PowerPoint File
... through the star, throwing off the outer layers of the star into space. As the outer layers are peeled back, it reveals the extremely hot, ultraviolet-emitting carbon and oxygen core which ionizes the stellar wind ...
... through the star, throwing off the outer layers of the star into space. As the outer layers are peeled back, it reveals the extremely hot, ultraviolet-emitting carbon and oxygen core which ionizes the stellar wind ...
Lecture 19 The Milky Way Galaxy
... • Romans called it ‘via lactia’ – milky road, or milky way • But what is it? • By the mid-18th century, astronomers new that it was made up of an enormous number of distant stars ...
... • Romans called it ‘via lactia’ – milky road, or milky way • But what is it? • By the mid-18th century, astronomers new that it was made up of an enormous number of distant stars ...
15-1 Notes - westscidept
... use a ________________ to separate a star’s light into a spectrum. The spectrum gives information about the ______________ and temperature of a star. When a chemical element emits ________, only some colors in the spectrum appear. These are called ____________ lines. The __________ atmosphere of a s ...
... use a ________________ to separate a star’s light into a spectrum. The spectrum gives information about the ______________ and temperature of a star. When a chemical element emits ________, only some colors in the spectrum appear. These are called ____________ lines. The __________ atmosphere of a s ...
Properties of Stars
... Starlight can be analyzed using a spectroscope to infer which gases make up the star. ...
... Starlight can be analyzed using a spectroscope to infer which gases make up the star. ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... • All stars begin as parts of nebulas • A large cloud of gas and dust • large amount of gas in a small volume, ...
... • All stars begin as parts of nebulas • A large cloud of gas and dust • large amount of gas in a small volume, ...
AST101_lect_12
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
HR Diagram and Life of a star
... temp This means that they are very large and can range in size from 100-1000 times the size of the sun GIANTS- large bright stars a bit smaller and fainter than Super giants Super giants in the Red temp range tend to be in their last stages of life. They are out of hydrogen and are now fusing Helium ...
... temp This means that they are very large and can range in size from 100-1000 times the size of the sun GIANTS- large bright stars a bit smaller and fainter than Super giants Super giants in the Red temp range tend to be in their last stages of life. They are out of hydrogen and are now fusing Helium ...
StarType
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
HR-Diagram
... FORMATION- Space contains gas and dust and stars are formed in nurseries called Nebulas or a contracting cloud of dust and gas Some Nebulas glow while others are dark Stars are created from Gravity pulling the nebula together and making a dense ball of gas PROTOSTAR- enough gas and dust to form a st ...
... FORMATION- Space contains gas and dust and stars are formed in nurseries called Nebulas or a contracting cloud of dust and gas Some Nebulas glow while others are dark Stars are created from Gravity pulling the nebula together and making a dense ball of gas PROTOSTAR- enough gas and dust to form a st ...
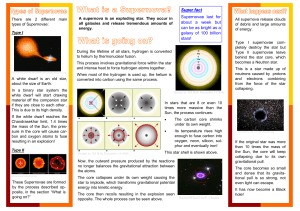
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... the Milky Way galaxy became visible on Earth . It was measured in detail by the German mathematician, Johannes Kepler, who noted that it was bright enough to see at night for a whole year! ...
... the Milky Way galaxy became visible on Earth . It was measured in detail by the German mathematician, Johannes Kepler, who noted that it was bright enough to see at night for a whole year! ...
The Life CyCLe of STarS - Origins
... successfully predicting the properties of new stars and star clusters that are discovered. How a star changes over its life cycle is described below. 33 Star Life. A typical star, like our sun, is stable for a very long time. It uses fusion reactions that convert hydrogen into helium, the same energ ...
... successfully predicting the properties of new stars and star clusters that are discovered. How a star changes over its life cycle is described below. 33 Star Life. A typical star, like our sun, is stable for a very long time. It uses fusion reactions that convert hydrogen into helium, the same energ ...
Krupp (1999) broadly defines the interdisciplinary field
... The night-adapted naked eye, under dark, moonless skies at sea level, may discern stars as faint as magnitude 6. (In the astronomical apparent-magnitude scale, increasing brightest corresponds to smaller numbers.) However, these conditions rarely exist on Rapa Nui, even in pre-historic times. It se ...
