the sun? _________________ 4. What is the luminosity of the sun on this diagram? __________ 5. There are other lines (diagonal lines) shown on the graph marked “solar radii” (radii is plural for radius) on the righthand side. These lines are used to represent the physical size of stars on the diagram. Using the diagonal solar radii lines, give the solar radius (size) of the sun. ___________ 6. What is the “luminosity” of the star marked “x”? _____________ 7. What is the size (solar radii) of the star marked “Y”? _____________ 8. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Interactive A. Use the “Star Evolution on the H-R Diag.” link or go to B. Setup: Click the “show regions” box (lower right) C. Setup: Set the “Speed” slider to approx. http://mrphome.net/mrp/HR_evolve.html 5 x 10^6 Y/s Experiment: How does a stars’ mass affect how long stars live? Hypothesis: If a star has a (circle one: greater / lesser) mass, then its life will be longer. Independent Variable: ___________________________ (what variable will you be changing?) Dependent Variable: ____________________________ (What variable will you be measuring?) Procedure: A. Using the “Mass” slider and the “Create Star” button, create 6 stars with the following masses: DO NOT X-OUT UNTIL YOU ANSWER BOTH QUESTIONS BELOW!! Set Mass To 1 2 5 10 30 Record Age (Life Span) (Wait until done) Conclusion: What have you found out? Question: Looking at your plots ON THE SIMULATION SCREEN, what other factor(s) does mass affect? 50 9. Use the information below to plot the stars on the H-R Diagram given, and identify each star using the numbers for each. Finally, DETERMINE THEIR SIZES USING THE DIAGONAL LINES. Stars Surface temp 1. Antares: 3,500 K 2. Pollux: 4,700 K 3. Capella: 4. Spica: Luminosity Stars Surface temp Luminosity Size (radius) 6. Vega: 9,500 K 32x 7. Deneb: 9,000 K 260,000x 5,000 K 141x 8. Arcturus: 4,400 K 113x 25,000 K 2,200x 9. Betelgeuse: 3,500 K 9,700x 1.5x 10. Sirius B 5. Alpha Centaurus 5,800 K 11,000x Size (radius) 25,000 K 50x 0.002x FILL IN THE “SIZE” BOXES AFTER YOU PLOT. Question: How is the size of a star related to luminosity (absolute brightness)?