Section 25.2 Stellar Evolution
... Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse into a white dwarf. Death of Medium-Mass Stars Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same ...
... Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse into a white dwarf. Death of Medium-Mass Stars Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same ...
Test #3
... a) nuclear fusion, b) nuclear fission, c) 21 cm radiation, d) E=MC 2 6. By what factor would the brightness of a star increase if an observer moved from 3 parsecs to 1 parsec from the star? a) 3 times, b) 9 times, c) 27 times, d) 81 times 7. What is the general name for stars which are converting hy ...
... a) nuclear fusion, b) nuclear fission, c) 21 cm radiation, d) E=MC 2 6. By what factor would the brightness of a star increase if an observer moved from 3 parsecs to 1 parsec from the star? a) 3 times, b) 9 times, c) 27 times, d) 81 times 7. What is the general name for stars which are converting hy ...
Evolution of Stars and Galaxies
... magnitude Main sequence – group of stars running diagonally across diagram; most stars fit into this band (90%) Hot, blue, bright in upper left Cool, red, dim stars in the lower right ...
... magnitude Main sequence – group of stars running diagonally across diagram; most stars fit into this band (90%) Hot, blue, bright in upper left Cool, red, dim stars in the lower right ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist between the brightness and temperature of a main sequence star? The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram shows ...
... White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist between the brightness and temperature of a main sequence star? The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram shows ...
Slides from Lecture04
... • 10 stars that are identical in every respect (all having, for example, the same intrinsic brightness) will appear to have different brightness in the night sky if they are all at different distances from us. • Apparent brightness varies as the “inverse square” of the distance. ...
... • 10 stars that are identical in every respect (all having, for example, the same intrinsic brightness) will appear to have different brightness in the night sky if they are all at different distances from us. • Apparent brightness varies as the “inverse square” of the distance. ...
Chapter 2 Knowing the Heavens
... 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one other? 3. Are the same stars visible every night of the year? What is so special about the North Star? 4. Are the same stars visible from any location on Earth? 5. What cause ...
... 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one other? 3. Are the same stars visible every night of the year? What is so special about the North Star? 4. Are the same stars visible from any location on Earth? 5. What cause ...
Page 1 Astronomy 110 Homework #08 Assigned: 03/13/2007 Due
... answer. Alternate justification techniques include math calculations and labeled sketches. Each question is worth 5 points: 2 for the letter response and 3 for the justification. Collaboration with your peers is permitted, but all justifications must be in your own words. If you are unsure about a q ...
... answer. Alternate justification techniques include math calculations and labeled sketches. Each question is worth 5 points: 2 for the letter response and 3 for the justification. Collaboration with your peers is permitted, but all justifications must be in your own words. If you are unsure about a q ...
The HR Diagram - Faculty Web Pages
... brightnesses. Now let's see if we can find some relationships between these stellar properties. We know that hotter stars are brighter, as described by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law, and we know that the hotter stars are also bluer, as described by Wien's Law. The H-R diagram is a way of displaying an im ...
... brightnesses. Now let's see if we can find some relationships between these stellar properties. We know that hotter stars are brighter, as described by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law, and we know that the hotter stars are also bluer, as described by Wien's Law. The H-R diagram is a way of displaying an im ...
Earth Science, 10th edition Chapter 23: Beyond Our Solar System I
... 1. Dim stars have large numbers a. First magnitude appear brighter b. Sixth magnitude are the faintest stars visible to the eye 2. Negative numbers are also used 2. Absolute magnitude a. "True" or intrinsic brightness of a star b. Brightness at a standard distance of 32.6 light-years c. Most stars' ...
... 1. Dim stars have large numbers a. First magnitude appear brighter b. Sixth magnitude are the faintest stars visible to the eye 2. Negative numbers are also used 2. Absolute magnitude a. "True" or intrinsic brightness of a star b. Brightness at a standard distance of 32.6 light-years c. Most stars' ...
Death of Stars
... • This pressure is balanced by gravity. • This stage of the star is called the stable state or main sequence star stage. • Star spends most of its life in this stage. • As long as hydrogen is available to be fused the star will remain in that stable state. ...
... • This pressure is balanced by gravity. • This stage of the star is called the stable state or main sequence star stage. • Star spends most of its life in this stage. • As long as hydrogen is available to be fused the star will remain in that stable state. ...
Sample Math problems
... These problems are meant to be representative of what you need to know for the final. They are not exactly the problems that will appear in the final exam, but they do require the same set of skills. They might not cover all the formulas and equations that we have seen in the class. I recommend goin ...
... These problems are meant to be representative of what you need to know for the final. They are not exactly the problems that will appear in the final exam, but they do require the same set of skills. They might not cover all the formulas and equations that we have seen in the class. I recommend goin ...
Stars - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. – The closer a star is, the larger its parallax, or apparent movement. The farther away a star is, the smaller its parallax. ...
... of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. – The closer a star is, the larger its parallax, or apparent movement. The farther away a star is, the smaller its parallax. ...
Binary Stars (Professor Powerpoint)
... Optical Binaries- are chance superpositions, where two stars appear close together but do not actually orbit one another. (Like Mizar & Alcor) ...
... Optical Binaries- are chance superpositions, where two stars appear close together but do not actually orbit one another. (Like Mizar & Alcor) ...
Stars
... of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. – The closer a star is, the larger its parallax, or apparent movement. The farther away a star is, the smaller its parallax. ...
... of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. – The closer a star is, the larger its parallax, or apparent movement. The farther away a star is, the smaller its parallax. ...
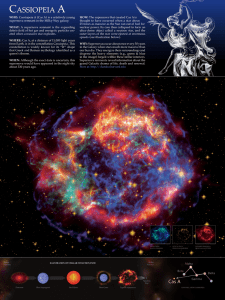
cassiopeia a - Chandra X
... debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constellation Cassiopeia. This constellation is widely known for its “W” shape that Greek and Roman mythology identified as a queen’s throne. ...
... debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constellation Cassiopeia. This constellation is widely known for its “W” shape that Greek and Roman mythology identified as a queen’s throne. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... Purpose: In this web quest, you will 1. Learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. Investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = mc2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and cau ...
... Purpose: In this web quest, you will 1. Learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. Investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = mc2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and cau ...
How to watch the Perseid meteor shower
... in or are close to the UK you will be in for a treat during the Perseid meteor shower in 2013 as the International Space Station is visible over UK skies. This orbital laboratory is the size of a football pitch, travels at 1,7500 mph and is around 200 miles up! It orbits the Earth every 90 minutes a ...
... in or are close to the UK you will be in for a treat during the Perseid meteor shower in 2013 as the International Space Station is visible over UK skies. This orbital laboratory is the size of a football pitch, travels at 1,7500 mph and is around 200 miles up! It orbits the Earth every 90 minutes a ...
Star Life Cycle
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.