... The night-adapted naked eye, under dark, moonless skies at sea level, may discern stars as faint as magnitude 6. (In the astronomical apparent-magnitude scale, increasing brightest corresponds to smaller numbers.) However, these conditions rarely exist on Rapa Nui, even in pre-historic times. It se ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 17 Nature of Stars
... 17-7 How H-R diagrams summarize our knowledge of the stars 17-6 How stars come in a wide variety of sizes 17-8 How we can deduce a star’s size from its spectrum ...
... 17-7 How H-R diagrams summarize our knowledge of the stars 17-6 How stars come in a wide variety of sizes 17-8 How we can deduce a star’s size from its spectrum ...
Beauty and the beast - University of Wyoming
... Keep your fingers crossed this may happen in our lifetime! Betelgeuse is over 600 light years away – so we should be safe. Orion is full of interesting objects and with binoculars or a telescope, look under his belt for a picturesque object known as the Orion Nebula. Spanning 24 light years in diame ...
... Keep your fingers crossed this may happen in our lifetime! Betelgeuse is over 600 light years away – so we should be safe. Orion is full of interesting objects and with binoculars or a telescope, look under his belt for a picturesque object known as the Orion Nebula. Spanning 24 light years in diame ...
Test - Hampton Science 8A 8B 8C 8D 8E Stars are classified on the
... Many stars a lot closer to Earth than 40 light years so their light waves will reach Earth faster than the Sun. The absolute magnitude of a star that is 40 light years away would be very dim to the people on Earth. All stars are 40 light years away because their sizes, in the sky, are all the same a ...
... Many stars a lot closer to Earth than 40 light years so their light waves will reach Earth faster than the Sun. The absolute magnitude of a star that is 40 light years away would be very dim to the people on Earth. All stars are 40 light years away because their sizes, in the sky, are all the same a ...
REACH FOR THE STARS MLK 2009
... 7. What was Messier looking for when he made his observations? _________________ 8. Why are there so few M Objects in the southern skies? __________________________________ 9. When did M 1 SN? _____________________ 10. What do Cas A and Tycho in Cassiopeia have in common? ___________________________ ...
... 7. What was Messier looking for when he made his observations? _________________ 8. Why are there so few M Objects in the southern skies? __________________________________ 9. When did M 1 SN? _____________________ 10. What do Cas A and Tycho in Cassiopeia have in common? ___________________________ ...
Document
... The Universe has only a finite number of stars. The distribution of stars is not uniform. So, for example, there could be an infinity of stars, but they hide behind one another so that only a finite angular area is subtended by them. The Universe is expanding, so distant stars are red-shifted into o ...
... The Universe has only a finite number of stars. The distribution of stars is not uniform. So, for example, there could be an infinity of stars, but they hide behind one another so that only a finite angular area is subtended by them. The Universe is expanding, so distant stars are red-shifted into o ...
Assignment Worksheet
... 1. Your full name, last name first, first name last, and remember to bubble in the letters. 2. Bubble in the 5-digit homework code, 11111, on the form under "Identification Number" in columns A-E (lower left-hand corner of the form). Do not enter your Student ID or any other info into this area, jus ...
... 1. Your full name, last name first, first name last, and remember to bubble in the letters. 2. Bubble in the 5-digit homework code, 11111, on the form under "Identification Number" in columns A-E (lower left-hand corner of the form). Do not enter your Student ID or any other info into this area, jus ...
Lecture 7 Stars and Galaxies and Nebula, (Oh My!) Feb 18 2003
... They orbit in the disk of our galaxy and don't last very long, members escape the group over time. All about the same age and composition so it is likely that they formed around the same time. ...
... They orbit in the disk of our galaxy and don't last very long, members escape the group over time. All about the same age and composition so it is likely that they formed around the same time. ...
Exercise 7
... Introduction: By looking at an apparently flat background of stars at night or at a star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of ...
... Introduction: By looking at an apparently flat background of stars at night or at a star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of ...
Star Formation
... theory. Agrees well with observed main sequence stars, which provides strong support for the modern theory of star formation and stellar structure ...
... theory. Agrees well with observed main sequence stars, which provides strong support for the modern theory of star formation and stellar structure ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.