* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18 Study Guide
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
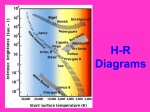
Chapter 18 Study Guide ANSWERS 1. What does a refracting telescope use as its objective to gather and focus light? A refracting telescope uses a lens as its objective. 2. What does a reflecting telescope use as its objective to gather and focus light? A reflecting telescope uses a mirror as its objective. 3. What characteristics are used to classify stars? Color, temperature, brightness, size and chemical composition. 4. What is the brightness of a star as seen from Earth called? Apparent brightness. 5. What does the absolute brightness of a star depend on? A star’s absolute brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. Absolute brightness is determined using the distance to a star and it’s apparent brightness. 6. What factor (variable) affects the color of a star? Temperature of the star 7. What color are the coolest stars? Red 8. What type of star has a high temperature but a low luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist between the brightness and temperature of a main sequence star? The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram shows that main sequence stars increase in brightness as they increase in temperature. 11. When is a star born? A star is born when nuclear fusion begins within a protostar. 12. What variable determines whether a protostar becomes a star? The protostar’s mass. If the protostar has enough mass there will be enough heat and pressure to begin nuclear fusion. 13. What is a supernova? A supernova is a large explosion that takes place at the end of massive star’s life cycle.