Cepheus (constellation)
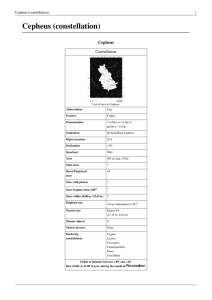
... Cepheus was the King of Aethiopia. He was married to Cassiopeia and was the father of Andromeda, both of whom are immortalized as modern day constellations along with Cepheus.[] ...
... Cepheus was the King of Aethiopia. He was married to Cassiopeia and was the father of Andromeda, both of whom are immortalized as modern day constellations along with Cepheus.[] ...
A Star is Born!
... • A proto-star’s temperature and luminosity can be plotted on a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram or HR diagram • Proto-stars tend to become hotter but less luminous during the process of gravitational contraction; the decrease in luminosity is mostly a result of the proto-star becoming smaller • The exac ...
... • A proto-star’s temperature and luminosity can be plotted on a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram or HR diagram • Proto-stars tend to become hotter but less luminous during the process of gravitational contraction; the decrease in luminosity is mostly a result of the proto-star becoming smaller • The exac ...
Document
... Many more supernovae than we do now. Many more stars being formed than we do now. None of the above. ...
... Many more supernovae than we do now. Many more stars being formed than we do now. None of the above. ...
Stars - Red, Blue, Old, New pt.3
... • At some stages stars can pulsate on timescales of days. • They constantly lose mass from outer layers. • We can follow these changes by calculating evolutionary tracks. ...
... • At some stages stars can pulsate on timescales of days. • They constantly lose mass from outer layers. • We can follow these changes by calculating evolutionary tracks. ...
ASTR101 Unit 10 Assessment Answer Key 1. Mass, luminosity, size
... from about 60 solar masses to about 1/12 solar mass, in luminosity from about 1,000,000 to 1/10,000 solar luminosities, in radius from about 1,000 to 1/10 solar radii, in surface temperature from about 35,000 to 3,000 K, and in age, from about 13 billion years to stars that are just now being born. ...
... from about 60 solar masses to about 1/12 solar mass, in luminosity from about 1,000,000 to 1/10,000 solar luminosities, in radius from about 1,000 to 1/10 solar radii, in surface temperature from about 35,000 to 3,000 K, and in age, from about 13 billion years to stars that are just now being born. ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
Problem 4: magnitude of the star?
... bright as the Sun. You are most likely observing A. A nova B. A pulsar C. A black hole D. A planetary nebula E. A collapsing cloud that will eventually form a star __E___10. Star #1 is 100 times more luminous than star #2. Star #1 is also 100 times farther away than star #2. The difference in appare ...
... bright as the Sun. You are most likely observing A. A nova B. A pulsar C. A black hole D. A planetary nebula E. A collapsing cloud that will eventually form a star __E___10. Star #1 is 100 times more luminous than star #2. Star #1 is also 100 times farther away than star #2. The difference in appare ...
Our Star - the Sun
... detected and analyzed, even though the system may be so distant or the two stars so close together that the two star images cannot be resolved A spectrum binary appears to be a single star but has a spectrum with the absorption lines for two distinctly different spectral types A spectroscopic binary ...
... detected and analyzed, even though the system may be so distant or the two stars so close together that the two star images cannot be resolved A spectrum binary appears to be a single star but has a spectrum with the absorption lines for two distinctly different spectral types A spectroscopic binary ...
Objects in the Sky
... • GLE 0107.6.1 Compare and describe features of the day and night sky. • GLE 0107.6.2 Realize that the sun can only be seen during the day, while the moon can be seen at night and sometimes during the day. • 0107.6.2 Identify objects in the sky and describe their observable similarities and differen ...
... • GLE 0107.6.1 Compare and describe features of the day and night sky. • GLE 0107.6.2 Realize that the sun can only be seen during the day, while the moon can be seen at night and sometimes during the day. • 0107.6.2 Identify objects in the sky and describe their observable similarities and differen ...
1. Star A has a distance of 3 parsecs. What is its parallax angle? 1a
... Which has a greater luminosity, a star with absolute magnitude -4 or a star with absolute magnitude +6? By how much? The -4 magntude star has a greater luminosity by a factor 2.51210 . Star I is of spectral type O2 and star II is of spectral type O3. Which star is hotter? Star I. Which of the follow ...
