How Bright is that star?
... Relates luminosity, temperature and Radius of a star. The luminosity/meter² (l), is determined by the temperature (T) of that area ) l = σT⁴ (σ is a constant which if T is in °K, l comes out in Watts) Surface area is determined by radius(R): A = 4πR² So the total Lumnosity of star becomes L = 4πR²σT ...
... Relates luminosity, temperature and Radius of a star. The luminosity/meter² (l), is determined by the temperature (T) of that area ) l = σT⁴ (σ is a constant which if T is in °K, l comes out in Watts) Surface area is determined by radius(R): A = 4πR² So the total Lumnosity of star becomes L = 4πR²σT ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ star ...
... Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ star ...
Today: Magnitude Terminology Photometry Applications Reading
... Vega); typically obtained by calculating differential magnitude w.r.t. a known standard star. ...
... Vega); typically obtained by calculating differential magnitude w.r.t. a known standard star. ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... • Main sequence stars are stars that are fusing hydrogen atoms to form helium atoms in their cores. • These stars can range from about a tenth of the mass of the sun to up to 200 times as massive. ...
... • Main sequence stars are stars that are fusing hydrogen atoms to form helium atoms in their cores. • These stars can range from about a tenth of the mass of the sun to up to 200 times as massive. ...
Nov - Wadhurst Astronomical Society
... in Cassiopeia to point to the “sword handle” in Perseus as shown in the above chart. From the star on the extreme left of Andromeda, draw a line in the general direction of the horizon that makes a 60º angle with Andromeda itself. This line will pass through Triangulum and then Aries. Drawing a lin ...
... in Cassiopeia to point to the “sword handle” in Perseus as shown in the above chart. From the star on the extreme left of Andromeda, draw a line in the general direction of the horizon that makes a 60º angle with Andromeda itself. This line will pass through Triangulum and then Aries. Drawing a lin ...
The Ever Expanding Universe
... 19th century when Friedrich Bessel successfully measured the first absolute distance to a star 11 light years away. Bessel’s technique, based on Greek trigonometry, was known as parallax and involved measuring the tiny angle a star makes when the Earth is 6 months apart as it journeys around the Sun ...
... 19th century when Friedrich Bessel successfully measured the first absolute distance to a star 11 light years away. Bessel’s technique, based on Greek trigonometry, was known as parallax and involved measuring the tiny angle a star makes when the Earth is 6 months apart as it journeys around the Sun ...
File - Science with Mrs. Schmidt
... _____ 10. A continuous spectrum is a spectrum that shows a. some of the colors. b. some of the colors and some black lines. c. all the colors. d. all the colors and some black lines. _____ 11. What instrument breaks a star’s light into a spectrum? a. a continuous spectrum b. a telescope c. a spectro ...
... _____ 10. A continuous spectrum is a spectrum that shows a. some of the colors. b. some of the colors and some black lines. c. all the colors. d. all the colors and some black lines. _____ 11. What instrument breaks a star’s light into a spectrum? a. a continuous spectrum b. a telescope c. a spectro ...
a description of planets and stars you may see
... third-largest member of the Local Group of galaxies, which includes the Milky Way Galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy. It is one of the most distant permanent objects that can be viewed with the naked eye. The Ring nebula (also known as M57) is a planetary nebula is located in the constellation of Lyra. It ...
... third-largest member of the Local Group of galaxies, which includes the Milky Way Galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy. It is one of the most distant permanent objects that can be viewed with the naked eye. The Ring nebula (also known as M57) is a planetary nebula is located in the constellation of Lyra. It ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... • Main sequence stars are stars that are fusing hydrogen atoms to form helium atoms in their cores. • These stars can range from about a tenth of the mass of the sun to up to 200 times as massive. ...
... • Main sequence stars are stars that are fusing hydrogen atoms to form helium atoms in their cores. • These stars can range from about a tenth of the mass of the sun to up to 200 times as massive. ...
Properties of Stars - Mr. Carter`s Earth
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
Ages of Star Clusters - Indiana University Astronomy
... Since brighter stars are designated with a smaller number for apparent magnitude, magnitudes are plotted in reverse order to put the brighter stars at the top. Investigating Stellar Evolution - For each cluster, identify the main sequence, and sketch in a line that follows the main sequence from its ...
