Star Life Guided Notes
... Once _____ is in the core, outwards pressure ceases Core ________ at 1/4 the speed of light & takes about 1/10 of a second Collapse of the core to about 100 km across Outer layers “bounce” of the solid core Releases 100x the energy of our sun produces in it’s lifetime -- in 1/10 of a ...
... Once _____ is in the core, outwards pressure ceases Core ________ at 1/4 the speed of light & takes about 1/10 of a second Collapse of the core to about 100 km across Outer layers “bounce” of the solid core Releases 100x the energy of our sun produces in it’s lifetime -- in 1/10 of a ...
Stars: Binary Systems
... Getting the separation, a Although we can measure the period, P, directly, we need to know the distance to get the separation, a. Recall that, d(pc) = 1/P, where P is in arc seconds, which is based on the definition that 1 arc sec is the angular separation of the Earth-Sun system (1 AU ) at a dista ...
... Getting the separation, a Although we can measure the period, P, directly, we need to know the distance to get the separation, a. Recall that, d(pc) = 1/P, where P is in arc seconds, which is based on the definition that 1 arc sec is the angular separation of the Earth-Sun system (1 AU ) at a dista ...
Stars and Galaxies
... a star actually gives off. 12. The amount of light received on Earth is ____________________________. 13. A star that is actually dim can appear very bright if it is close to _______________. The opposite is true also. A star that’s actually bright can appear ____________ if it is far away. 14. ____ ...
... a star actually gives off. 12. The amount of light received on Earth is ____________________________. 13. A star that is actually dim can appear very bright if it is close to _______________. The opposite is true also. A star that’s actually bright can appear ____________ if it is far away. 14. ____ ...
the stars - Uni Heidelberg
... sequence and red stars on the lower right corner. The Sun is located in the middle of the main sequence. In the diagram there are also stars that do not belong any more to the main sequence and are approaching the end of their life. For example giant and supergiant stars lie on the upper right secti ...
... sequence and red stars on the lower right corner. The Sun is located in the middle of the main sequence. In the diagram there are also stars that do not belong any more to the main sequence and are approaching the end of their life. For example giant and supergiant stars lie on the upper right secti ...
Sydney Observatory night sky map June 2014
... June evenings are great for seeing the brightest part of the Milky Way high overhead. June 21st is the shortest day of the year (winter solstice; 9 hours and 48 minutes of daylight) when the Sun is at its most northerly position in the sky. Saturn is located towards the east in Libra. Mars can be se ...
... June evenings are great for seeing the brightest part of the Milky Way high overhead. June 21st is the shortest day of the year (winter solstice; 9 hours and 48 minutes of daylight) when the Sun is at its most northerly position in the sky. Saturn is located towards the east in Libra. Mars can be se ...
THE STARS G. Iafrate(a), M. Ramella(a) and V. Bologna(b) (a) INAF
... sequence and red stars on the lower right corner. The Sun is located in the middle of the main sequence. In the diagram there are also stars that do not belong any more to the main sequence and are approaching the end of their life. For example giant and supergiant stars lie on the upper right secti ...
... sequence and red stars on the lower right corner. The Sun is located in the middle of the main sequence. In the diagram there are also stars that do not belong any more to the main sequence and are approaching the end of their life. For example giant and supergiant stars lie on the upper right secti ...
File
... • A star like our Sun was probably 100 x’s bigger as a protostar. • As it continues to form it shrinks, becomes more dense, and increases in temperature. • The protostar has a large amount of hydrogen in it. • The hydrogen begins to fuse together to form helium. • The energy of hydrogen fusion is th ...
... • A star like our Sun was probably 100 x’s bigger as a protostar. • As it continues to form it shrinks, becomes more dense, and increases in temperature. • The protostar has a large amount of hydrogen in it. • The hydrogen begins to fuse together to form helium. • The energy of hydrogen fusion is th ...
Star Questions 2008 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... brightness of the star as seen from 10 parsecs from the Earth, the apparent brightness or magnitude is the brightness of the star as seen from the Earth. 7. What is the H-R Diagram? A graph showing the relationship of star absolute magnitude, luminosity, color, spectral class and temperature. The ma ...
... brightness of the star as seen from 10 parsecs from the Earth, the apparent brightness or magnitude is the brightness of the star as seen from the Earth. 7. What is the H-R Diagram? A graph showing the relationship of star absolute magnitude, luminosity, color, spectral class and temperature. The ma ...
constellations are not real!
... distinguished, not by their brightness, but by their nearness to the western edge of the constellation by assigning an arabic numeral. Thus, the closest star to the western edge of the constellation Cygnus is called 1-Cygni in the Flamsteed system and 61Cygni denotes the star that is the 61st closes ...
... distinguished, not by their brightness, but by their nearness to the western edge of the constellation by assigning an arabic numeral. Thus, the closest star to the western edge of the constellation Cygnus is called 1-Cygni in the Flamsteed system and 61Cygni denotes the star that is the 61st closes ...
M = 5.5 - The Millstone
... stellar distance (by other means). Absolute magnitude, M, expresses the brightness of a star as it would be if it were placed 10 parsecs away. Since all stars would be placed at the same distance, absolute magnitudes show differences in actual luminosities. It is a measure based on stellar analysis ...
... stellar distance (by other means). Absolute magnitude, M, expresses the brightness of a star as it would be if it were placed 10 parsecs away. Since all stars would be placed at the same distance, absolute magnitudes show differences in actual luminosities. It is a measure based on stellar analysis ...