... Which has a greater luminosity, a star with absolute magnitude -4 or a star with absolute magnitude +6? By how much? The -4 magntude star has a greater luminosity by a factor 2.51210 . Star I is of spectral type O2 and star II is of spectral type O3. Which star is hotter? Star I. Which of the follow ...
Life cycle of a star
... star) is now in its final stages. The core becomes a White Dwarf the star eventually cools and dims. When it stops shining, the now dead star is called a Black Dwarf. ...
... star) is now in its final stages. The core becomes a White Dwarf the star eventually cools and dims. When it stops shining, the now dead star is called a Black Dwarf. ...
Stars - Science
... The first star is larger than the second star. The first star is smaller than the second star. The first star is hotter than the second star. The first star is cooler than the second star. ...
... The first star is larger than the second star. The first star is smaller than the second star. The first star is hotter than the second star. The first star is cooler than the second star. ...
NIE10x301Sponsor Thank You (Page 1)
... arranged into three large groups. The smallest are scruffy little dwarf galaxies comprising “only” millions of stars in a rough blob. Dwarf galaxies are often satellites of larger galaxies, the way moons orbit planets. The rest are broadly divided into elliptical and spiral galaxies. Our own Milky W ...
... arranged into three large groups. The smallest are scruffy little dwarf galaxies comprising “only” millions of stars in a rough blob. Dwarf galaxies are often satellites of larger galaxies, the way moons orbit planets. The rest are broadly divided into elliptical and spiral galaxies. Our own Milky W ...
Teacher Sheet 1. What variables does the HR Diagram compare
... Although they are cool [red], they are very luminous, and therefore bright. In the Main Sequence, stars that are cool are not as luminous. 13. How do white dwarf stars differ from stars in the Main Sequence? White dwarf stars are very hot [blue], but dim because they are so small. 14. Describe stars ...
... Although they are cool [red], they are very luminous, and therefore bright. In the Main Sequence, stars that are cool are not as luminous. 13. How do white dwarf stars differ from stars in the Main Sequence? White dwarf stars are very hot [blue], but dim because they are so small. 14. Describe stars ...
Ursa Major, the Great Bear
... the end of the handle – is a famous optical double star with it fainter companion, Alcor. With good eyesight, one can make out Alcor with just the naked eye, and the mydarksky.org ...
... the end of the handle – is a famous optical double star with it fainter companion, Alcor. With good eyesight, one can make out Alcor with just the naked eye, and the mydarksky.org ...
Friday, August 29
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
Sample Midterm - IUPUI Physics
... • D) these will all supernova at the end of their lives 5) RR Lyra and Cepheid Variable stars are stars on which part of their lifetime? • A) main sequence • B) horizontal branch • C) protostar • D) these could occur at any time in their lives as it has nothing to do with the star’sevolution 6) If y ...
... • D) these will all supernova at the end of their lives 5) RR Lyra and Cepheid Variable stars are stars on which part of their lifetime? • A) main sequence • B) horizontal branch • C) protostar • D) these could occur at any time in their lives as it has nothing to do with the star’sevolution 6) If y ...
eneb_form
... • There are two stars, star A and star B. Star A is approaching the Earth at 100 km/s and Star B is moving away from the Earth at 200 km/s. • Compare the Doppler shift for these two stars by explaining how the spectra will be shifted and by how much. (I am not looking for a number here, just a quali ...
... • There are two stars, star A and star B. Star A is approaching the Earth at 100 km/s and Star B is moving away from the Earth at 200 km/s. • Compare the Doppler shift for these two stars by explaining how the spectra will be shifted and by how much. (I am not looking for a number here, just a quali ...
canopus e.g procyon
... period of about one million years. Proxima Centauri is 4.22 light years from the Earth (now) and about 0.24 light years from Alpha-Centauri A and B. • Alpha-Centauri A and B – a double star system with a period of about 80 years. Component A is a near twin of the sun (Type G2). Component B is a lit ...
... period of about one million years. Proxima Centauri is 4.22 light years from the Earth (now) and about 0.24 light years from Alpha-Centauri A and B. • Alpha-Centauri A and B – a double star system with a period of about 80 years. Component A is a near twin of the sun (Type G2). Component B is a lit ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.