... Since brighter stars are designated with a smaller number for apparent magnitude, magnitudes are plotted in reverse order to put the brighter stars at the top. Investigating Stellar Evolution - For each cluster, identify the main sequence, and sketch in a line that follows the main sequence from its ...
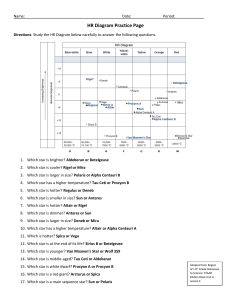
HR Diagram Practice Page
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
Problem Set #3
... where needed, and also be careful with significant figures. Calculations given without “showing the work” will receive zero credit even if the final answer is correct. While you may discuss these problems with other students, you must work out the details and write up the answers yourself. Each ques ...
... where needed, and also be careful with significant figures. Calculations given without “showing the work” will receive zero credit even if the final answer is correct. While you may discuss these problems with other students, you must work out the details and write up the answers yourself. Each ques ...
Astronomy Teaching that Focuses on Learning Subtitled
... world works. If their initial understanding is not engaged, they may fail to grasp the new concepts and information that are taught, or they may learn them for the purposes of a test but revert to their preconceptions outside the classroom. ...
... world works. If their initial understanding is not engaged, they may fail to grasp the new concepts and information that are taught, or they may learn them for the purposes of a test but revert to their preconceptions outside the classroom. ...
Astronomy Unit Period
... __________ 34. Which of the following statements is NOT true of supernovas? a. They are explosions in which a massive star collapses. b. They are explosions that occur at the beginning of a star’s life. c. They can be brighter than an entire galaxy for several days. d. They are explosions in which a ...
... __________ 34. Which of the following statements is NOT true of supernovas? a. They are explosions in which a massive star collapses. b. They are explosions that occur at the beginning of a star’s life. c. They can be brighter than an entire galaxy for several days. d. They are explosions in which a ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 1 ...
... Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 1 ...
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III
... Example III–7. We measure the trigonometric parallax of a visual binary star as 0.20 arcsec and measure an angular separation between the pair of stars in this binary as 5 arcsec. Over a few years of observations, we determine the orbital period of this pair to be 30 years. What is the combined mass ...
... Example III–7. We measure the trigonometric parallax of a visual binary star as 0.20 arcsec and measure an angular separation between the pair of stars in this binary as 5 arcsec. Over a few years of observations, we determine the orbital period of this pair to be 30 years. What is the combined mass ...
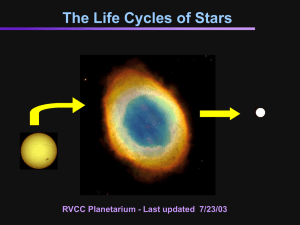
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
doc - IAC
... Massive stars are much heavier than the Sun. They can be up to 10 or 100 times more massive. They stand out because of their high luminosity. These stars can become a million times brighter than the Sun. Their masses can be measured dynamically, in the same way as planetary masses are measured. The ...
... Massive stars are much heavier than the Sun. They can be up to 10 or 100 times more massive. They stand out because of their high luminosity. These stars can become a million times brighter than the Sun. Their masses can be measured dynamically, in the same way as planetary masses are measured. The ...
Level 6 Stars and Constellations
... If you observe a planet, say Mars, for one complete revolution, you will see that it passes successively through 12 constellations. All planets (except Pluto at certain times) can be observed only in these 12 constellations, which form the so-called zodiac, and the Sun also moves through the zodiaca ...
... If you observe a planet, say Mars, for one complete revolution, you will see that it passes successively through 12 constellations. All planets (except Pluto at certain times) can be observed only in these 12 constellations, which form the so-called zodiac, and the Sun also moves through the zodiaca ...
Mar 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
Jeopardy 2015
... Type G2 star, middle of HR diagram-average size and luminosity, end of life will be white dwarf, only known star to support a planet with life. Why is our star (the sun) frequently referred to as an “average” star? Compare the important physical characteristics of the Sun with the most common types ...
... Type G2 star, middle of HR diagram-average size and luminosity, end of life will be white dwarf, only known star to support a planet with life. Why is our star (the sun) frequently referred to as an “average” star? Compare the important physical characteristics of the Sun with the most common types ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.