Introduction to Stars ppt
... Most stars fall along the main sequence – upper left to lower right. These stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores and have a wide range of life spans, which depend on their mass. Higher mass stars on main sequence have shorter life spans. A star has a limited supply of core hydrogen and ther ...
... Most stars fall along the main sequence – upper left to lower right. These stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores and have a wide range of life spans, which depend on their mass. Higher mass stars on main sequence have shorter life spans. A star has a limited supply of core hydrogen and ther ...
Basic Observations of Stars
... The apparent distribution of stars as seen on the sky can be monitored and the ‘sideways’ motions measured as changing directions, expressed as angles. This is called the star’s proper motion. (To calculate the actual speeds through space, we need to know their distances as well.) The changes are mo ...
... The apparent distribution of stars as seen on the sky can be monitored and the ‘sideways’ motions measured as changing directions, expressed as angles. This is called the star’s proper motion. (To calculate the actual speeds through space, we need to know their distances as well.) The changes are mo ...
HR Diagram of a Star Cluster
... A cluster of stars which is localized in space is usually localized in time also. Surprisingly, the brightness (magnitude) of the stars in two different color bands can be interpreted to tell the cluster's age and distance from Earth. This is done by plotting a magnitude vs. color diagram (as Hertzs ...
... A cluster of stars which is localized in space is usually localized in time also. Surprisingly, the brightness (magnitude) of the stars in two different color bands can be interpreted to tell the cluster's age and distance from Earth. This is done by plotting a magnitude vs. color diagram (as Hertzs ...
The H-R Diagram
... The Main Sequence: The main sequence goes from the upper left to the lower right. The stars at the upper left are hotter, larger, and more massive than the Sun. The Sun is near with an absolute magnitude of MV=+5 and a spectral type G2. Like all m.s. stars it is of luminosity class V. Those stars to ...
... The Main Sequence: The main sequence goes from the upper left to the lower right. The stars at the upper left are hotter, larger, and more massive than the Sun. The Sun is near with an absolute magnitude of MV=+5 and a spectral type G2. Like all m.s. stars it is of luminosity class V. Those stars to ...
cancer, la constelac..
... Gamma () and delta () Cancri are known as Asellus borealis and Asellus australis respectively. Their names mean the Northern Donkey and the Southern Donkey, and they are eating from the large open star cluster called Praesaepe, which means "the Manger." Some stories say they are the donkeys in the ...
... Gamma () and delta () Cancri are known as Asellus borealis and Asellus australis respectively. Their names mean the Northern Donkey and the Southern Donkey, and they are eating from the large open star cluster called Praesaepe, which means "the Manger." Some stories say they are the donkeys in the ...
The Stars
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
Spectral analysis for the RV Tau star R Sct: In this section, we will
... Many of our stars are monitored photometrically by the AAVSO. Their web site (http://www.aavso.org)) provides a light curve generator which can give (as the default) the latest few week time period or (what we usually need to do) a light curve covering the date of our specific spectroscopic observat ...
... Many of our stars are monitored photometrically by the AAVSO. Their web site (http://www.aavso.org)) provides a light curve generator which can give (as the default) the latest few week time period or (what we usually need to do) a light curve covering the date of our specific spectroscopic observat ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 5
... scopes in the 4” range under medium to high magnification may glimpse a faint dust lane and some surface mottling. Cassiopeia (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 1 – 3) This constellation is one of the most recognized in the sky due to its prominent M (or W) asterism. Cassiopeia is also a circumpolar constel ...
... scopes in the 4” range under medium to high magnification may glimpse a faint dust lane and some surface mottling. Cassiopeia (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 1 – 3) This constellation is one of the most recognized in the sky due to its prominent M (or W) asterism. Cassiopeia is also a circumpolar constel ...
Death of Stars - Astronomy @ Walton High School
... Most astronomers accept they exist but there is a lot about them that we don't know. When a very large star explodes, the mass condenses so much that is collapses in on itself. The gravity is still present. It appears to pull in any material in the vicinity. Once matter goes past the boundary of a b ...
... Most astronomers accept they exist but there is a lot about them that we don't know. When a very large star explodes, the mass condenses so much that is collapses in on itself. The gravity is still present. It appears to pull in any material in the vicinity. Once matter goes past the boundary of a b ...
galaxy
... Nuclear Fusion hydrogen atoms fuse into helium creating the intense energy found in stars ...
... Nuclear Fusion hydrogen atoms fuse into helium creating the intense energy found in stars ...
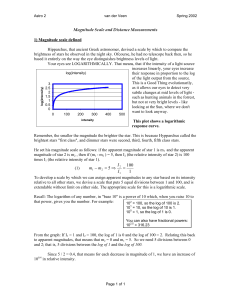
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... and this give us a way to find the relative intensities of any two stars, based on their apparent magnitudes. Try a few examples: 1. The apparent magnitude of Spica is +0.98, and the apparent magnitude of Sirius A is -1.44. How many times brighter is Sirius A than Spica? 2. The apparent magnitude of ...
... and this give us a way to find the relative intensities of any two stars, based on their apparent magnitudes. Try a few examples: 1. The apparent magnitude of Spica is +0.98, and the apparent magnitude of Sirius A is -1.44. How many times brighter is Sirius A than Spica? 2. The apparent magnitude of ...
Document
... some constellations, such as Ursa Minor and Ursa Major, circle around Polaris. • They appear to move because the Earth is in motion. They are visible all year. ...
... some constellations, such as Ursa Minor and Ursa Major, circle around Polaris. • They appear to move because the Earth is in motion. They are visible all year. ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.